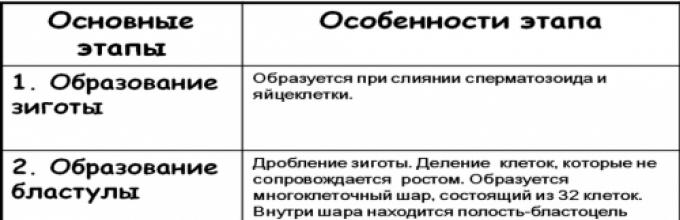
The process of human embryonic development has 4 stages, and in time lasts 8 weeks. It begins from the moment of meeting the male and female genital cells, their mergers and education of the zygota, and ends with the formation of an embryo.
What stages consist of embryogenesis?After the merger of the sperm with an egg takes place educationIt is it that for 3-4 days is moving in the uterine pipes and reaches the uterus. In this case, it is observed a period characterized by a strong intense cell division. At the end of this stage of the development of the embryo Formed blastula - accumulation of individual blastomers, in the form of a ball.
The third period, gastruption, assumes the formation of a second embryonic leaf, resulting in formed gastrol. After that, the third embryonic leaflet arises - Mesoderm. Unlike vertebrates, embryogenesis in person is complicated by the development of the axial complex of organs, the launches of the nervous system of the nervous system, as well as the axial skeleton and the muscles with it occurs.
At the fourth stage of the development of a person's embryo occurs separation formed by this moment the incidents of future bodies and systems. Thus, of the first germinal sheet, the aforementioned nervous system is formed, and partly organs of feelings. From the second entoderma, the epithelial tissue, the lining digestive channel and the glands in it are located. The mesenchym is formed by connecting, cartilage, bone tissue, as well as a vascular system.
 What can the stadium data sequence be broken?
What can the stadium data sequence be broken?
The stages of the embryonic development of the person presented in the table below are not always going in the order in which it is necessary. So, under the influence of a certain kind of factors, mostly exogenous, the course of the development of individual bodies and systems may violate.  Among such reasons can be allocated.
Among such reasons can be allocated.
Ontogenesis is the individual development of the body from the moment of its origin to death. Ontogenesis begins S. fertilization (Sperm and egg fusion). In this case, the zygote is formed, in which the hereditary material of the father and mother is combined.
Germinal (embryonic) development
This is the period from the moment of fertilization before the release of the child from the egg (birth). Includes stages of crushing, gastralization, organogenesis.
Splitting up - This is a series of zygota division by mitosis. The gap between divisions is very short, it takes only DNA doubling, and the growth of cells does not occur (the egg and so was very large). In the process of crushing, the cells gradually decrease until they reach normal sizes. After crushing is formed morula (ball of cells) and then blastula (hollow ball of cells; cells - blastomeres, cavity - blastocel, single-layer wall).
Then Blastuly turns into gastrul - Two-layer ball. Outer layer of gastrula cells is called etoderma, internal - entodermaThe hole in the gastraul is called the primary mouth, it leads to the intestinal cavity.
Organogenesis (organ formation) begins with the formation of a nervous plate in ectoderma on the dorsal side of the embryo. Further
- from the ectoderma is formed a nervous system and leather;
- from Entoderma - digestive and respiratory system;
- mesoderma - everything else (skeleton, muscles, blood, separation, sexual system).
Post-emptilic development
It continues from birth (hatch) before the start of reproduction (on the occurrence of puberty). There are two types:
- Direct "When a child looks like a parent, only less in size and some organs are underdeveloped (mammals, birds).
- Indirect (with transformation, with metamorphosis) - When the child (larva) is very different from the parent (frogs, insects). The advantage of indirect development is that parents and children do not compete with each other for food and territory.
