From simple to complex. From the simplest airplane to amazing multi-level 3D compositions. On the pages of this thematic section, you can find class notes and GCD for origami of any level of complexity. This kind of creativity is more than just folding paper models.
Origami classes, the abstracts of which are presented here, contribute to the formation of a work culture and improve work skills; contribute to the creation of exciting game situations. And also expand the communication skills of children; instill good artistic taste; develop spatial thinking, creative and logical abilities.
Learn for yourself and teach children how to create real masterpieces using the origami technique.
Contained in sections:By groups:
Showing publications 1-10 of 858.
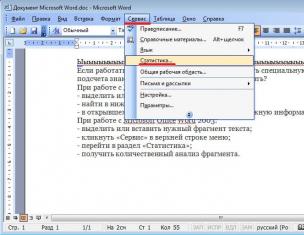
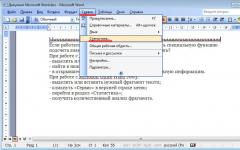
All sections | Origami, paper construction. Lesson notes, GCD
Integrated origami lesson in the preschool group "Dove of Peace" Target: To develop children's creativity in the process of learning about art origami Tasks : Educational - to introduce children to different types of pigeons; learn to fold a figure "pigeon" based on the basic shape of the triangle; keep learning to target ...
Target: organization of leisure activities, fostering interest in paper art. Tasks: Educational: to teach children to fold a fish, to consolidate the children's knowledge of basic geometric concepts (angle, side, to form ideas about fish. Developing: development of small ...
Origami, paper construction. Summaries of classes, GCD - Summaries of origami classes with children 5-7 years old on artistic and aesthetic development "Rowan Branch"
Publication "Outline of origami classes with children 5-7 years old ..." Summary of classes with children 5 - 7 years old on artistic and aesthetic development "Rowan branch" (origami) Topic: "Rowan branch". Objective: To continue teaching children to fold the paper in half diagonally, aligning opposite corners, clearly ironing the folds. Train to act in ...
 Library of images "MAAM-pictures"
Library of images "MAAM-pictures"
Abstract of the OOD for designing from paper using waste material "Raketa" in the senior group OOD for design in the senior group "Rocket" Purpose: to teach how to design a rocket out of paper using waste material. Tasks: Educational: to form the ability to create a volumetric structure from paper using a sample. To consolidate the ability to twist a circle into a cone ...
Summary of the lesson "Designing a boat from paper" The work of the shift worker Abstract of the lesson of the shift worker "Designing a boat out of paper". 2019 educator: Kondrashova T.N. Summary of the lesson (the work of the second teacher-shift teacher) on designing from paper "Ship" Program content: 1) Continue to teach to bend the sheet in different ...
Prospective planning of classes "Magic paper transformation" (origami) PROSPECTIVE PLANNING OF CLASSES ON ORIGAMI "MAGIC PAPER TRANSFORMATIONS" (senior group) MONTH WEEK TOPIC OBJECTIVES, OBJECTIVES REFERENCES September 1 week "In a certain kingdom, in a certain state" Acquaintance with the "Origami" technique, its origin. Introduction to properties ...
Origami, paper construction. Summaries of classes, GCD - Synopsis of the lesson "Goldfish" in the circle "Origami"
 Lesson "Goldfish" Objectives: - To strengthen the ability of children to combine various techniques in their work: drawing, work with plasticine and sequins. - Foster a desire to do your job as best you can by folding the paper neatly and correctly. Preliminary work: -...
Lesson "Goldfish" Objectives: - To strengthen the ability of children to combine various techniques in their work: drawing, work with plasticine and sequins. - Foster a desire to do your job as best you can by folding the paper neatly and correctly. Preliminary work: -...
Abstract of the GCD “Types of transport. Ship "using origami technique Purpose: To acquaint children with the art of origami. To teach how to design a boat out of paper. Objectives: Raising interest in origami; we cultivate the ability to neatly fold a sheet of paper, ironing the folds well. We consolidate knowledge about geometric shapes - square, triangle; ...
Technology Lesson Cards
on the topic "Origami".
Compiled by A.A. Postnikova, an elementary school teacher.
for learning basic origami shapes.
All crafts are united by the theme: "Animals".
Lessons from these cards combine knowledge of the surrounding world and technology into a single whole.
Schemes of various levels of complexity allow you to work according to the minimax principle (from simple to complex):
Turtle (intermediate).
Hare (difficult level).
Duck (hard).
Mouse (difficult level).
