Lesson 6. Chemical composition
cells. Water and organic compounds.
room
Training
Element
Guide to assimilation
Educational material
UE-0.
Integrating goal: to identify which chemical elements are included in the cells and their biological significance; Examine the biological functions of water.
Read carefully
the purpose of the lesson.
UE-1
Purpose: Reveal what chemical elements are included in the cells of living organisms, and determine their biological significance.
Perform a task.
1. Here, which of the chemical elements listed below relate to macroelements, which to trace elements. Why are they called that?
N, K, B, BP, O, CO, SI, R, C,
Microelements
macroelements
2. Electric composition in human organism cells and in the environment (in% by weight)
a) write down the chemical elements that in the amount are 98% of the entire contents of the cell.
b) write down the chemical elements, the content of which in the cell is calculated with tenth and hundredths of the percent. In sum, they make up 1.9%.
c) write down as examples the name of several elements that are contained in cells in exceptionally small
quantities (less than 0.01%).
d) Using the table on C.27, answer the question: what is the value for the cell: s, n, o,.
3.What does the presence of the same chemical elements in the bodies of living and inanimate matter?
Read the textbook text A.A.Kamensky. § 6.c.26.
Work individually.
Fill in the table in the notebook.
The correct answer is estimated
18 points.
Work with drawings on the task. Work individually in the notebook. The correct answer is 4 points.
For example, A.A.Kamensky §6, p.26. We work in a group, write down in the notebook. The correct answer is 1Ball.
Work with the class. Maximum score for work on UE-1-23 points.
UE-2
Purpose: Explore the characteristics of the water structure, specify its biological functions.
1. Complete the task.
1. It is known that most cells are more than 60-80% consist of water. What conclusion can be made from this fact?
2. Put the biological functions of the water:
but)
b)
at)
3. Insert the missed definitions into the text: "In relation to water, the substance is divided into _________, and ____________.
4. Distribute hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances in the table.
Hydrophilic
Hydrophobic
1.Norganic
2.organic
2. Cover the results of the work.
See textbook 1, p.8.A.A.Kamensky with. 29. We work in the group. The correct answer is 1Ball.
See Paper D.K. Belyaeva 1, C.10, A.A.Kamensky, C.29. Work in the group, write a response in notebooks. The correct answer is 4 points.
See Tutorial D.K. Belyaeva, 1, p.10.
A.A.Kamensky C.29. Work individually. The correct answer is 1 point.
See the tutorial A.A.Kamensky with. 30-31.Y.m. Polyansky 37, p.147. Work individually. The correct answer is 9 points.
Work with the class. Maximum evaluation for work on
UE-2-
15 points.
UE-3.
1. Enter the results of the lesson.
2. Up the purpose of the lesson.
Have you reached the purpose of the lesson? In what degree?
32-39-rating 4; 5-31 estimates-3; less than24-rating 2.
2. Master the task.
If you have been grated-5 in the lesson, you are given a creative task, to prepare the message "Water-cradle of life". If you have experienced difficulties, allowed a lot of errors, read again §6.7 tutorial A.A. Kamensky.
Individually.
Together with the class.
Your mark.
Take a notebook to check the teacher.
Lesson 7. The exercise and their role in the vital cells of the cell. Lipids and their role in the vital cells of the cell.
room
training
element
Educational material indicating tasks
Guide
learning learning
material
UE-0.
Integrating goal: Meet features
structures and biological functions of carbohydrates and
lipids.
Attentively
read the purpose of the lesson.
UE-1
Purpose: Meet the features of the structure and
functions of carbohydrates.
1. Complete the task.
From the given list of carbohydrates, write separately: monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides. Specify them
properties (solubility, taste).
Carbohydrates: glucose, glycogen, fructose, starch, ribose,
deoxyribosis, cellulose, lactose, sucrose.
Monosaccharides
Disaccharides
Polisachary
Dy
Properties:
Properties:
Properties:
2. The carve is an important component of the cell. List their biological functions:
but)
b)
at)
d)
3. Demonstrate experience when characterizing polysaccharides.
A drop of an alcohol solution of iodine is added to the starch solution. The blue color appears. When heated, the color disappears, after cooling, it appears again.
Conclusion: Changing the color is associated with changing the position of the chains in the polymer.
4. Complete the test task.
1. What cells contain more carbohydrates?
a) in vegetable
b) in animals
c) the same amount in those and other cells.
2. What properties have polysaccharides?
a) well soluble in water, sweet taste.
b) poorly soluble in water, sweet taste.
c) lose the sweet taste and the ability to dissolve in water.
3. Very starch called:
a) Ribosu
b) lactose
c) Glycogen
4. Mioner starch is:
a) amino acid
b) Deoxyrbosis
c) glucose
5. If you were given 2 substances and it was said that one of them is glucose, and another starch, which way you can absolutely definitely install, where you have glucose, and where is the starch?
a) by smell
b) water solubility
c) in color.
The correct responses of the test task: 1-A; 2-B; 3-B; 4-in; 5-b.
5. Watch the results of the work.
See Paper
A.A.Kamensky, p.34-35.
Work
Individually.
The correct answer is 15 points.
See A.A. textbook Kamensky p.35-36.
A.O. Ruvinsky 5, p.35-36.
The correct answer is 4 points.
Starch, iodine solution.
laboratory equipment.
