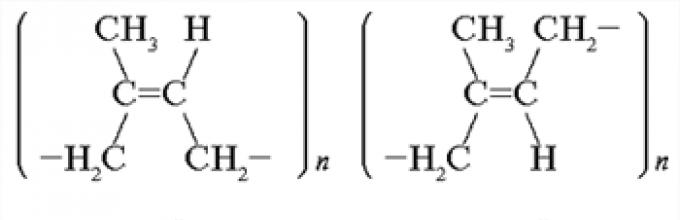The dependence of the properties of substances from the structure of molecules
Open thoughts
Goal. Educational - consolidate and deepen knowledge of students on the theory of chemical structure, its main positions.
Educational - promote the formation of causal relationships and relationships.
Developing - Development of mental skills, the ability to transfer knowledge and skills to new situations.
Equipment and reagents.Set of scale model models; Samples of natural and synthetic rubber, diethyl ether, butanol, ethanol, phenol, lithium, sodium, solution of laccus, bromine water, formic and acetic acid.
Motto. "Any substance - from the simplest to the most difficult - it has three different, but interrelated parties - property, composition, structure"(V.M.Kedrov).
DURING THE CLASSES
What includes the concept of "dependence"? (Find out the opinion of students).
On the board Write the definition: "Dependence -
1) the attitude of one phenomenon to another as a result of the cause;
2) subordination to others in the absence of independence, freedom "(Dictionary of S.I.Ogova).
The objectives of the lesson we define together, reaching the scheme:
Motivational orientation block
Intellectual warm-up
Determine the faithfulness of the following judgments, confirm your answers examples.
The theory of the chemical structure was opened by D.I. Indelaeev.
Answer. A.M. Butlerov, 1861
Carbon valence in organic compounds may be II and IV.
Answer. Carbon valence - most often IV.
Atoms forming organic matter molecules are randomly associated, excluding valence.
Answer. Atoms in molecules are connected in a certain sequence according to their valence.
Properties of substances do not depend on the structure of molecules.
Answer. Butlers in the theory of chemical structure argued that the properties of organic compounds are determined by the composition and structure of their molecules.
Operating and executive block
Factor of spatial structure
What do you know about the spatial structure of alkanov and alkenes molecules?
Answer. In alkanes, with each carbon, four adjacent atoms, which are located in the tops of the tetrahedron. Carbon itself is located in the center of Tetrahedron. Type of hybridization of carbon atom - sP 3., corners between connections (n-s-s, n-sch, s - s-s) - 109 ° 28 ". The structure of the carbon chain is zigzag.
In alkens, two carbon-bound atoms associated with double bond, and four atoms with single connections are in the same plane. Type of hybridization of atoms - sP 2., Corners between bonds (H-C \u003d C, C - C \u003d C) - 120 °.
Remember, in the difference between the spatial structure of natural rubber molecules and synthetic.
Answer. Natural rubber - a linear polymer isoprene - has a structure cis-1.4-polyisoprene. Synthetic rubber can have a structure trance-1.4-polyisoprene.

Is the elasticity of these rubbers?
Answer. Cisform is more elastic than a transform. Natural rubber molecules are longer and more elastically spinned (first in the helix, and then in the ball) than the synthetic rubber molecules.
Starch (C 5 H 10 O 5) M is a white amorphous powder, and cellulose (C 5 H 10 O 5) N is a fibrous substance.
What is the reason for such a difference?
Answer. Starch - polymer-glucose, while cellulose - glucose polymer.

Are the chemical properties of starch and pulp?
Answer. Starch + i 2 blue rr,
Cellulose + HNO 3 nitrocellulose.
Output. The spatial structure depends on both physical and chemical properties.
Factor chemical structure
What is the main idea of \u200b\u200bthe theory of chemical building?
Answer. The chemical structure reflects the dependence of the properties of substances from the order of the compound of atoms and their interaction.
Determine what is common to substances:
Answer. Structure.
Compare the physical properties of these substances. What do you see the reason for this difference?
Based on the distribution of electronic chemical communication density, determine which molecule is more polar? What is it connected with?
Answer. -One hydrogen bond.
Demonstration experiment

Output. The reactivity of the alcohol is determined by the mutual influence of atoms in the molecule.
Factor electronic structure
What is the essence of the mutual influence of atoms?
Answer. The mutual influence consists in the interaction of the electronic structures of atoms, which leads to a displacement of electron density of chemical bonds.
Laboratory work
Teacher. On your tables are sets for laboratory work. Perform the task and prove the experimentally dependence of the properties of substances from the electronic structure. Work in pairs. Strictly follow safety rules.
Option I.. Spend a study of the chemical properties of ethanol and phenol. Prove the dependence of their reactivity from the electronic structure. Use reagents - metal lithium and bromine water. Make equations of possible reactions. Show the shift of the electron density of chemical bonds in molecules.
Option II.. Explain the essence of the mutual influence of the carboxyl group -Oson and the substituent during carbonyl carbon in molecules carboxylic acids. Consider the example of formic and acetic acids. Use a solution of Lacmus and Lithium. Make the reaction equations. Show the shift of the electron density of chemical bonds in molecules.
Output. Chemical properties Depend on the mutual influence of atoms.


Total knowledge control
Teacher. Let's summarize our lesson. We confirmed that the properties of substances depend on the spatial chemical and electronic structure.