The results of the work on this section are summarized in the form of a / r, which consists of two parts: theoretical (two options are attached) and practical (any options from the proposed schemes)
Objectives of the work:
Creation of conditions for the formation of the child's skills in making models from paper using origami techniques.
Acquisition of skills to create elements of artistic and aesthetic design of various compositions.
Creating conditions for improving the fine motor skills of the child's hands.
Application of a holistic approach to the formation of a child's cognitive motivation.
The use of origami knowledge gained in class by children in everyday life.
Work tasks:
Educational:
Introducing children to the history of origami.
Ability to compose a coherent story based on key words.
Developing:
Development of speech in children, expansion of vocabulary.
Development of creative and logical thinking of children.
Develop the ability to work in a group.
Educational:
Formation of children's interest in the art of origami.
Planned result:
Acquiring knowledge of the art of origami by children.
The ability to apply the knowledge of origami learned in the lesson in everyday life.
1. Examination of cards for technology lessons on the topic "Origami", compiled by an elementary school teacher Postnikova Angela Alexandrovna.
2.Experts:
Beloshapkina N.A. - primary school teacher of the highest category,
Gainatulina T.P. - Primary school teacher of the 1st category.
3.Examination parameters:
a) The material of the assignments corresponds to the declared topic in terms of technology when working with paper: "Origami";
b) The cards use schemes with an increasing level of complexity;
c) The cards are colorfully decorated, which corresponds to the individual age characteristics of students of primary school age;
d) When working with these cards:
Ø Conditions are created for the formation of the child's skills in making models from paper using origami techniques.
Ø Skills are acquired to create elements of artistic and aesthetic design of various compositions.
Ø Conditions are created to improve the fine motor skills of the child's hands.
Ø A holistic approach is applied to the formation of the child's cognitive motivation.
Ø Children apply the knowledge about origami, gained in class, in everyday life.
e) This material provides an opportunity for students to work independently in technology lessons, an integrated approach to the study of this topic (technology - the world around them);
f) The developed exercises are suitable for individual work with students, as well as for collective group work with younger students.
4. The results of the examination made it possible to draw conclusions about the compliance of this material with the standards of the second generation, work on these cards contributes to the development of personal and communication skills of children of primary school age and ensures the implementation of the main directions of state standards.
Advanced pedagogical experience in kindergarten preschool
Technological map KOP TN Origami fish from a square of paper with elements of the application "Fish in an aquarium"
Elena Vasilievna Nekrasova, teacher of MADOU d / s No. 4, Perm
Institution name MADOU "Kindergarten No. 4", Perm
Name of the Short-term educational practice of technical orientation: "Fish in the aquarium"
Educator: Nekrasova Elena Vasilievna
Annotation. Main idea: origami is a mediator between artistic and scientific comprehension of the world. It serves as a means of developing various mental processes, including constructive thinking.
Target: mastering the elementary techniques of paper folding according to the schemes.
Number of hours: 1 hour.
Maximum number of participants: 10 people.
Materials used: algorithm for performing actions, squares of colored paper 15 * 15cm, strips of colored paper for decorating crafts,
large sheet of paper (aquarium) with a pre-drawn underwater landscape, napkins, oilcloth, glue, scissors.
Bibliography:
- "Origami for preschoolers" ed. O. M. Zhikharev ed. "Gnome" Moscow - 2012
- "Origami in kindergarten" auth. Svetlana Musienko electronic version - 2015
- "Origami with children 3-7 years old" methodical manual auth. V.N.Degteva - 2012
Activities of a preschooler: reading fiction, examining the thematic album "Inhabitants of the Seas", Didactic game "Catch a Fish".
Brief description of the content of KOP TN:
Step-by-step performance of the work by the teacher with an explanation, simultaneous duplication by children:
- Reading fiction. Consideration of the thematic album "Inhabitants of the Seas", we play the didactic game "Catch a Fish".
- Look, I'll take a square and show you how it turns into an aquarium fish.
- We put a square in front of us and bend it diagonally, matching the corners. We try to combine evenly, iron the fold line well.
- We unfold it, and bend the square, aligning the other two corners diagonally, also ironing the fold line.
- We unfold, turn over to the other side and bend the square, aligning the sides, iron the fold line.
- Now we expand the square and bend the sides along the fold line inward so that we get a double triangle. And we iron all the fold lines well.
- Now we take the side corner of the upper triangle and bend it to the middle so that the corner is just below the side of the triangle, iron the fold line well.
- We do the same with the other side corner of the upper triangle.