1. All terms below are used to describe the embryo animal type chord. Determine the two terms "dropping" from the general list and write the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) crushing
2) gastruption
3) chitinization
4) Organogenesis
5) Mesoglya
Answer
2. All terms listed below, except for two, are used in describing the embryonic stage of ontogenesis. Determine the two terms "dropping" from the general list, and write the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) Lictery
2) Blastula
3) Gastralla
4) Imago
5) Mesoderma
Answer
3. All terms below, except for two, are used to describe the ontogenesis of the lancing. Determine the two terms "dropping" from the general list, and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) Blastopor
2) Blastomer
3) crushing
4) parthenogenesis
5) Metamorphosis
Answer
Install the correspondence between the process and stage of the embryogenesis of the lancing: 1) Blastuly, 2) gastrol. Write down the numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) an increase in the number of blastomers
B) mitosis zigotes
C) the formation of germinal sheets
D) the formation of blastocel
E) intensive movements of cells inside the embryo
Answer
1. Install the sequence of the stages of individual human development, ranging from the zygote. Record the appropriate sequence of numbers.
1) formation of mesoderma
2) education of a two-layer embryo
3) formation of the nervous system
4) the formation of blastomers
5) Formation of a four-chamber heart
Answer
2. Install the sequence of the stages of the embryonic development of animals
1) the appearance of mesoderm
2) the formation of two germinal leaflets
3) the formation of blastomers
4) Formation of tissues and organs
Answer
3. Install in which sequence the processes of embryogenesis occur in the lancing. Record the appropriate sequence of numbers.
1) formation of a single-layer embryo
2) Education Mesoderma
3) Entoderma Education
4) Differentiation of organs
5) the formation of blastomers
Answer
4. Set the correct sequence of ontogenesis processes in the lancing.
1) Zygota
2) Blastula
3) organogenesis
4) Neurula
5) Gastralla
Answer
5. Install the sequence of the stages of the germinal development of the lancing. Record the appropriate sequence of numbers.
1) formation of a single-layer embryo
2) crushing zigotes
3) the formation of internal organs and systems of organs
4) The formation of the nervous plate and chord
5) Formation of a two-layer embryo
Answer
Select one, the most correct option. In the first stages of its development, the embryo is a multicellular two-layer represents
1) Neurulu
2) Gastrul
3) Morulu
4) Blastulu
Answer
A) brain
B) Skeleton
C) muscles
D) skin glands
E) lungs
E) liver
Answer
Select one, the most correct option. In the embryonic development of chord animal organogenesis begins with
1) mitotic fission zygota
2) formation of a single-layer embryo
3) the formation of a nervous tube
4) the emergence of the first groove of division
Answer
Install the correspondence between the features of development and type: 1) incomplete transformation, 2) complete transformation. Write down the numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) the larva differs from Imago on the structure
B) the habitat and food at the larvae and imago are similar
C) the larva looks like imago
D) passes in 3 stages
D) passes 4 stages
E) larvae underdeveloped sex system
Answer
Set the correspondence between the characteristic of the vertebral embryogenesis process and the stage for which it is characteristic: 1) Blastuly, 2) gastraul
A) Formation of Entoderma
B) the formation of a spherical embryo with cavity inside
C) crushing zigotes
D) the formation of a single-layer embryo
E) the formation of a two-layer embryo
E) the formation of two germinal leaves
Answer
Select one, the most correct option. In embryogenesis, the difference of Blastuly from Gastrul consists
1) in the formation of a two-layer embryo
2) in the development of germinal sheets
3) in active movement of cells
4) in the formation of a single-layer embryo
Answer
Select one, the most correct option. In case of individual development of an animal from the zygota, a multicellular body is formed as a result
1) Gametogenesis
2) fertilization
3) MEIOSA
4) Mitosa
Answer
Select one, the most correct option. The development of the body is promoted between parents and offspring
1) germinal
2) historical
3) Light
4) Indirect
Answer
Select one, the most correct option. Individual development of the human body begins with the process
1) birth
2) Formation of genital cells
3) Education Blastuly
4) fertilization
Answer
Install the correspondence between the organ, the fabric of the spinal animal and the germs, from which they are formed: 1) Entoderma, 2) Mesoderma
A) intestine
B) blood
C) kidneys
D) lungs
D) cartilage cloth
E) heart muscle
Answer
1. Set the correspondence between the structure of the human body and the embryonic leaflet from which it formed: 1) Ektoderma, 2) Mesoderma
A) pain receptors
B) hair cover
C) lymph and blood
D) adipose tissue
E) nail records
Answer
2. Install the correspondence between the organ, the fabric of the spinal animal and the germs, from which they are formed during embryogenesis. Record the numbers in the order corresponding to the letters: 1) Ektoderma, 2) Mesoderma
A) blood
B) enamel teeth
C) cartilage cloth
D) heart muscle
E) skin glands
Answer
Set the correspondence between the characteristic and stage of the formation of the lancing embryo: 1) Single-layer embryo, 2) two-layer embryo. Write down the numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) piercing cell group inside blastuly
B) mitosis zigotes
C) the formation of the walls of the primary intestine
D) the formation of blastocel
E) the formation of blastomers
Answer
1. Install the correspondence between the structures and germs indicated in the figure figures. Write down the numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) internal mucosa
B) adrenal glands
C) tissue fluid
D) Lymph.