For example, A.A. Kamensky.
p.35. Depositories
C.35 Tutorial A.A. Kamensky.
Work with the class. Maximum assessment for work on UE-1-24 score
UE_2.
Purpose: get to know organic lipid compounds; Resect their biological functions.
1. Complete the task. From the listed organic compounds, write lipids and their derivatives: lactose, glycolipids, amino acids, sucrose, sex hormones, vitamin A, ribose, vitamin D, deoxyribosis, cholesterol.
2. Put the main biological functions of lipids:
but)
b)
at)
d)
e)
e)
g)
2. Cover the results of the work.
For example, A.A. Kazamensky§10, p.37-38. Work individually. Correct answer-5 points
For example, A.A. Kazamensky§10, p.39.
The correct answer is 7 points.
Work with the class. Maximum assessment for work on UE - 12 points
UE-3.
1. Enter the results of the lesson.
Read the purpose of the lesson.
3. Master task.
If you have received a rating "5", you are released from homework. If you have experienced difficulties, allowed a lot of errors, read again §9.10 in the tutorial A.A. Kamensky
Individually.
Together with the class.
Your mark:
Take a notebook to check.
Lesson 8. Equipment and proteins.
room
training
element
Educational material indicating tasks
Guide to absorb training material
UE-0.
Integrating purpose: As a result of working with a textbook, you should get acquainted with the structure of a protein molecule, identify the biological functions of proteins.
UE-1
Purpose: Get acquainted with the features of the structure of a protein molecule.
1. Complete the task.
Find out which of the organic compounds listed below is a protein-natural polymer monomer:
a) glucose
b) amino acid
c) fructose
2. Write in the general formula formula of amino acids. Indicate which functional groups are included in its composition, which is the value of the radical.
3. The composition of proteins includes only 20 amino acids, but the variety of proteins is infinite. What is this explained?
4. Here in the proposed dipeptide peptide communications.
2. Cover the results of the work.
Read the text of the textbook
A.A.Kamensky, §11,
p.40. Work individually.
The correct answer is 1 point.
See Tutorial D.K. Belyaeva §3, p.15, Fig.5.
Work in a band in a notebook.
The correct answer is 4 points.
see Poland A.A.Kamensky §11, S.40.Yu.I. Polyansky,
§38, p.150
Work in the group
in the notebook.
The correct answer is 3 points.
UE-2
Purpose: Get acquainted with the structural organization of the protein molecule and its properties.
1. Complete the task.
Protein molecules have a large molecular weight. The cell contains a huge number of a wide variety of proteins. How can the microscopic cell be fitted with many such large molecules?
2. In the figure schematically depicts the structures of the protein molecule. Determine which digit Each structure is indicated and record their names.
3. The proteinmolecules have the property of denaturation. What it is? Why, as a result of denaturation, proteins lose their functions?
2. Cover the results of the work.
Work individually in the notebook. See Yu.I. Polyansky, §38, pp. The correct answer is 1 point.
For example, A.A. Kamensky, §11, p.43 or D.K. Belyaeva, p.19. Rapid response-4 points.
For example, A.Kamensky §11, p.43 or Yu.I.Polyansky §39, p.153. Right response-2 points.
Work with the class. Maximum assessment for work on UE-2-7 points.
UE-3.
Purpose: Get acquainted with the functions of proteins.
1. Complete the task.
1. The cells in the cell perform many vital functions. List them:
but)
b)
at)
d)
e)
e)
g)
2. In each cell contains thousands of enzymes. What is their chemical nature? What role do they perform in the cell?
3. Using Figure16 of the tutorial A.A. Kamensky, explain the mechanism of interaction of the enzyme and substrate.
4. Model from the most important properties of enzymes -specificity. This means that one enzyme catalyzes one reaction or a group of similar reactions. What is this explained?
5fines are active only under certain conditions: temperature, pH of the medium, saline concentration. Why when changing the pH of the medium enzymes lose activity? What is the reaction of the medium in the stomach of a person ensures the activity of enzymes?
2. Cover the results of the work.
See Packaging A.A.Kamensky§11, p.43-46
Work in the notebook individually. The correct answer is 7 points.
See A.Kamensky A.Kamensky P.44. Work individually in the notebook. The correct answer is 2 points.
Work in a band in a notebook. The correct answer is 3 points.
See Yu.I. Polyansky, §39, p. 154-155. Work in a group in a notebook.
The correct answer is 5 points.
For example, A.A. Kamensky, P.44.47,
Yu.I. Polyansky, p.153.I A.S.Batuev "Man",
C.104. We work in the group in the notebook.
Correct answer-4 points
Work with the class. Maximum assessment for work on UE-3-21 points.
UE-3.
Summing up the lesson.
1. Read the purpose of the lesson.
2. Do you have a lesson goals? In what degree?
4. Maximum task: If you received an estimate "5", then you are freed from the task; Difficulties were experienced, allowed a lot of mistakes, read the textbook A.A.Kamensky§11 Drop to questions p.43 -46.
Individually.
Your mark.
Lesson 9.Nukleinic acids and their role in the vital cells of the cell.
room
Educational element
Educational material indicating tasks
Guide to assimilation
Educational material
UE-0.
Integrating goal: to get acquainted with the peculiarities of the structure and the functions of nucleic acids (NK) and the characteristics of the structure of the DNA molecule.