1. Nson formulas, from 6 H 5, and C 4 H 9 CONNECTION Clause in order of increasing acidic properties of substances.
2. Place the CH 3 formula 3 coxy, with 3N 7 coxy, CH 3 it, CHCH 2 coxy in descending order acid properties substances.
3. What Aldehyda:

more active aldehyde group? Why?
Rate your work at the lesson.
L.A. Emermin,
Chemistry teacher school number 24
(ABakan, Khakassia)
Test A6 substance of molecular and non-elastic structure. Type of crystal lattice. The dependence of the properties of substances from their composition and structure. 1. Crystal grate of calcium chloride 1) ionic 2) molecular 3) metal 4) atomic 2. Molecular structure has 1) mercury 2) bromine 3) sodium hydroxide 4) potassium sulfate 3. Atom is a structural particle in a crystal lattice 1) methane 2 ) hydrogen 3) oxygen 4) silicon 4. Substances with hardness, refractory, good solubility in water, as a rule, have a crystal lattice: 1) molecular 2) atomic 3) ionic 4) metal 5. Molecular crystalline lattice has 1) HBR 2) K2O 3) WAO 4) KSL 6. Substances with a atomic crystal lattice 1) Very solid and refractory 2) fragile and low-melting 3) electrical current in solutions 4) The electric current in the melts is carried out. 7. The molecular crystal lattice has 1) CA3R2 2) CO2 3) SO2 4) ALF3 8. The ionic crystal lattice has each of the substances located in the row 1) sodium, sodium chloride, sodium hydride 2) calcium, calcium oxide, calcium carbonate 3 ) sodium bromide, potassium sulfate, iron chloride (II) 4) magnesium phosphate, potassium chloride, phosphorus oxide (V) 9. Crystal grate grate 1) ionic 2) molecular 3) atomic 4) metal 10. Substances with hardness, refractory , good solubility in water, as a rule, have a crystal lattice 1) molecular 2) ionic 3) atomic 4) Metal 11. The molecular crystal lattice has 1) silicon 2) carbon oxide (IV) 3) silicon dioxide 4) ammonium nitrate 12. Crystal grate of halogens 1) Atomic 2) ionic 3) Molecular 4) Metal 13. To substances with a atomic crystal lattice include 1) sodium, fluorine, sulfur oxide (IV) 2) Lead, nitric acid, magnesium oxide 3) Bor, diamond, Silicon carbide 4) Chloride Cal yia, white phosphorus, iodine 14. The molecular structure has 1) zinc 2) barium nitrate 3) potassium hydroxide 4) bromomarodine 15. Solid substances, durable, with high melting point, the melt of which is carried out electric current, have a crystal lattice 1) Metallic 2 ) molecular 3) atomic 4) ionic 16. ions are structural particles 1) oxygen 2) water 3) carbon oxide (IV) 4) sodium chloride 17. Nemolecular structure have all non-metals of group 1) carbon, boron, silicon 3) oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen 2) fluorine, bromine, iodine 4) chlorine, phosphorus, selenium 18. Crystal structure, similar to the structure of diamond, has 1) silica 2) sodium oxide 3) carbon oxide (II) 4) white phosphorus P4 19. Atom is Structural particle in crystal lattice 1) methane 2) hydrogen 3) oxygen 4) silicon 20. Molecular crystal lattice has each of two substances 1) graphite and diamond) silicon and iodine 3) chlorine and carbon oxide (IV) 4) barium chloride and barium oxide 21. Atomic crystal solit ku has each of two substances 1) silica (IV) oxide and carbon oxide (IV) 2) graphite and silicon 3) potassium chloride and sodium fluoride 4) chloride and iodine 22. molecular structure has 1) sodium 2) fructose 3) phosphate Sodium 4) Sodium oxide 23. Molecular crystal lattice is characteristic of each of the substances located in row 1) Potassium chloride, nitrogen, methane 2) iodine, carbon dioxide, ozone 3) aluminum, bromine, diamond 4) hydrogen, magnesium sulfate, oxide Iron (III) 24. Silicon oxide of refractory, insoluble in water. Its crystal lattice 1) atomic 2) molecular 3) ionic 4) metal 25. Depending on the nature of the particles forming the crystal, and on the nature of the interaction forces between them there are four types of crystal lattices: 1) ion, atomic, molecular and metallic 2) ionic, covalent, atomic and molecular 3) metal, covalent, atomic and molecular 4) ion, cubic, triangular and layered 26. Crystal ice grid: 1) Atomic 2) Molecular 3) ionic 4) Metal 27. Specify the substance that in the solid state has a molecular crystalline grille. 1) graphite 2) sodium 3) sodium hydroxide 4) hydrogen 28. Specify the substance that in the solid state has a atomic crystal lattice: 1) chloride chloride 2) chlorine 3) silicon oxide (IV) 4) calcium oxide 29. For solids with The metal crystal lattice is characterized by high ... 1) solubility in water 2) electronegability of atoms 3) volatility 4) electrical conductivity 30. The crystalline substance is formed by Na + and ON particles. What type of crystal lattice belongs to this substance? 