D) epithelium alveol
Answer

2. Splender the correspondence between the structures of the embryo and the embryonic leaflets marked in the figure of 1 and 2, from which these structures are formed: write the numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) muscles
B) Alveola
C) liver
D) blood vessels
D) Heart
Answer

Install the correspondence between the structures and germs indicated in the figure in the figures 1, 2: 1) ectoderma, 2) entoderma. Write down the numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) skin epidermis
B) nervous fabric
C) liver
D) pancreas
E) teeth enamel
Answer
Set the correspondence between organs and germs, from which they were formed: 1) Ektoderma, 2) Entoderma, 3) Mesoderma. Write down the numbers 1, 2 and 3 in the correct order.
A) brain
B) liver
C) blood
D) bone
E) pancreas
E) leather
Answer
Install the sequence of embryogenesis processes in the lancing
1) Formation of Blastuly
2) crushing zigotes
3) Formation of three germinal leaves
4) the formation of gastrol
Answer

Select three options. What fabrics and organs of the vertebral animal are formed from cells marked in Figure 1?
1) sweat glands
2) bone tissue
3) nail records
4) connecting tissue
5) Skin epidermis
6) Smooth muscular fabric
Answer
Set the sequence of the processes of the embryonic development of the chord animal. Record the appropriate sequence of numbers.
1) gastruption
2) Neuruul formation
3) Education Morula
4) Education Mesoderma
5) Education Blastuly
6) crushing zigotes
7) histogenesis
Answer

1. Install the correspondence between the structures and germs labeled in the figure figures 1, 2, of which these structures are formed. Write down the numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) nervous fabric
B) blood
C) Skeleton
D) smooth muscular fabric
E) skin epidermis
Answer

2. Set the correspondence between the structures of the embryo and the germs designated in the figure in the figures 1, 2, of which these structures are formed. Write down the numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) nails
B) senses
C) blood
D) Lymph.
E) bone skeleton
Answer

3. Install the correspondence between the structures and germs indicated in the figure figures 1 and 2. Record the numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) nervous fabric
B) blood
C) bone
D) kidney
E) teeth enamel
E) muscle
Answer
Set the correspondence between organs and germs, from which they develop: 1) Etoderma, 2) Entoderma, 3) Mesoderma. Write down the numbers 1-3 in the correct order.
A) brain
B) small bowel
C) cartilage
D) muscles
E) pancreas
E) Hair
Answer
Set the correspondence between the characteristic and type of germs: 1) Entoderma, 2) Mesoderma. Write down the numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) is formed at the stage of neurules
B) formed as a result of gastralization
C) participates in the formation of digestive organs
D) absent in ontogenesis hydra
E) participates in the formation of a circulatory system
Answer
Select one, the most correct option. Are the following judgments about the individual development of organisms? A) In the embryonic period of the development of animals there is an increase in the number of cells, and then their differentiation. B) The process of formation of the two-layer embryo occurs during the crushing period when dividing blastomers.
1) is true only
2) true only b
3) Both judgments are true
4) both judgments are incorrect
Answer
Choose from the processes listed below, relating to fertilization. Record the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) Merging Male and Women Games
2) Education Games
3) Zigota Education
4) crushing zigotes
5) colony education
Answer
Select from the processes listed below two relating to embryogenesis. Record the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) Games Education
2) the education of the zygote
3) Blastulation
4) post-emptilic development
5) gastruption
Answer
Install the correspondence between the processes and stages of the embryonic period: 1) crushing, 2) gastrulation. Record the numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) the directional movement and differentiation of cells is carried out.