- Look what we got! Fish!
- Provide individual assistance, instructions, reminders as needed.
Children's decoration of fish with applique.
- Guys, now we need to decorate our fish. (Children decorate the fish using familiar cutting techniques for appliqués. Remind them to work safely with scissors. Encourage creativity when decorating the fish. Provide personalized assistance as needed.)
- Now you can place your fish in our beautiful aquarium.
- Take glue, carefully smear the back of the fish and glue each of your fish to any place in the aquarium.
Analysis of children's work (introspection).
- Guys, how many different beautiful fish we got!
- What can you tell everyone about your fish?
- You are great! Everyone tried very hard!
- Invite the children to come up with small stories about their fish in the evening.
Product description: layout of an aquarium with fish, diagrams, models, algorithms, etc. (optional).
Technological lesson map
Subject: English
Teacher: Sergeeva Elena Sergeevna
Class: 5 g Author and name of the teaching materials: Vereshchagina I.N. English. Grade V: a textbook for general education. institutions and schools. with deepening studying English. lang. with adj. to the electron. carrier. At 2 o'clock, Part 1 / N.I. Vereshchagin, O. V. Afanasyev. - M.: Education, 2012
Lesson topic: Recurring events in the past. "Used to" turnover
Lesson type: Lesson in studying and primary consolidation of new knowledge Forms of work Paired, group, frontal, individual
Resources. - Textbook; Handout
- Sound application (CD);
-Multimedia, presentation of material.
UUD:
Personal: the formation of a responsible attitude to learning, readiness for self-development and self-education; the formation of communicative competence through the development of language competence in communication and cooperation with peers.
Regulatory: the implementation of regulatory actions of self-observation, self-control, self-assessment in the process of communicative activity in a foreign language.
Cognitive: the construction of logical reasoning, including the establishment of cause-and-effect relationships; highlighting the necessary information, building a speech utterance in oral form, finding answers to questions in illustrations; mastering, with the support of the teacher, educational-organizational, educational-informational and educational-communication skills.
Communicative: the formulation of one's own opinion and position, the ability to argue and coordinate it with the positions of partners in cooperation in developing a common solution in joint activities; the ability to ask questions; to adequately use speech means for solving various communication tasks. Working in pairs and groups in accordance with the norms of communication, mutual understanding, rules of conduct and etiquette.
Planned results:
Subject Personal Metasubject
Formation of language skills of phonetic, spelling, lexical and grammatical within the framework of the theme “Recurring events in the past. "Used to" turnover "
Development of speaking skills through the practice of dialogical speech
Development of listening, speaking, reading, writing skills within the proposed topic;
Formation of socio-cultural awareness, acceptance and development of the social role of the student, the development of motives for learning activities and the formation of the personal meaning of learning;
developing the skills of cooperation with peers in different social situations, the ability not to create conflicts and find ways out of controversial situations;
awareness of a foreign language as a means of intercultural communication, bringing people together, providing friendly contacts and business interaction;
the formation of a responsible attitude to learning, readiness for self-development and self-education; mastering the ability to accept and maintain the goals and objectives of educational activity, search for means of its implementation;
mastering the methods of solving search problems;
the formation of the ability to understand the reasons for the success / failure of educational activities and the ability to act constructively even in situations of failure;
mastering the initial forms of cognitive and personal reflection;
mastering the skills of conscious construction of speech utterance in accordance with the tasks of communication
willingness to listen to the interlocutor and conduct a dialogue; willingness to recognize the possibility of the existence of different points of view and the right of everyone to have their own; express your opinion and give reasons for your point of view and assessment of events;
defining a common goal and ways to achieve it; the ability to agree on the distribution of functions and roles in joint activities; exercise mutual control in joint activities, adequately assess their own behavior and the behavior of others;
the development of the social skills of the student, necessary for communication in a foreign language within the limits of his linguistic abilities.
formation of communicative competence in communication and cooperation through the development of language competence
Lesson steps
Teacher activities Students activities
Cognitive Communicative Regulatory
Actions carried out Formable methods of activity Carried out actions Formable methods of activity Carried out actions Formable methods of activity
1st stage "Organizational"
Purpose: psychologically attune students to educational activities
Greet students using persistent speech cliches
Checking student readiness for a lesson
Students give a verbal response in the form of a greeting
Speech interaction at the level of phrases in compliance with the norms of speech etiquette
Acceptance of the signal to start learning activities
Psychological readiness for the lesson
2nd stage "Motivational"
Purpose: inclusion in educational activities at a personally significant level
1. The teacher sets the children up for work; introduces into the atmosphere of foreign language speech
2. The teacher seeks to create a situation of success, inviting students to name the topic and purpose of the lesson, focusing on the alphabet - creates a problematic situation that will push students to define the topic and formulate the purpose of the lesson
(shown slides with letters that make up the grammatical phrase Used to)
3 The teacher draws the attention of children to the exercise in the presentation, asks to name a new form of grammatical phenomenon, asks a number of leading questions that help to establish causal relationships Get acquainted with the lexical-grammatical unit, highlight the known and unknown moments, formulate a cognitive goal based on the information received
Formulate cognitive tasks.