1) atomic 2) molecular 3) ionic 4) metal 31. Nemocecular structure has each of two substances: 1) S8 and O2 2) Fe and NaCl 3) CO and MG 4) Na2CO3 and I2 32. The substance of the molecular structure is 1) Ozone 2) Barium oxide 3) graphite 4) Potassium sulphide 33. Atomic crystal lattice at a simple substance: 1) Diamond 2) Copper 3) fluorine 4) Tin 34. The assertion that the structural particle of this substance is the molecule only for the structural particle 1) diamond 2) salt 3) silicon 4) nitrogen 35. Ionic crystal lattice has 1) water 2) sodium fluoride 3) silver 4) bromine 36. Simple substanceshaving the same type of crystal lattice, formed by elements 1) of small periods 3) side subgroups 2) of the main subgroups 4) of large periods 37. The crystal structure similar to the structure of the diamond has: 1) silica SiO2 2) sodium oxide Na2O 3) carbon oxide ( Ii) CO 4) White phosphorus P4 38. Phosphine pH3 is gas. Its crystal lattice 1) atomic 2) molecular 3) ionic 4) metal 39. Crystals consist of molecules. 1) Sugar 2) Salts 3) Diamond 4) Silver 40. From the variestly charged ions consist of crystals 1) of sugar 2) sodium hydroxide 3) diamond 4) silver 41. What particles form a sodium nitrate crystal? 1) NA, NA, N and 3) atoms Na +, NO3 + 5+ 22) ions Na, N, O 4) NA3 42 molecules. Evaluate the correctness of the links between the structure and properties of the substance. A. Among the substances of the molecular structure there are gaseous, liquid and solid under normal conditions. B. Substances with an atomic crystal lattice under normal conditions solid. 1) It is true only a 2) is true only b 3) Both judgments are true. 4) Both judgments are incorrect to 43. Evaluate the correctness of the relationship between the structure and properties of the substance: A. If there is a solid chemical connection between particles in a crystal, then the substance is Tuglav. B. All solid substances NEnets have a non-alarular structure 1) is true only and 2) True only b 3) Both judgments 4) Both judgments are incorrect than 44. Which of the above statements are true: A. Substances with a molecular lattice have low melting points and low electrical conductivity. B. Substances with an atomic lattice are plastic and have high electrical conductivity. 1) It is true only a 2) is true only b 3) both judgments 4) both judgments are incorrect 45. Install the correspondence between the substance and the type of its crystal lattice. Substance Type of crystal lattice 1) Salver Sol a) Molecular 2) Silver b) ionic 3) Gas carbon dioxide) Atomic 4) Graphite D) Metal 5) Glucose 46. Install the correspondence between the type of crystal lattice and the properties of substances. Type of crystal properties of grate a) ionic 1) solid, refractory, not dissolved in water b) metal 2) fragile, low-melting, no electric current C) atomic 3) plastic, have different melting temperatures, electric current d) molecular 4 ) Solid, refractory, well soluble in water 47. Specify a series characterized by a decrease in the chemical communication length 1) SICL4, MGCl2, AlCl3, NaCl 2) NaCl, MgCl2, SiCl4, AlCl3 3) NaCl, SiCl4, MgCl2, AlCl3 4) NaCl, MgCl2, AlCl3, SiCl4 48. Rate the correctness of the relationship between the structure and properties of the substance. A. If there is a durable chemical connection between particles in the crystal, then the substance is easily evaporated. B. All gases have a molecular structure. 1) It is true only a 2) is true only b 3) both judgments 4) both judgments are incorrect
Lecture 7.The dependence of the properties of substances from their
Buildings. Chemical bond. Maintenance
Types of chemical bond.
Considered questions:
1. Levels of the organization of a substance. Hierarchy of the structure.
2. Substances of the molecular and non-ethics.
3.
4. Causes of chemical bond.
5. Covalent Communication: Education Mechanisms, Methods
Overlapping atomic orbitals, polarity, dipole moment
molecules.
6. ion connection.
7. Comparison of a covalent polar and ion connection.
8. Comparison of properties of substances with covalent polar and
ionic connections.
9. Metal connection.
10. Intermolecular interactions. Substance (more than 70 million)
What you need to know about each substance?
Formula (from which consists)
Structure (as arranged)
Physical properties
Chemical properties
Methods for getting
(Lab. And industrial.)
6. Practical use
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.Hierarchy of the structure of the substance
All substances
consist of
atoms but not
All - out
molecules.
Atom
Molecule
All substances
Only in substances
Molecular
Buildings
Nano-level
All substances
Volumetric (Macro)
level
All substances
All 4 levels - the object of studying chemistry Molecular substances
and non-mehangular structure Substances
Molecular
Buildings
Nemolecular
Buildings
Consist of molecules
Consist of atoms
or ions
H2O, CO2, HNO3, C60,
Almost all org. Substances
Diamond, graphite, SiO2,
Metals, salts
The formula reflects
Molecule composition
The formula reflects the composition
Formular unit Substances
Sodium chloride
Formular Unit NaCl. Substances
Silica
Formular unit SiO2.
The Mineralogical Museum named after Fersman is located near the entrance to the Justice Garden.
Address: Moscow, Leninsky Prospekt, House 18, Corps 2. A variety of chemical structures.
propellan
C5H6.
Koronen
(Superbenzene)
C24H12.
Kavitad
C36H32O8. A variety of chemical structures.
Katen. A variety of chemical structures.
Katen. A variety of chemical structures.
Leaf of Mebius Molecule
Molecule - a steady system consisting of several
atomic cereals and electrons.
Atoms are combined into molecules by formation
Chemical ties.