Carefully read the purpose of the lesson
UE-1
Purpose: get acquainted with the characteristics of the structure and the properties of the DNA molecule.
1. Complete the test task:
1. But from biologists first described nucleic acids:
B) Wilkins
2. It is known that the NK is natural polymers. What is the monomer of the NK?
A) amino acid
B) glucose
C) nucleotide
3. What scientists first offered a DNA molecule model (double spiral)?
A) Timofeev-Resovsky
B) Watson and Creek
C) Chargaff
4. How is it called each of the DNA chains?
A) polypeptide
B) polynucleotide
C) polysaccharide
5. Found information is encoded in the DNA molecule in the form of a sequence:
A) amino acids
B) simple carbohydrates
C) nucleotide
2. Communicate the following tasks:
1. Write on the diagram of the Nucleotide components of DNA.
2. Support 4 types of nitrogen bases characteristic of DNA molecule.
3. The basis of the structure of DNA molecules is the principle of complementarity. Using it, on the following DNA molecule suggested below. Build a second chain.
A-A-T-Mr. TS-T-Mr.
4. Product, which process is depicted in the diagram.
A- -t
T - -A + T- -A
Right answers of the test task.
1-B; 2-B; 3-b; 4-b; 5-century.
The correct answer to each question of the test task is estimated at 1 point.
Work individually in the notebook.
Carefully read the appropriate text of the textbook A.A.Kamensky "General Biology"
See Tutorial A.A.Kamensky §12 on p.48 or textbook VB Zakharova "General Biology" §3.2.4.c.106
See Tutorial A.A. Kamensky §12 on p.53 or textbook VB Zakharova "General Biology" §3.2.4.c.106
See Tutorial A.A. Kamensky §12 on p. 50 or textbook VB Zakharova "General Biology" §3.2.4.c.106
See Tutorial A.A.Kamensky §12 at p. 50 or textbook VB Zakharova "General Biology" §3.2.4.c.108
Work individually.
See textbooks.A.Kamensky§12 p.48 Fig.17 or textbook VB Zakharova "General Biology" §3.2.4.c.108
106-107 Fig.3.6.
The correct answer is 3 points.
See Pets. А.Kamensky§12 p.49 Fig.18 or textbook VB Zakharova "General Biology" §3.2.4.c.108
106-107 Fig.3.7.
The correct answer is 4 points.
See Tutorial A.A.Kamensky§12 pp.
The correct answer is 4 points.
See Tutorial A.A.Kamensky§12
The correct answer is 4 points.
Work with the class. Maximum number of points for the work of UE-1-20 points
UE-2
Purpose: get acquainted with the characteristics of the structure and types of RNA. Compare DNA and RNA molecules.
1. Complete tasks.
1. Release on the diagram of the Nucleotide components of RNA.
2. Support 4 types of nitrogen compounds characteristic of RNA molecule.
3. Anxiety similarities and differences in the structure of DNA and RNA molecules. Data Put in the table.
Similarities of DNA and RNA molecules
Differences
4. Fill the table:
Basic species of RNA
See Packaging A.A.Kamensky §12 S.51. Work individually. The correct answer is 1 point.
See Packaging A.A.Kamensky §12 S.51. Work individually.
The correct answer is 4 points.
For example, A.A.Kamensky §12. Work in the group. The correct answer is 7 points.
For example, A.A. Kamensky §12, p.51-52. Work in the group. The correct answer is 4 points.
Work with the class. Maximum number of points
For work on UE-2-16 points.
UE-3.
Summing up the lesson.
1. Read the purpose of the lesson.
2. Do you have a lesson goals? In what degree?
If you have scored the final number of points from: 32-36 points, then your rating is "5", if 28-31, then the rating "4", 17-27, then your rating "3", less than 16 points - estimate "2 "
4. Maximum task: If you received an estimate "5", then you are freed from the task; Difficulties have been experienced, allowed a lot of mistakes, read the textbook A.A. Kamensky§12 Assist on questions S.52-53.
Individually.
Your mark.
Lesson 10.ATF and other organic substances.
room
training
element
Educational material indicating tasks
Guide to assimilation
educational material
UE-0.
Integrating goal: Determine the initial level of knowledge (input control)
Write down the date and name of the topic studied in the notebook.
Perform a task.
1. Transfer.
One of the chains of the fragment of the DNA molecule has the following structure:
Mr.-Mr.-T-A-A-C-A-G-A-T
a) Specify the structure of the opposite chain.
b) Specify the sequence of nucleotides in the molecule and RNA, built on this section of the DNA chain.
2. Possession:
On the fragment of one DNA chain nucleotides are located in the sequence:
A-A-Mr. T-T-T-CC-Mr. T-T-T
1. Draw the diagram of the structure of double-stranded DNA
2. To reflect what the DNA property at the same time you were guided.
3.Kakova Length (nm) of this DNA fragment? (Each nucleotide takes 0.34 nm along the DNA chain length)
4. How much (in%) contains nucleotides (separately) in this DNA?
3. Translation. In the DNA molecule, 880 guanilla nucleotides were found, which constitute 22% of the total number of nucleotides of this DNA. Determine: a) how much containing other nucleotides (separately) in this DNA molecule; b) What is the length of DNA.
Solving the task yourself in the notebook.
The correct answer is 3 points.