B) germinal sheets are formed
C) multilayer embryo
D) cellular material accumulates for further development
E) Form Blastuly
Answer
All processes below, except for two, occur when gastroling the lancing embryo. Determine two processes, "dropping" from the general list, and write down the numbers under which they are specified.
1) crushing zigotes
2) patching the cell layer in the blastuly cavity
3) Formation of the cavity of the primary intestine
4) the formation of the nervous tube
5) the formation of two germinal sheets
Answer
All the characteristics below, except two, belong to the indirect type of post-mixed development. Determine the two characteristics, "dropping" from the general list, and write down the numbers under which they are specified.
1) contributes to the weakening of the struggle for the existence between parents and offspring
2) the birth of offspring, externally similar to the adult organism
3) The born organism may differ from the adult organism in morphological features, lifestyle (type of food, nature of movement)
4) maybe egglades and intrauterine
5) Metamorphosis occurs
Answer

Consider the drawing. Determine a) Stage of the embryogenesis of the chordan animal, b) an embryonic leaf, marked in the figure with a question mark, and c) organs that develop out of it. For each letter, select the appropriate term or the corresponding concept from the proposed list.
1) Gastralla
2) Neurula
3) Blastula
4) Ektoderma
5) Entoderma
6) Mesoderma
7) kidneys, muscles, heart
8) liver, pancreas
Answer
Set the correspondence between the characteristics and stages of the ebogenesis of the lancing: 1) Blastuly, 2) gastrol, 3) neuroula. Write down the numbers 1-3 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) the formation of mesoderm
B) the presence of undifferentiated cells
C) patching of blustula cells in the cavity
D) the formation of the cavity of the primary intestine
E) three-layer embryo
Answer
© DV Pozdnyakov, 2009-2019
The stages of the embryonic development of chords.
General stages of the embryonic development of chords.
1. Fertilizationand the education of zygotes;
2. Splitting upzygotes and education of Blastuly;
3. Gastraland the appearance of two germinal leaflets (ectoderms and entoderms);
4. Differentiationecto- and Entoderma, with the advent of the third germinal sheet - Mesoderm and axial organs (chords, nervous tube and primary
5. Organogenesis and histogenesis(development of organs and tissues).
Fertilization- This is the process of mutual assimilation of a sperm egg, in which a single-cell organism occurs - zygota, with double heredity. In mammals, sperm, using Reyataxis and Chemotaxis moves in the sex paths in the upper third of the egg, where fertilization occurs. Wherein:
1. The egg generates substances (ferlisins), to which sperm moves;
2. Cumsions produces antifestilizin substances, due to which it is attached on the radiant crown of the egg;
3. Sperm is isolated by the enzyme hyaluronidase, which splits the hyaluronic acid in the secondary shells of the egg cell. Initially disintegrates on separate follicular cells radiant crown. Then the shiny shell is dissolved;
4. The first sperm, which comes into contact with the plasmolem of the egg, is drawn into it (only its head and neck with a proximal centriol).
5. A durable fertilization sheath is formed on the egg, which does not transmit the remaining sperm into the egg;
6. Cores sperm and eggs merge. So formed a single core - Sinkarion, with a complete set of chromosomes;
7. The zygote was formed - a single-cell organism.
Splitting up- The process of multiple fission of zigotes by mitosis. So the multicellular organism is formed - the blastuly consisting of a variety of cells - blastomers. Crushing happens:
1. Full or housing - if the whole zygota is crushed to blastomeres (lancing, mammals);
2. incomplete or meroblastic - if only part of the zygota is crushed (birds);
3. Uniform - if the cells of blastomer equal (lancing);
4. Uneven-if the cells of blastomeres will be different magnitudes and shapes (amphibians, mammals, birds).
Gastral- This is the formation of a two-layer embryo. The outer germinal sheet is called Etoderma. Inner germinal sheet - Entoderma.