The main driving force of the formation of a molecule from
Atoms - a decrease in total energy.
Molecules have geometric shapeCharacterized
distances between nuclei and corners between connections. Main driving force
Chemical Communication Education
between particles of substance -
Reducing overall energy
Systems. The main types of chemical
Communications:
1.Ionna
2. Known
3.Metallic
Main intermolecular
Interaction:
1. Hardening bonds
2.Van-der Waals link Ion communication
If the connection is formed atoms with sharply distinguish
electronegability values \u200b\u200b(ΔOeo ≥ 1.7),
Total electronic couple almost completely
shifts towards more electronegative
Atom.
Na Cl.
OEO 0.9 3,16
∆ 2,26
+ Na.
Anion
: CLKATION
Chemical bond between ions arising for
The account of their electrostatic attraction,
called ionic. Ion communication
Coulomb potential spherical
Symmetrical, directed in all directions,
Therefore, ionic communication is not right.
Coulomb potential has no
restrictions on the number
Attached counterions -
Therefore, ion connection
unsaturated. Ion communication
Connections with ion connection type
solid, well soluble in
Polar solvents, have high
Melting and boiling temperatures. Ion communication
Curve I: Attraction of ions if
would they represented
Point charges.
Curve II: Pumping nuclei in
case of strong rapprochement of ions.
Curve III: Minimum Energy Energy on
Curve corresponds
The equilibrium state of ionic
Couples in which power
Electron attraction to kernels
Compacted by forces
repulsion nuclei
distance R0, Chemical Communications in Molecules
Chemical bond in molecules can be described with
Positions of two methods:
- Method of valence relations, MVS
- Molecular orbitals, MMO Method of valence ties
Guitler-London theory
The main provisions of the Sun method:
1. Communication forms two electrons with opposite
spins, while overlapping wave
functions and increases electronic density between
nuclei.
2. Communication is localized towards the maximum
Overlapping ψ-functions of electrons. The stronger
overlapping, the stronger communication.
DCV - Length
links;
ERV - Energy
Communication. The formation of hydrogen molecule:
N · + · n → n: n
When converging two atoms
arise the forces of attraction and
repulsion:
1) attraction: "electron-core"
neighboring atoms;
2) repulsion: "core-core",
"Electron electron" adjacent
Atoms. The formation of hydrogen molecule:
Molecular
two-electron cloud,
Possessing Maximum
electron density. Chemical Communication
electronic pairs are called covalent.
General electronic pair can form two
ways:
1) As a result of the combination of two non-parliament electrons:
2) as a result of society
electronic pair of one atom (donor) and empty
Other orbital (acceptor).
Two covalent communication mechanisms:
Exchanged and donor-acceptor.
communication density occurs through the line,
connecting the centers of atoms (kernel), then
Overlapping is called σ-bond: Methods for overlapping atomic orbitals when
The formation of covalent bond
If the formation of maximum electronic
communication density occurs on both sides
lines connecting atom centers (kernel)
Such overlapping is called π-bond: Polar and non-polar covalent bond
1) if the connection form the same atoms,
The two-electronic cloud of communication is distributed in
space is symmetrically between their kernels - such
Communication is called non-polar: H2, CL2, N2.
2) if the connection is formed different atoms, cloud of communication
shifted towards a more electronegative atom
- Such a connection is called polar: HCl, NH3, CO2. Polar covalent communication
Dipole moment of communication
Dipole
H + ΔCl-Δ or H + 0.18Cl-0,18
Where ± δ is effective
Atom charge, share
Absolute charge
Electron.
+δ
-δ
Do not confuse with the degree of oxidation!
L.
The work of an effective charge for the length of the dipole
called the electric moment of the dipole: μ \u003d ΔL
This is a vector value: directed from positive
Charge to negative. Polar covalent communication
Dipoletime Molecule
The dipole moment of the molecule is equal to the sum
Vectors of dipole moments tie
Vicious electronic pairs.
Dipolet Measurement Unit
Is Deboy: 1d \u003d 3.3 · 10-30 KL · m. Polar covalent communication
Dipoletime Molecule
In the product μ \u003d ΔL, both variables are multidirectional.
Therefore, it is necessary to carefully track the cause
Changes μ.
For example,
Csf.
CSCL
24
31
Δ "lost" L
CSI
HF.
HCL
HBR
HI
37
5,73
3,24
2,97
1,14
On the contrary Polar covalent communication
Dipoletime Molecule
Can molecule be notolar if
All connections in it polar?
Molecules type av are always polar.
AB2 type molecules can be polar and
Notoary ...
H2O
ABOUT
N.
CO2.
μ>0
N.
ABOUT
FROM
μ=0
ABOUT Polar covalent communication
Molecules consisting of three atoms and more
(Av2, AB3, AB4, AV5, AB6),
may be non-polar, if they are symmetrical.
What is affected by the presence of a dipole moment
Molecules?
There are intermolecular interactions, and
Therefore, the density of the substance increases,
T ° Melting and T ° boil. Comparison of ion and covalent polar connections
General: general education
electronic couple.
Difference: degree
Displacement common
electronic couple
(Communication Polarization).
Ion connection should be considered as extreme
Case of covalent polar communication.
polar connections
Covalent Communication: saturated and sent
Saturability (maximum valence) -
determined by the ability of an atom to form
limited number of connections (including both
Education mechanisms).