Maximum score-9 points
UE-1
Purpose: get acquainted with the features of the ATP structure and its functions.
Perform the following tasks.
1.Dow the names of the components of the ATP molecule.
2. What can be said about the chemical structure of ATP?
3. Does the difference between ATP from ordinary nucleotides?
but)
b)
4. What function performs ATP in a cell? Where is the place of her education?
2. Cover the results of the work.
Read the purpose of the lesson carefully.
See Yu.I. Polyansky§42, p. 163, or A.A.Kamensky§13, p.54.
Work in the notebook individually. Right
Reply-3 points.
For example, A.A. Kazamensky§13, or Yu.I.Polyansky§42, p.163.
Work in the group.
Correct answer -1 score.
See Paper A.A.Kamensky §13, p.53, or A.O. Ruvinsky §7, p.45. We work in the group.
The correct answer is 4 points.
For example, A.A. Kazamensky§13, p.53.
Work individually. The correct answer is 2 points.
Together with the class.
Maximum amount
points for work on UE-1-9 points.
UE-2
Summing up the lesson.
1. Read the purpose of the lesson.
2. Do you have a lesson goals? In what degree?
28-26Ballov, then your rating "5", from25-23Ballov - "4", 22-20Balles - "3", less than19 points, then "2".
4. Maximum task: If you received a rating "5" -votable from homework; Tested difficulties repeat 13 A.A.Kamensky.
Under the influence of the enzymes of the ATP molecule is hydrolyolism, the energy (40 kJ) is released.
1st stage: ATP + H2O \u003d ADP \u003d N3RO4
It is carried out individually.
Your mark.
Take a notebook to check the teacher individually.
MBOU "Ust-Mutinskaya Secondary School"
Modular biology lesson
"Chemical composition of the cell. Water and organic compounds. "
Masted teacher biology
MBOU "Ust-Mutinskaya SOSH"
Sankova Marina Nikolaevna
S. Us-Muta, 2011
"Modular learning technology
In biology lessons "
Introduction
The main goal of the modern school is to create a system of learning that would provide the educational needs of each student in accordance with its inclinations, interests and opportunities. To achieve this goal, it is necessary to radically change the attitude of the student and teacher in this educational process. Currently, the educational process in the mass school continues to maintain an explanatory-illustrative character, which leads to increased contradiction between the student's requirements in the development of its inconsistencies, interests and the traditional training system. Therefore, before school practice, the problem of finding individual learning technology was faced, allowing to ensure the student to develop its intelligence, independence, collectivism, inclinations, carry out self-government to educational activities.
The traditional system with its explanatory-illustrative methods, in which the teacher only explains and asks, controls and evaluates, and students work in one specified rhythm monotony and boring. And most importantly, it does not make it possible to develop the skills of independent work in schoolchildren. In addition, the acquired knowledge without intellectual development of students lie "dead cargo" in the head of the student. It is difficult to agree with this. The development of thinking and other mental processes should be paid to special attention. But it is quite difficult to systematically and regularly implement such ideas in practice. There are several reasons for it. The most serious one of them is the time of learning is limited, and the volume of knowledge that the teacher should give a student is quite large. As a result, the teacher arises the problem: as for a limited time, not overworking the guys, not only to give them knowledge, but also to pay attention to the formation of mental functions.
There are many opportunities to combine one with another. Moreover, there are techniques that allow you to create a kind of symbiosis. In the long term, they lead to the development of thinking and other mental functions, and on the nearest segment of time it contributes to a more rapid absorption of the material. Knowledge is not just becoming more meaningful (which means more flexible, it is easier to transfers into practice), children begin to learn from a greater hunt. After all, the reluctance to learn from children often arises because they are taught without understanding. And overlooking this: the mechanical memory is overloaded, and the rest "sleeps".
All this prompted the teacher to look for such technologies that would allow not only to give knowledge, but also to teach children to extract these knowledge, objectively evaluate themselves and their capabilities, to work independently, to help someone who needs help to learn to communicate with classmates and adults and respond For the result of his labor.
The decision of this task is the organization of the educational process on the modular learning technology. The most deeply and systemically didactic specificity of modular learning managed to explore and describe P.A. Utsyaviche According to the views of this author, the modular system of organizing the educational process has some differences between a principled nature from the traditional system. The learning content is submitted to the finished, independent modules that are simultaneously the information bank and the methodological guidance on its use. At the heart of such training lie subject - subjectiverelationship between teacher and student. It is ensured by an independent, conscious achievement of a certain level in the teaching. There is a high degree of adaptability of elements to the conditions of the pedagogical process.
The purpose of modular learning (According to P.A. Yusyavichene):
Comfortable pace of work of the student, defining them of their capabilities, flexible construction of the content of learning, the integration of its various types and forms, achieving a high level of end results.
Leading principles of modular training:
Mobility;
Structuring the content of learning;
Dynamic;
Effectiveness and efficiency of knowledge;
Flexibility;
Conscious perspective;
Versatility of methodological consulting;
Parity;
Purpose of the study: Determine and substantiate the basic elements of modular technology that improve the effectiveness of the educational process in biology lessons.
Object of study: Educational process in biology lessons.
Subject of study: The main organizational and meaning elements of the modular technology.
Research tasks: Describe the basic elements of the modular technology.
Research methods:analysis of pedagogical and methodological literature, school documentation, modeling, testing, surveillance, observation, comparative analysis.