Interact with the teacher during a frontal conversation
Listen to the interlocutor, be able to correctly respond to the proposed questions.
Formulate their own opinion Make decisions and make independent choices in educational and cognitive activities Be able to listen and express opinions in accordance with the target setting.
Be able to accept the educational goal and objectives, clarify and supplement
2nd stage "Updating and fixing the difficulty"
4. The teacher invites students to listen to and read a poem on the topic "USED TO", draws attention to the grammatical form, to its ending and the meaning of the poem itself
5. The teacher asks the students to list the difficulties that arise and name
the content of knowledge missing for solving a new practical problem.
6. The teacher encourages children to formulate the learning task independently. They formulate their own difficulties and establish their causes through the description of the missing knowledge. List what knowledge they lack to solve a practical problem and formulate what they would like to learn Formulate problems Interact with the teacher during a conversation carried out in frontal mode remember what is known on the issue (simple past tense, verb form, ending assistant),
make assumptions Listen to the interlocutor, build statements that are understandable to him, formulate their own opinions and positions.
Carry out an independent choice of educational and cognitive activities and, with the help of the teacher, determine what you need to know. Exercise self-control and analyze the mistakes made.
Be able to plan activities in accordance with the target
3rd stage "Primary assimilation"
Tasks aimed at achieving results: listening to the audio recording, placing the missing parts of the sentence in the correct order)
7. Organizes the activities of students to solve the educational problem: creating a poem based on the perception of the audio text and checking the finished text. Search for the necessary information, build it in a logical sequence Extract information, build logical chains
Listen to audio recording Manage partner behavior
Listen to the recording
They make notes on the sheets of paper with the assignment, compare parts of the proposals. Control, correct the partner's actions. Exercise mutual control and evaluate the partner, compare the answers with the sample in the textbook.
Mutual control and analysis of the mistakes made, and reflection
Results-Based Assignments: Substitution Exercises
8. The teacher asks students to write their own sentences on a topic from a lookup table and write a few examples in a notebook.
They are involved in independent activities, looking for ways to solve the educational problem
Carry out the choice of the most effective ways to complete the task
Highlight keywords, use iconic characters
Carry out the choice of the most effective solutions to plan educational cooperation with the teacher and peers, listen to the interlocutor
Listen to the interlocutor, formulate your own position
Argue, defend your point of view Set the required goal and objectives,
Assess the correctness of the task
Compare the method of action and its result with a predetermined standard in order to detect deviations and differences from the sample
Determine the quality of assimilation, make the necessary adjustments Compare the method of action and its result with a given standard
Be aware of the quality of assimilation, make the necessary adjustments
5th stage "Primary consolidation"
Assignments aimed at achieving results: exercises 13, 14, pp. 81-82
9. The teacher encourages you to express your own opinion about past events to be believed in order to initially consolidate knowledge
10. The teacher organizes independent work in pairs with self-test according to the standard: creating mini-dialogues at the level of replica-reaction
11 The teacher includes students in the knowledge system through playing mini-dialogues
12 Organizes independent work with textbooks
Implementation of a conscious construction of a speech utterance based on samples and thematic pictures in the textbook
Carry out a conscious construction of a speech utterance Express their thoughts with sufficient completeness and accuracy in accordance with the tasks and conditions of communication
They listen to the interlocutor, make clear statements in accordance with the task in the textbook Express their thoughts in accordance with the tasks and conditions of communication
Cooperate with a partner, determine the functions of a dialogue participant and ways of interaction,
Build statements that are understandable to the interlocutor Check the final quality of their own knowledge and the knowledge of their comrades, evaluate their activities and correct them. Realize the level of their own achievements, the quality of knowledge, mistakes and their causes,
ways to eliminate them.