The direction of communication sets the valence angle depending on
Type of hybridization of the orbitals of the central atom.
Ion connection: unsaturated and non-directional. Comparison of the characteristics of ion and covalent
polar connections
The focus of communication is set by valence angles.
Valence angles are determined experimentally or
predict based on the theory of hybridization
Atomic orbitals L. Polling or theory
Gillespi.
In detail about it at seminars.
Covalent bonds
Covalent bonds
Atomic crystals
Between atoms
in the crystal itself
High hardness
High Tº Plav, TºKep
Bad heat- I.
Electrical conductivity
Molecular crystals
Between atoms
in molecule
Moderate softness
Low enough
Tº Plav, TºKep
Bad heat- I.
Electrical conductivity
Insoluble in water Comparing properties of substances with ion and
Covalent bonds
Molecular Crystal
Melting point 112.85 ° C Comparing properties of substances with ion and
Covalent bonds
Atomic covalent crystal
Melting point ≈ 3700 ° С Comparing properties of substances with ion and
Covalent bonds
Ion ties
between ions
in crystal
Hardness and fragility
High melting point
Bad heat and electrical conductivity
Soluble in water Comparing properties of substances with ion and
Covalent bonds
Ion crystal
Melting point ≈ 800 ° C Metal communication
Metal communication is carried out by electrons,
owned by all atoms at the same time.
Electronic density
Delocalized "Electronic Gas".
Characteristic
Metal shine
Plastic
Ductility
High heat- I.
Electrical conductivity
Melting temperature
very different. Intermolecular ties.
1. Hydrogen Communications
Attraction between hydrogen atom (+) one
molecules and atom f, o, n (-) other molecule
F.
F.
H.
H.
H.
H.
F.
F.
O.
H3C.
H.
F.
C.
H.
Polymer
(HF) N
O.
C.
O.
H.
CH3.
Dimer
acetic acid
O.
Hydrogen bonds are weak individually,
But strongly collectively Intermolecular ties.
2. Hydrogen bond in DNA Intermolecular ties.
3. Hydrogen bonds in water
Liquid water
ice Intermolecular ties.
4. Formation of hydrogen ties in
water
Liquid water
Transformation
Water in ice. Intermolecular ties.
5. Van der Wales
Even if there are no hydrogen bonds between molecules,
Molecules are always attracted to each other.
The attraction between molecular dipoles is called Vantern Waals bond.
V-d-in attraction is the stronger than more:
1) polarity; 2) Molecules size.
Example: Methane (CH4) - Gas, Benzene (C6H6) - Liquid
One of the weakest v-d-in ties - between molecules
H2 (m. Pl. -259 OS, T. Kip. -253 OS).
The interaction between molecules is many times weaker communication between atoms:
Ekov (CL-CL) \u003d 244 kJ / mol, EVDV (CL2-CL2) \u003d 25 kJ / mol
But it is precisely it ensures the existence of a liquid and solid state of matter The lectures used professor materials
Chemical Faculty of Moscow State University. Lomonosov
Eremin Vadima Vladimirovich
Thank you
For attention!
The current doctrine of the properties of organic is the development of the idea of \u200b\u200bA. M. Butlerov on dependence on its structure. The expressive structure gives an idea of \u200b\u200bthe whole manifold, although the predictions are not a consequence of strict mathematical laws, but are only a qualitative character and provide a lot of talent and intuition of the experimenter chemical.
The characteristics of the physical properties of compounds are often expressed as the sum of several terms relating to the corresponding elements that are included in this compound. Application such additive schemesto find any physicochemical characteristics of the compound by the formula of its structure, it is also equivalent to the assumption that the element, entering the composition of various compounds, always makes one and the same share of this characteristic.
In the simplest cases, this assumption is to be very close to the truth (additive, for example, the magnitude of molecular volumes and
Lecture 7 The dependence of the properties of substances from their structure. Chemical bond. The main types of chemicals. Questions under consideration: 1. Levels of the organization of a substance. Hierarchy of the structure. 2. Substances of the molecular and non-ethics. 3. A variety of chemical structures. 4. Causes of chemical bond. 5. Covalent Communication: Education Mechanisms, Methods for overlapping atomic orbitals, polarity, molecule dipole moment. 6. ion connection. 7. Comparison of a covalent polar and ion connection. 8. Comparison of properties of substances with covalent polar and ionic connections. 9. Metal connection. 10. Intermolecular interactions.
 Substance (more than 70 million) What should be known about each substance? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Formula (from which) structure (as arranged) Physical properties Chemical properties of the preparation methods (lab. And industrial.) 6. Practical application
Substance (more than 70 million) What should be known about each substance? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Formula (from which) structure (as arranged) Physical properties Chemical properties of the preparation methods (lab. And industrial.) 6. Practical application
 The hierarchy of the structure of the substance is all substances consist of atoms, but not everything is from molecules. Molecule atom in all substances only in substances of the molecular structure Nano-level in all substances volumetric (macro) level of all substances all 4 levels - the object of studying chemistry
The hierarchy of the structure of the substance is all substances consist of atoms, but not everything is from molecules. Molecule atom in all substances only in substances of the molecular structure Nano-level in all substances volumetric (macro) level of all substances all 4 levels - the object of studying chemistry

 Substances Molecular structure The non-molecular structure consists of molecules consist of atoms or ions H 2 O, CO 2, HNO 3, C 60, almost all org. Diamond substances, graphite, Si. O 2, metals, salts of the formula reflect the composition of the formula molecule reflects the composition of a formular unit
Substances Molecular structure The non-molecular structure consists of molecules consist of atoms or ions H 2 O, CO 2, HNO 3, C 60, almost all org. Diamond substances, graphite, Si. O 2, metals, salts of the formula reflect the composition of the formula molecule reflects the composition of a formular unit

 Silicon dioxide substances Formular Si unit. O 2 The Mineralogical Museum named after Fersman is located near the entrance to the Justice Garden. Address: Moscow, Leninsky Prospekt, House 18, Corps 2.