Modular learning technology
Modular technology - a combination of goals, principles, design methods, designing didactic materials, rating system for assessing and controlling achievement.
The leading characteristics of the technology is flexibility - the ability to respond quickly and mobile to adapt to changing scientific and technical and socio-economic conditions. This is the mobility of the module structure, and the differentiation of the content of learning, and the variability of training methods, and the flexibility of the control and evaluation system, and the individualization of the educational activities of the student. The principle of modularity implies integrity and completeness, completeness and logicality of the construction of the units of the educational material in the form of modules within which the educational material is structured as a system of training blocks (elements). These blocks are interchangeable and movable. The development of educational material occurs in the process of a completed cycle of educational activities. This flexibility is based on the variability of the levels of complexity and the difficulty of educational activities.
Since modular training involves the formation of self-education skills, the whole learning process is based on the achievement of neighbor (knowledge, skills, skills), medium (general educational skills and skills) and promising (development of personality abilities) goals. The awareness of training activities translates the teacher from the reporting mode to consulting and management regime. Modular technology provides for the creation of positive motives for learning thanks to the novelty of content, enormality, emotional content, organization of study search, support for life experience, overcoming cognitive difficulties.
Modular Training Tool - Module
A modular learning tool - a module is a target functional node, which combines the study content and taking training activities for these content. This is an instruction to achieve the goal of educational and cognitive activity, an individual program containing a target action plan, a bank of information, instructions for the implementation of self-control, self-assessment, self-analysis.
The module includes:
Action plan with specific goals;
Information bank;
Methodological guide to achieve these goals.
This is a structural unit of a holistic learning system.
The value of this unit depends on the level:
Level 1 - educational element - module;
Level 2 - lesson module;
Level 3 - block lessons (theme);
Level 4 - Item - module.
Methodical essence of modular technology.
Providing a central location in the teacher - student system, the translation of a schoolboy from the state of learning and education in the state of active activity as a subject of life.
The main characteristics of the modular technology.
motivation activities;
parity relations of teachers and students;
opportunity to communicate with comrades;
the openness of the final results of the activity and the warranty of their achievement;
"Soft" control in the process of mastering the study content;
psychological comfortable climate in class.
General educational skills and skills of students with modular technology.
the ability to put the goal of its activities and subordinate all its actions of this goal;
the ability to independently produce knowledge, acquire certain special skills;
evaluate and analyze their activities;
self-control skills, interconnection, educational, business communication, self-study,
the ability to work in a pair, group, independently according to the algorithm and creative.
The role of the teacher at modular training.
Drawing up modules - instructions;
Clarification of instructions in practical work with them;
Knowledge control and skills correction.
The teacher should definitely formulate the purpose of the lesson, the tasks of each stage of the lesson, to smash the learning content to separate logically completed training elements, consider the algorithm for the execution of each of them, to determine the ways of studying students, predict the result, prepare the required number of copies of the lesson's text (the technological card should be Each student or at least on each desk).
The element of the modular learning technology is a modular lesson.
The modular lesson consists of two academic hours. When drafting a modular lesson, I use the following items:
wording theme lesson;
definition and wording of the lesson and final learning outcomes;
breakdown of learning content into separate logically completed training elements (UE);
selection of the necessary actual material;
determining the methods of educational activities of students;
selection of methods and forms of teaching and control;
compilation of the module of this lesson.
Each learning element in a modular lesson is a step towards achieving an integrating lesson objective, without mastering the content of which the goal will not be achieved. The educational element (UE) should not be a lot (maximum number - 7), but I must use the following:
UE-0. - The integrating point is determined to achieve learning outcomes.
UE-1 - includes, as a rule, tasks to identify the level of source knowledge on the topic; Tasks for mastering new material, etc.
UE-2 etc. - testing of educational material.
UE-P. (where n is the number of the last educational material) - includes the output control of knowledge, summing up the lesson (assessment of the degree of lesson's goals), the choice of homework (it should be differentiated depending on the success of the work, taking into account the assessment of others).
During modular training, a targeted formed formation and development of educational techniques are carried out. The study content here is a means to achieve the goals of this most important process.
In the process of studying the module, students learn to independently produce knowledge by working with a textbook and D.R. Sources of information. As a result of curriculum in the lessons, interest in the subject increases, since one type of activity replaces the other.
On modular lessons, students can work individually, pairs, in groups of constant and variable composition. The fit form is free, each of them has the right to choose: one he will work or with some of the comrades.
The role of the teacher in the lesson is to manage the learning process, counseling, helping and supporting students.
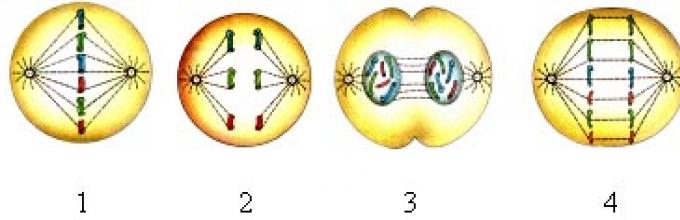
"Cell division. Mitosis".
Cell division. Mitosis.
Objectives:
as a result of mastering the contents of the modules, you will know about the value of the cell division for reproduction, growth and development of organisms, processes occurring in a cell, forms of cull breeding: mitotic cell division;
develop self-study skills.