Exercise self-control
6th stage "The result of educational activities, information about homework, instruction"
Homework: 14, from 82, 15 from 83 (basic level - build sentences based on a model and learn a poem; advanced level - write a coherent story about Mr. Brown using a new grammatical structure and learn a poem)
13. The teacher asks to name the students the difficulties they had to face in the lesson and answer the question whether they managed to overcome these difficulties
14. The teacher asks to get acquainted with the homework. Organizes the activities of students to independently determine the amount of work that each student needs to do individually at home. Systematize the information received
Get acquainted with homework. Identify and formulate a cognitive goal on their own.
Carry out actualization of the knowledge gained on the subject, using familiar vocabulary to build an utterance Interact with the teacher in the process of a generalizing conversation in the frontal mode Listen to the interlocutor, formulate their own opinion
Correctly assess the difficulty of homework Understand the reasons for the success or failure of the learning situation and activities
Determine the scope of their homework Develop the ability to recognize difficulties and the reasons for success or failure and ways to overcome them
Be aware of the quality and level of assimilation of knowledge, forecasting the results of work
Extracurricular activity flow chart
Full name of the educator - Donova Galina Anatolyevna
Class - 3
Direction - artistic and aesthetic
Theme - "Modular Origami"
Lesson type: Lesson with elements of integration with the use of information technology.
Purpose: Formation of skills for joint activities through the use of personal experience in project activities. Planned results:
Subject knowledge, subject actions | UUD |
|||
regulatory | cognitive | communicative | personal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Course of the lesson
Name of the lesson stage | Duration in minutes | Target | Methods and techniques of work | FOOD (form of organizational learning activity) | Teacher activity | Students' activities | Expected Result |
|
1. Organizational moment. Psychological attitude. | 2 minutes. | Slide number 1 | Frontal | Set up students for work. | Children get ready for work. | Good mood. |
||
2. Actualization of knowledge. | 5 minutes. | Summarize children's knowledge of modular origami. | Slide number 2 Slide number 3 Blitz survey | Frontal | Ask questions | Learning motivation. Lead to the topic of the lesson. |
||
3. Formulation of the topic and purpose of the lesson. | 2 minutes. | Improve the ability to formulate the topic and purpose of the lesson. | Slide number 4 Slide number 5 | Problem-dialogue. | Frontal, individual. | Create a situation for formulating a topic and goal. | They answer, reason, analyze. | Acceptance of the theme and purpose. |
4. Statement of the problem. | 5 minutes. | Improve the ability to identify and formulate a problem. | Working with instructions. | Problem-dialogue. | Steam room | Guide, help in formulating the problem. | Read, reason, formulate | Students' interest in finding a solution to the problem. |
5. Search for a solution to the problem. Group work. | 10 min. | Build collaborative skills | Independent work in pairs. | Problem-dialogue. | Steam room, frontal. | Provide assistance to couples in need of support. | They work independently. | A way to solve the problem. |
6. Practical work. | 15 minutes. | Repeat and reinforce origami techniques. | Slide number 7 Independent work. | Explanatory and illustrative. | Steam room. | Explain origami techniques, provide assistance. | Do the work (hare). | Hare models. The desire of children to use their work. |
7. Consolidation of the acquired knowledge. | 4 minutes | Creation of an educational and practical project. | Placing hares in a clearing. | Project activities. | Group | Hares are placed in a clearing. | Glade model with hares |
|
8. Reflexive-evaluative stage. | 2 minutes. | Improve student self-esteem. | Generalizing questions. Verbal assessment. | Frontal, individual. | Asking questions, suggesting options for verbal self-assessment. | They answer, evaluate themselves. | Fulfillment of the purpose of the lesson. |
|
Diagnostics of the results of the lesson | ||||||||
Homework. | Make a swan yourself according to the instructions. |
|||||||
Appendix No. 1
PRODUCTION OF TRIANGULAR MODULES
Take an ordinary A4 sheet and fold it in half each time, cut the sheet into 16 pieces.
1. Bend the rectangle in half
2. Next, fold and unfold the sheet. This is necessary in order to outline the middle. Turnmountain
to yourself
3. Bend the edges of the blank to the middle of the sheet
4. Flip your future module to the other side
5. Raise the edges of the sheet up
7. Now unbend back
8. And now fold the small triangles again along the already marked lines and lift the edges of the craft up
9. Now fold the sheet in half.
Hooray! Now we got a module with two corners and two pockets.
How to connect modules to each other
After you have created two or more modules according to the above diagram, they can be connected to each other in various ways. It can be connected by nesting one into one, as shown in the figure.
Appendix 2
Instructions