Silicon dioxide substances Formular Si unit. O 2 The Mineralogical Museum named after Fersman is located near the entrance to the Justice Garden. Address: Moscow, Leninsky Prospekt, House 18, Corps 2.
 A variety of chemical structures. Propellan C 5 H 6 Coronen (Superbenzene) C 24 H 12 Kavitand C 36 H 32 O 8
A variety of chemical structures. Propellan C 5 H 6 Coronen (Superbenzene) C 24 H 12 Kavitand C 36 H 32 O 8



 Molecule is a steady system consisting of several atomic nuclei and electrons. Atoms are combined into molecules by forming chemical bonds. The main driving force of the formation of a molecule of atoms is a decrease in total energy. Molecules have a geometric shape characterized by distances between nuclei and corners between connections.
Molecule is a steady system consisting of several atomic nuclei and electrons. Atoms are combined into molecules by forming chemical bonds. The main driving force of the formation of a molecule of atoms is a decrease in total energy. Molecules have a geometric shape characterized by distances between nuclei and corners between connections.

 Main types of chemical bond: 1. ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metal main intermolecular interactions: 1. Hydrogen bonds 2. Van der Wales
Main types of chemical bond: 1. ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metal main intermolecular interactions: 1. Hydrogen bonds 2. Van der Wales
 Ion connection If the connection form atoms with sharply differing electronegability values \u200b\u200b(ΔOeo ≥ 1, 7), the total electron pair is almost completely shifted towards the more electronegative atom. Na Cl OEO 0, 9 3, 16 δ 2, 26 + Na Anion: Cl. Cation of chemical bond between ions arising from their electrostatic attraction is called ionic.
Ion connection If the connection form atoms with sharply differing electronegability values \u200b\u200b(ΔOeo ≥ 1, 7), the total electron pair is almost completely shifted towards the more electronegative atom. Na Cl OEO 0, 9 3, 16 δ 2, 26 + Na Anion: Cl. Cation of chemical bond between ions arising from their electrostatic attraction is called ionic.
 The ionic relationship Coulomb potential is spherically symmetrical, directed in all directions, so the ion connection is not right. Coulomb potential has no restrictions on the number of opponents of the counterions - therefore, an ion connection is unsaturated.
The ionic relationship Coulomb potential is spherically symmetrical, directed in all directions, so the ion connection is not right. Coulomb potential has no restrictions on the number of opponents of the counterions - therefore, an ion connection is unsaturated.
 The ionic connection of the compound with the ionic type of communication is solid, well-soluble in polar solvents, have high melting and boiling temperatures.
The ionic connection of the compound with the ionic type of communication is solid, well-soluble in polar solvents, have high melting and boiling temperatures.
 Ionic connection Curve I: Attraction of ions if they were point charges. Curve II: Pumping nuclei in case of strong rapprochement of ions. Curve III: Minimum Energy E 0 on a curve corresponds to the equilibrium state of the ion pair, in which the strength of the electron attraction to the nuclei is compensated by the reversal of the nuclei between themselves at the distance R 0,
Ionic connection Curve I: Attraction of ions if they were point charges. Curve II: Pumping nuclei in case of strong rapprochement of ions. Curve III: Minimum Energy E 0 on a curve corresponds to the equilibrium state of the ion pair, in which the strength of the electron attraction to the nuclei is compensated by the reversal of the nuclei between themselves at the distance R 0,
 Chemical bond in molecules Chemical bond in molecules can be described from the standpoint of two methods: - The method of valence relations, MVS - molecular orbitals method, MMO
Chemical bond in molecules Chemical bond in molecules can be described from the standpoint of two methods: - The method of valence relations, MVS - molecular orbitals method, MMO
 The method of valence relations The theory of Gaitler-London The main positions of the Sun method: 1. Communication form two electrons with opposite spins, while overlapping wave functions and the electron density between the kernels increases. 2. Communication is localized towards the maximum overlapping of ψ-functions of electrons. The stronger the overlap, the stronger the connection.
The method of valence relations The theory of Gaitler-London The main positions of the Sun method: 1. Communication form two electrons with opposite spins, while overlapping wave functions and the electron density between the kernels increases. 2. Communication is localized towards the maximum overlapping of ψ-functions of electrons. The stronger the overlap, the stronger the connection.

 The formation of hydrogen molecule: H · + · N → H: H with a convergence of two atoms, the forces of attraction and repulsion arise: 1) of attraction: "electron-core" of adjacent atoms; 2) repulsion: "core-core", "electron-electron" of neighboring atoms.
The formation of hydrogen molecule: H · + · N → H: H with a convergence of two atoms, the forces of attraction and repulsion arise: 1) of attraction: "electron-core" of adjacent atoms; 2) repulsion: "core-core", "electron-electron" of neighboring atoms.