Equipment:
tables in general biology;
table "Mitz";
Educational material indicating tasks
UE-0.
Objectives lesson: As a result of working on the module, you will receive an idea of \u200b\u200bcell division, mitotic division, municipal and sexual reproduction; Continue developing self-study skills
Carefully read the purpose of the lesson
UE-1
Preparation for work
1. Discuss and prepare oral answers to questions:
Why is a live cell is the main unit of the structure, vital and development of organisms?
Are there fundamental differences in the structure between pricing cells and eukaryotes?
What substances determine the individual development of organisms?
What tasks are facing cell and genetic engineering?
Prove that the cell is a structural and functional unit of living organisms?
Work in the group
2. Discuss the results of tasks.
Evaluation Criteria: Each correct answer to the question is 1 point. The maximum number of points is 5.
Together with the class.
Your mark__
UE-2
Goal:get an idea of \u200b\u200bcell division, mitosis.
1. Lecture "Cell division. Mitosis".
Plan lectures
Cell division in single-cell organisms. Division of cells of multicellular organisms.
Preparation for division.
Phase mitosis.
Listen carefully, allocate new terms when recording.
Your mark__
UE-3.
Goal:examine the crucible and sexual reproduction.
1. The reproduction of organisms is the basis of the existence of a species and in general life on Earth. (Conversation).
2. Forms of reproduction of organisms (story with the simultaneous sketch of the circuit with the corresponding name).
(Independent work with a textbook)
3. Comparison of the crucible and sexual reproduction according to the following characteristics:
The number of individuals involved in reproduction;
Are the games formed?
Which method is missing MEIOS?
Who are the descendants like?
What organisms are characteristic?
Where is the increase in the number of numbers?
(Conversation on questions with answers)
Work independently with a textbook and write to the notebook.
Alone with textbooks, record the scheme in the notebook.
Independently make up the characteristic
4. The structure and function of genital cells.
Comparable signsWomen's Gamets.
Men's gametes
1. Form and dimensions
2. Features of the structure
3. Functions
Fill in your own table
Discuss the results of the work.
Together with the class.
Your estimates __
UE-4.
Goal: Determine the quality of knowledge on the topic studied.
1. Answer questions and follow the tasks.
2. Why is the reproduction is considered the most important and necessary attribute of the living?
3. What are the main form of breeding? Explain them.
4. Select the correct answer.
The cell center is called:
a) the period of life of the cell during the interphase.
b) the period from the opposity to the BELFAZ.
c) the period from division to division.
d) the period from the appearance of the cell before its death.
Which of the processes precedes mitosis?
a) the disappearance of the nuclear shell.
b) doubling chromosomes.
c) the formation of the separation of division.
d) the discrepancy of chromosomes to the poles of the cell.
How much chromatide contains a pair of homologous chromosomes in mitosis metaphase?
a) four.
b) two.
d) eight.
The most extended:
a) metaphase.
b) Profas.
d) interfac.
d) Bulfase.
Which of the named organisms prevails the useless reproduction ?
a) peas.
b) shark.
c) May beetle.
d) amoeba.
Self give answers to questions.
Choose the correct answer
5. Install the sequence of the mitosis stage.

Answer:________________________________
Write down in the "answer"
6. Distribute events in accordance with the phases of the cell cycle.
EventsPhase mitosis
1. Synthesis of proteins and doubling chromosomes
a) PROFADA
2. The location of chromosomes by equator, the formation of the separation of division
b) metafas
3. Education of new nuclei
c) Anafhaza
4. Difference chromosome to poles
d) Bulfasa
Chromosome spiralization, disappearance of nuclear membrane
e) interfac
Check your work.
Right answers:
4 - in, b, a, a, g;
5 – 2, 1, 4, 3;
6 - 1-d, 2-b, 3-g, 4-in, 5-a.
All four are performed correctly - "5".
Three tasks are performed correctly - "4".
Two tasks are performed correctly - "3".
One or all tasks is incorrect - "2"
Together with the class.
Alone.
Your mark______
UE-5.
Lay the results of the lesson.
1. Read the purpose of the lesson.
2. Have you reached the purpose of the lesson? In what degree?
4. Take a notebook to check the teacher.
5. If at the end of the lesson you got "5", then you are freed from your homework. If you have experienced difficulties, made a lot of mistakes, work with the textbook:
Individually.
Together with the class.
Stress the desired word.
For help contact the teacher
Thus, with modular learning technology, the principle of level differentiation is implemented, which makes it possible to learn to absorb not only the standard of education, but also to move to a higher level.
Advantages and disadvantages of modular learning
Problems related to the implementation of modular technology.
These are the money costs for photocopying modular lessons, as well as insufficient training of students Motivation to independent work.
In systematic use of modular learning technology, students are formed and improved skills of independent learning activities. If the student manages to score the right number of points, then its self-esteem increases, self-confidence, an interest in the study of the subject appears, the desire to higher results.
What do I like most in the modular learning technology?
there are no vacationers in the classroom and bored;
the demanding of strong students to a weak working in one pair;
the possibility for strong disciples to manifest itself, the possibility of self-realization;
replies of students to questions during reflection, their prediction of the results of their future activities; originality and optimisticity.
How is the calculation of points during the lesson?