Types of gastruption:
1. Invagination or phenomenon of blastomeres (lancing);
2. Epibolia or the drawing of small blastomers around large (amphibians);
3. Decamination - bustterization of blastomeres (birds, mammals);
4. Migration - Moving cells (birds, mammals).
Differentiation- This is a genetically determined cell variability due to the functions performed. As a result of the variability of the cells of the ECTO and Entoderma, a third embryonic leaflet appears - Mesoderma and; axial organs. The processes of histogenesis and organogenesis occur throughout life.
The period of embryonic development is most complicated in higher animals and consists of several stages.
The period begins with the stage crushing zygota(Fig. 1), i.e., series of consecutive mitotic divisions of the fertilized egg. Two cells formed as a result of division (and all the subsequent generations) at this stage are called blastomeria. One division follows after another, and the growth of the formed blastomers occurs and the cells are becoming increasingly small. Such a feature of cell divisions and determined the appearance of a figurative term "crushing zygota".
Fig. one.Crushing and gastruction Eggs of the lancing (side view)
The figure indicates: but- Mature egg with a polar tel; b.- 2-cell stage; in- 4-cell stage; g.- 8-cell stage; d.- 16-cell stage; e.- 32-cell stage (in the context to show Blastocel); Well - Blastuly; s - incision of Blastuly; and - early gastrol (on the vegetative pole - arrow - invagination begins); K - Late gastrol (invagination ended and blasopor; 1 - polar taurus; 2 - blastocel; 3 - Ektoderma; 4 - Entoderma; 5 - the cavity of the primary intestine; 6 - Blastopor).
As a result of crushing (when the amount of blastomer reaches a significant number), the blastule is formed (see Fig. 1, z, h). Often it is a hollow ball (for example, in the lancing), the wall of which is formed by one layer of cells - blastoderma. The cavity of Blastuly - Blastocel, or the primary cavity, filled with liquid.
At the next stage, the process of gastrolation is carried out - the formation of gastraul. In many animals, it is formed by prying blastoderm inside on one of the poles of Blastuly with intensive multiplication of cells in this zone. As a result, the gastrol arises (see Fig. 1, and ,k).
The outer cell layer was called Etoderma, and internal - Entoderma. The inner cavity bounded by entoderma, the cavity of the primary intestine communicates with the external medium in the primary mouth, or blastopor. There are other types of gastralization, but all animals (except sponges and intestinal) this process is completed by the formation of another cellular reservoir - Mesoderm. It is laid between the ento and ectoderma.
Upon completion of the gastrojulation stage, three cellular reservoirs appear (ecto, endo- and mesoderma), or three germinal sheets.
Next begin the processes of histogenesis (formation of tissues) and organogenesis (organ formation) in the embryo (embryo). As a result of differentiation of germinal leaf cells, various fabrics and organs of the developing organism are formed. The embodiments and the nervous system are formed from the ectoderm. At the expense of the Entoderma, an intestinal tube, liver, pancreas, lungs are formed. Mesoderma produces all other systems: musculoskeletal, blood, excretory, sexual. The detection of homology (similarities) of three germinal leaves is hardly in all animals served as an important argument in favor of the point of view of the unity of their origin. The stands outlined above were set at the end of the XIX century. I. I. Mesnikov and A. O. Kovalevsky and formed the basis of the "teachings on germinal sheets" formulated by them.
Throughout the embryonic period, there is an acceleration of growth and differentiation rates in a developing embryo. Only in the process of crushing the growth zigotes does not occur and blastulously (by its mass) can even significantly give up the zygote, but since the gastration process, the weight of the embryo increases rapidly.
The formation of diversioned cells begins at the stage of crushing and underlies the primary tissue differentiation - the occurrence of three germinal leaves. The further development of the embryo is accompanied by an increasingly increasing process of differentiation and morphogenesis. By the end of the embryonic period, the embryo already has all major organs and systems that provide viability in the external environment.
The embryonic period is completed by the birth of a new individual capable of independent existence.