 Chemical bond carried out by common electronic pairs is called covalent. The total electron pair can be formed in two ways: 1) as a result of the combination of two unpaired electrons: 2) as a result of the generalization of the vulnerable electronic pair of one atom (donor) and empty orbital of the other (acceptor). Two Covalent Communication Education Mechanism: Exchanged and donor-acceptor.
Chemical bond carried out by common electronic pairs is called covalent. The total electron pair can be formed in two ways: 1) as a result of the combination of two unpaired electrons: 2) as a result of the generalization of the vulnerable electronic pair of one atom (donor) and empty orbital of the other (acceptor). Two Covalent Communication Education Mechanism: Exchanged and donor-acceptor.
 Methods of overlapping atomic orbitals in the formation of a covalent bond if the formation of the maximum electron communication density occurs through the line connecting the centers of atoms (kernel), then such an overlapping is called σ-bond:
Methods of overlapping atomic orbitals in the formation of a covalent bond if the formation of the maximum electron communication density occurs through the line connecting the centers of atoms (kernel), then such an overlapping is called σ-bond:
 Methods of overlapping atomic orbitals in the formation of a covalent bond If the formation of the maximum electron communication density occurs on both sides of the line connecting the centers of atoms (kernels), then such an overlapping is called π-bond:
Methods of overlapping atomic orbitals in the formation of a covalent bond If the formation of the maximum electron communication density occurs on both sides of the line connecting the centers of atoms (kernels), then such an overlapping is called π-bond:
 Polar and non-polar covalent bond 1) If the connection form the same atoms, the two-electron cloud of communication is distributed in space symmetrically between their kernels - this connection is called non-polar: H 2, CL 2, N 2. 2) If the connection is formed by different atoms, the connection cloud is shifted in The side of the more electronegative atom is such a connection is called polar: HCl, NH 3, CO 2.
Polar and non-polar covalent bond 1) If the connection form the same atoms, the two-electron cloud of communication is distributed in space symmetrically between their kernels - this connection is called non-polar: H 2, CL 2, N 2. 2) If the connection is formed by different atoms, the connection cloud is shifted in The side of the more electronegative atom is such a connection is called polar: HCl, NH 3, CO 2.
 Polar covalent bond Dipolet momentum Communication dipole H + ΔCl-δ or H + 0, 18 CL-0, 18 + δ -δ where ± δ is an effective atom charge, the proportion of an absolute charge of an electron. Do not confuse with the degree of oxidation! L The product of an efficient charge on the length of the dipole is called the dipole's electric moment: μ \u003d ΔL is a vector value: directed from a positive charge to negative.
Polar covalent bond Dipolet momentum Communication dipole H + ΔCl-δ or H + 0, 18 CL-0, 18 + δ -δ where ± δ is an effective atom charge, the proportion of an absolute charge of an electron. Do not confuse with the degree of oxidation! L The product of an efficient charge on the length of the dipole is called the dipole's electric moment: μ \u003d ΔL is a vector value: directed from a positive charge to negative.
 Polar covalent bond Dipolet moment of the molecule is equal to the sum of the vectors of dipole moments with taking into account vapor electronic pairs. The unit of measurement of the dipole moment is Debu: 1 d \u003d 3, 3 · 10 -30 kl · m.
Polar covalent bond Dipolet moment of the molecule is equal to the sum of the vectors of dipole moments with taking into account vapor electronic pairs. The unit of measurement of the dipole moment is Debu: 1 d \u003d 3, 3 · 10 -30 kl · m.
 Polar covalent bond Dipolet moment of the molecule in the product μ \u003d ΔL Both variables are multidirectional. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor the reason for the change μ. For example, CS. F CS. Cl 24 31 Δ "lost" L CS. I HF HCl HR HI 37 5, 73 3, 24 2, 97 1, 14, on the contrary
Polar covalent bond Dipolet moment of the molecule in the product μ \u003d ΔL Both variables are multidirectional. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor the reason for the change μ. For example, CS. F CS. Cl 24 31 Δ "lost" L CS. I HF HCl HR HI 37 5, 73 3, 24 2, 97 1, 14, on the contrary
 Polar covalent bond Dipolet moment molecule can molecule be non-polar, if all the connections in it are polar? Molecules type av are always polar. AV 2 molecules can be polar, and non-polar. . . H 2 O O H CO 2 μ\u003e 0 N O C μ \u003d 0
Polar covalent bond Dipolet moment molecule can molecule be non-polar, if all the connections in it are polar? Molecules type av are always polar. AV 2 molecules can be polar, and non-polar. . . H 2 O O H CO 2 μ\u003e 0 N O C μ \u003d 0
 The polar covalent bond of the molecule consisting of three atoms and more (AB 2, AB 3, AB 4, AB 5, AB 6) may be non-polar, if they are symmetrical. What is affected by the presence of a dipole moment of the molecule? There are intermolecular interactions, and, therefore, the density of the substance, T ° of melting and T ° of boiling increases.
The polar covalent bond of the molecule consisting of three atoms and more (AB 2, AB 3, AB 4, AB 5, AB 6) may be non-polar, if they are symmetrical. What is affected by the presence of a dipole moment of the molecule? There are intermolecular interactions, and, therefore, the density of the substance, T ° of melting and T ° of boiling increases.