On a separate leaf, each student fixes points for the execution of each task according to the instructions available. This happens under the control of a teacher or a student working in a pair. At the end of the lesson, glasses are summed up, the sheet is surrendered to the teacher to place the appropriate assessment, if the teacher has doubts about the correctness of the tasks, it takes on checking a notebook to correct an objective assessment.
How reflexia is carried out?
Usually by the method of unfinished proposals. Most often in writing due to various pace of work of students. Some offers are allowed to miss if they cause difficulties in children.
Sometimes I have questions about the choice of answers as reflection.
For example:
Are you satisfied with your work at the lesson?
A) yes; b) and yes, and no; c) no; D) I find it difficult to answer.
How are you going to eliminate gaps, difficulties?
A) I will ask the teacher; b) I will ask the comrade; c) Clean myself; d) I do not know.
Would you be able to explain the new material to your comrade?
A) yes; b) partially; c) no; D) I find it difficult to answer.
What form of work in the lesson do you prefer?
A) individual; b) pair; c) group; d) collective when the whole class participates.
Thus, when using modular learning technology, all the skills of "self-" student are being implemented: self-study, self-determination, self-control, self-assessment, self-analysis, self-realization.
With a cool-urgent training, the teacher is the only person interested in this process, which knows the goals and ways of activity. The teacher explains, asks, assesses, and children act as passive participants in training. They mostly listen and answer.
In modular training, the teacher acts as an organizer of learning. He manages the learning process. Teacher here is a consultant, assistant students. Part of its functions, he transmits children (interconnection and self-control) in the process of working out the material on the criteria developed by the teacher.
This allows you to create conditions for analytical creative activity of students, form the ability to speak in mathematical language, draw conclusions, defend your point of view.
Conclusion
For the transition to modular training requires certain conditions:
sufficient teacher training, his desire to master new teaching technologies;
schoolchildren's readiness for independent educational and educational activities, formation of students of a minimum of knowledge and general training skills;
the ability to replicate modules, as each student must be provided by the Action Program.
This training system requires a great pre-work teacher, from a student - intense labor. But it brings good results, motivating the educational needs of a schoolboy, providing them and taking into account individual capabilities. According to the results of the survey, the question "What gives you modular training?", Children answer in this way: the main thing is that everyone works independently, it is possible to receive consultation from the teacher, helping the comrade is aware of the training content, all Time can be controlled.
Examine biology more deeply helps the modular approach.
Thus, it can be argued that the modular biology learning technology is quite effective. Compared with traditional teaching technology, the modular technology guarantees an increase in high-quality academic performance, an increase in knowledge strength, an increase in overall efficiency.
In this academic year, I use elements of modular technology in 8, 9 and 10th grade. As an illustration, I propose technological maps to block modular biology lessons.
Performance:
the number of students learning on "4" and "5" is 89%;
students constantly occupy prizes on the district biology competitions;
the interest of students to the study of biology remains stable;
the number of graduates of 11 classes entering universities and the types in specialty associated with biology is 22%.
Terms of performance :
subject and methodological competence of the teacher, a high level of pedagogical culture;
careful selection and training of educational and additional material;
accounting for the basic training of children's education, the use of a differentiated approach;
permanent monitoring and self-control of the level of knowledge, which allows you to move from simple algorithms to more complex, creatively apply the knowledge obtained during modular learning.
Literature:
Burtseva O.Yu. Modular learning technology // Biology in school, 1999, No. 5.
Burtseva O.Yu. Modular biology lessons: practice practices in school (section "Animals"). - M.: School Press, 2003
Berseneva L.A. "Two modular lessons in natural science." Issue number 1, 1996;
Inoshetseva N.A. The cell is a structural unit of living (modular theme planning) // Biology in school, 2003, No. 2 .. The concept of profile training at the elder step of general education // Teacher's newspaper, 2002, No. 31.
Holyurekina L.P., Zbarovsky b .c. Modular learning technology: guidelines. - St. Petersburg: Uniti-Dana, 1993. -135c
Guzeev V.V. Director of the School "General Technology: from reception to philosophy". Issue No. 4, 1996;
Selko G.K. Modern educational technologies: Tutorial. - M.: Uniti-Dana, 1998. - 344c.
Tretyakov P.I., Sennovsky I.B Technology of modular training in school: Practical-oriented monograph / Ed. P.I. Tretyakova. - M.: New School, 1997. - 352c.
Shamova T.I. Modular training: Essence and technology // Biology in school, 1994, No. 5.
Shamova T.I., Davydenko T.M. Rogacheva N.A. Technological map as the basis of the planning of the educational process // Biology in School, 1992, No. 5-6.
Yucentavichene P.A. The theory and practice of modular learning - Kaunas, 1989.-286c.



Algorithm for compiling a modular lesson. educational material for separate logically completed training elements and determining the purpose of each of them

Advantages of a modular lesson 1. The lesson is clearly structured and a certain amount of time is given to each educational element 2. Each student works in a tempo convenient for himself 3. Psychological comfort of students is provided 4. Students independently master the material, the teacher directs the activities of students 5. Individualization of students' knowledge control


Ue 3 Tsel: to study the methods of the most powerful reproduction. Task: Read the text of the tutorial Determine the type of reproduction of 4 minutes UE 4цел: Examine the process of sexual reproduction. Task: read the text of the tutorial, fill in the table. 10 Min UE 5Tzel: To study the advantages and disadvantages of sexual and powerful reproduction. Task: Resect 3 advantages and lack of sexual and powerful reproduction 5 min


Graphic dictation 1. Present is reproducing yourself like. 2. The onboard reproduction occurs with the help of Games. 3. Plants can multiply with a dispute. 4. The most ancient way of reproduction is sexual reproduction. 5. The connection is the method of useless reproduction. 6. The genetic material does not change during sexual reproduction. 7. Animals do not multiply with the help of cull breeding.