The period of embryonic development is the most complicated in higher animals and consists of several stages:
1. Siegota formation
2. Details
3. Education Blastuly
4. Gastral
5. Histo- and organogenesis
The first stage of the embryonic period is the education of the zygota. The zygote of a single-celled germ or single-celled stage of the body's development.
In the zygote there is a number of processes:
a) The movement of cytoplasm (cytoplasmic structures) is leading to the formation of bilateral symmetry and polarity.
b) Perestroika CPM. A superficial (cortical) layer appears. This eliminates the fusion of the zygotes with other male sex cells.
c) the formation of a nuclear shell around the creamypronucleus (Sinkarion)
d) Synthesis of RNA, protein synthesis.
Crushing is accompanied by mitosis, as a result of which a unicellular embryo becomes multicellular. However, the embryo does not increase in size, no cell growth, the volume of the embryo does not change, very short interphase, is missing G1.
Cells formed during crushing are called blastomer. The size of cells with each division becomes smaller. The nature of crushing is not the same in different animals and depends on the amount of yolk and the distribution of it in the cytoplasm. The more yolk, the slower this part of the cytoplasm is divided.
Crushing ends with the formation of Blastuly. Blastula - This is a multicellular single-layer embryo.
Blastulu has a wall (cell layer) - blastoderma. Inside Blastul, the cavity is a blastocel or the primary body cavity filled with liquid. The liquid is secreted by blastomer. In Blastuly, the roof is distinguished (where there was an animal pole of an egg) and the bottom (vegetative pole cell) and between them the edge zone.
Gasastruly - the period of formation of germinal leaves. Gastruption The complex process of chemical and morphological changes, which are accompanied by cell divisions, increasing cells to move the movement and differentiation of cells. As a result of these processes, two-layer embryo - gastrol, consisting of an exterior germinal leaf - ectoderma and internal - Entoderma. This stage is called an early gastrol. At the stage of late Gastrul, a third embryonic leaflet is formed - Mesoderma.
The embryonic leaflets differ from each other not only by their location, but also the size of the cell form. Each embryonic leaf is subsequently the beginning of certain tissues and organs. It was at the stage of gastralization that was first possible to detect in large concentrations of proteins, specific for some directions of cell differentiation of an adult organism (for example, muscle protein - myozin).
Histogenesis - The process of forming tissues in embryogenesis. Organogenesis - The process of forming systems of organs in embryogenesis.
At this stage of embryonic development, two phases are isolated.
1. Subject - formation of axial organs: nervous tube, chords. The embryo at this stage is called neuroula.
This phase proceeds as follows: from the ectoderm on the dorsal side of the embryo, the cell group laying is placed and a nervous plate is formed. The edges of the nervous plate are raised and nervous rollers are formed. In the midline of the nervous plate, the cells are moving and the recess occurs - the nervous groove. The edges of the nervous plate are closed.
As a result of these processes, a nervous tube with a cavity - a nevvotzema. The nervous tube is immersed under the ectoderma. The front department of the nervous tube forms a brain, and the rest of the nervous tube is the spinal cord.
Conditionally the process of forming the nervous tube can be divided into 3 stages:
The formation of the nervous plate,
The formation of a nervous groove,
The fascination of the edges of the nervous plate with the formation of a nervous tube.
A part of the ectoderma cells of the spinal side of the embryo is not part of the nervous tube and forms cell accumulation along the nervous tube, called a ganglionic plate. Of which the pigment cells of the skin, hair, feathers, nerve cells of spinal and sympathetic nerve nodes are formed.
The formation of chords also occurs at an early stage of neuroulation from the entom-modelmal (common with the entoderm and mesoderm) the primary intestine wall. Chord is located under the nervous tube
The second phase of the estate and organogenesis of embryonic development is associated with the development of individual organs and tissues.
An epithelium, stomach and intestines, liver cells, a part of the pancreas cells, lung cells and air pathways, secreting pituitary cells and the thyroid gland are formed from the Entithelism.
From the Etoderm material, the epidermis of the skin and its derivatives - feather, claws, hair, dairy glands, skin glands (greasy and sweat), nerve cells of the organs of vision, hearing, smell, the epithelium of the oral cavity, the enamel of the teeth are developing.