 Comparison of ionic and covalent polar ties General: the formation of a common electron pair. The difference: the degree of displacement of the general electronic pair (polarization of communication). Ion connection should be considered as an extreme case of covalent polar communication.
Comparison of ionic and covalent polar ties General: the formation of a common electron pair. The difference: the degree of displacement of the general electronic pair (polarization of communication). Ion connection should be considered as an extreme case of covalent polar communication.
 Comparison of the characteristics of ionic and covalent polar bonds covalent bond: saturated and satisfactory (maximum valence) - is determined by the ability of an atom to form a limited number of connections (taking into account both Education mechanisms). The direction of communication sets a valence angle depending on the type of hybridization of the central atom orbitals. Ion connection: unsaturated and non-directional.
Comparison of the characteristics of ionic and covalent polar bonds covalent bond: saturated and satisfactory (maximum valence) - is determined by the ability of an atom to form a limited number of connections (taking into account both Education mechanisms). The direction of communication sets a valence angle depending on the type of hybridization of the central atom orbitals. Ion connection: unsaturated and non-directional.
 Comparison of the characteristics of ionic and covalent polar bonds the focus of communication is set by valence angles. Valence angles are determined experimentally or predicted on the basis of the theory of hybridization of atomic orbitals L. Polling or the theory of Gillespi. In detail about it at seminars.
Comparison of the characteristics of ionic and covalent polar bonds the focus of communication is set by valence angles. Valence angles are determined experimentally or predicted on the basis of the theory of hybridization of atomic orbitals L. Polling or the theory of Gillespi. In detail about it at seminars.
 Comparison of properties of substances with ionic and covalent bonds covalent bonds Atomic crystals between atoms in the crystal itself High hardness high Tº Plav, TºKEP Bad heat and electrical conductivity Molecular crystals between atoms in the molecule moderate softness are sufficiently low Tº molecule, TºKepite bad heat and electrical conductivity
Comparison of properties of substances with ionic and covalent bonds covalent bonds Atomic crystals between atoms in the crystal itself High hardness high Tº Plav, TºKEP Bad heat and electrical conductivity Molecular crystals between atoms in the molecule moderate softness are sufficiently low Tº molecule, TºKepite bad heat and electrical conductivity

 Comparison of properties of substances with ion and covalent bonds Atomic covalent crystal melting point ≈ 3700 ° C
Comparison of properties of substances with ion and covalent bonds Atomic covalent crystal melting point ≈ 3700 ° C
 Comparison of properties of substances with ion and covalent bonds ionic bonds between ions in crystal hardness and fragility High melting point of bad heat and electrical conductivity soluble in water
Comparison of properties of substances with ion and covalent bonds ionic bonds between ions in crystal hardness and fragility High melting point of bad heat and electrical conductivity soluble in water

 Metal communication is carried out by electrons belonging to all atoms at the same time. Electronic density is delocalized by "Electronic Gas". Characteristic metal glitter Plasticity Purility High heat and electrical conductivity of melting temperature is very different.
Metal communication is carried out by electrons belonging to all atoms at the same time. Electronic density is delocalized by "Electronic Gas". Characteristic metal glitter Plasticity Purility High heat and electrical conductivity of melting temperature is very different.
 Intermolecular ties. 1. Hydrogen bond attraction between the hydrogen atom (+) of one molecule and an atom F, O, N (-) of another polymer molecule (HF) N dimer of acetic acid hydrogen bonds weak individually, but strongly collectively
Intermolecular ties. 1. Hydrogen bond attraction between the hydrogen atom (+) of one molecule and an atom F, O, N (-) of another polymer molecule (HF) N dimer of acetic acid hydrogen bonds weak individually, but strongly collectively
 Intermolecular ties. 5. Van der Walsov communication even if there are no hydrogen bonds between molecules, the molecules are always attracted to each other. The attraction between molecular dipoles is called Vantern Waals bond. V-d-in attraction is the stronger than the greater: 1) polarity; 2) Molecules size. Example: Methane (CH 4) - gas, benzene (C 6 H 6) - Liquid One of the most weak V-D-in Relations - between Molecules H 2 (m. Pl. - 259 o. C, t. Kip. - 253 o. c). The interaction between molecules is many times weaker communication between atoms: EOK (CL-CL) \u003d 244 to. J / mol, EVDB (CL 2-CL 2) \u003d 25 to. J / mol, but it is that the existence of a liquid and solid state of matter
Intermolecular ties. 5. Van der Walsov communication even if there are no hydrogen bonds between molecules, the molecules are always attracted to each other. The attraction between molecular dipoles is called Vantern Waals bond. V-d-in attraction is the stronger than the greater: 1) polarity; 2) Molecules size. Example: Methane (CH 4) - gas, benzene (C 6 H 6) - Liquid One of the most weak V-D-in Relations - between Molecules H 2 (m. Pl. - 259 o. C, t. Kip. - 253 o. c). The interaction between molecules is many times weaker communication between atoms: EOK (CL-CL) \u003d 244 to. J / mol, EVDB (CL 2-CL 2) \u003d 25 to. J / mol, but it is that the existence of a liquid and solid state of matter
 The lectures used the materials of Professor of the Chemical Faculty of Moscow State University. Lomonosov Eremin Vadim Vladimirovich Thank you for your attention!
The lectures used the materials of Professor of the Chemical Faculty of Moscow State University. Lomonosov Eremin Vadim Vladimirovich Thank you for your attention!