biology teacher MBOU SOSH with. Ilyinka Kaa-Hem district
Modular learning in biology lessons
The technology of modular learning is characterized by an advanced study of the theoretical material by enlarged blocks - modules, algorithmization of educational activities, the completion and coherence of cycles of knowledge and other activities.
The fundamental concept in modular learning technology is a module. The module is the target functional node, which combines the study and technology of ownership.
The construction of the module itself begins with the formulation of goals for each educational element and the task itself. Output control, which is created as a separate educational element, implies verification by mastering the module content.
What is different learning from other training systems?
First, the learning content is submitted to the completed independent information blocks, the assimilation of which is carried out in accordance with the complex didactic goal. In addition, each student receives advice from the teacher in writing, as more rational to act, where to find the necessary educational material, etc.
Secondly, the form of communication of the teacher and the student is changing.
Thirdly, the student works for a maximum of time independently, learns self-spanking, self-organization, self-control, self-esteem. This makes it possible to realize yourself in activities, determine the level of learning of knowledge, see spaces.
Fourth, the presence of modules allows the teacher to individualize work with individual disciples (especially lagging).
Traditional methods and teaching techniques are not so fully and effectively enable students to learn knowledge on software material. Block-modular learning efficiently and more productive, contribute to the high level of special professional skills, changing the functions of the teacher: it becomes a consultant, the interlocutor of students.
The use of various learning methods, expanding the possibilities of inclusion in the lesson of independent activities of students, their activation contributes to a block-modular study, which involves the union of various forms of academic work into a single block of lessons on the topic.
When studying the material, the following conditions are needed by large blocks:
- Clear organization of the entire educational process.
- Setting goals and learning tasks for the entire topic block.
- The combination of verbal visual methods (including the use of reference abstracts).
- Widespread involvement of students in various types of independent activities in individual, steaming, group forms.
- Combined method of control: a written response, an oral presentation, mutual control.
- Faith teacher by virtue of the ability of students.
To improve interest in the teachings and facilitate the assimilation of the material, we use various forms and methods of teaching. Now I work on modular technology. I think this direction is quite promising. In my opinion, modular learning has a number of advantages compared to traditional:
- first, it provides an opportunity for students to work individually, in the inherent pace, in pairs or groups;
- secondly, provides "soft" forms of control.
The structured content of the educational material involves consideration of the object as a system. The configuration and nature of links inside the system is its structure remaining unchanged when the system changes under certain limits.
The question of the possibilities of block-modular structuring of education in high school, primarily associated with the problem of the age of trainees and with the level of their skills and the skills of organizing independent labor. So, in junior grades, the emphasis should be made to the pedagogical process, organized and managed directly by the teacher. And starting from middle classes, you can enter the elements of modular learning technology. Such elements may be simplified modules in which the emphasis is on management and self-government activities of students, control and self-control of their knowledge.
The modules in the educational process are advisable to introduce gradually: undertakings from individual lessons, courses, subjects and specific students with well-formed skills of self-education activities in high school modular learning technology can be fully introduced into the pedagogical process. The degree of possession of the school skills of high school students allows you to fully structure the content of the curriculum using the modular learning system.
Algorithms block and modular structuring on the example of the content of biology:Stage I. In the content of the training course, it is necessary to highlight the leading directions of the educational subject as the basis for the development of students' discipline of biology (Table1)
BIOLOGY |
|||||
Starting course | Living organism | General biology |
|||
Nature. Grade 5. | Living organism. 6th grade | Variety of living organisms. 7th grade | Human. 8th grade | Common laws. Grade 9. | General biology. 10-11 class |
Studying the universe, land, living organisms, man's place on earth | Studying the structure and properties of living organisms, their livelihoods and interaction of the body and the environment | Study of various kingdoms of wildlife: prokaryotov, mushrooms, plants and animals, viruses | Study of the features of origin, structure, functions of various systems of human organs and its behavior | Studying the general patterns of wildlife, the emergence and development of life on earth, structural organization of living organisms, their breeding of heredity and the basics of ecology | The study levels organizations alive matters, Origin And the development of life On Earth, Building cells basis reproduction of organisms, patterns genetics, Ontogenesis and evolutionary the teachings of the development of the organic world on Earth, the basics of the ecology and interaction of the biosphere and man |
IIETAP. Structuring the content of the educational material calculated for one year of study (Table2)
The school course "Diversity of Living Organizations" consists of 4 main blocks of educational material.
I block (MP modular program) talks about the overall characteristic, origin and features of the structure, livelihoods and roles in the nature and life of a person of various simple organisms.
II block dedicated to the kingdom of mushrooms. It describes the classification, features of the structure, nutrition, reproduction and values \u200b\u200bof mushrooms in nature and human life.
III Block Includes the study of two fabrications of plants: the lower and higher, in which the variety, classification, structure and processes of vital activity, as well as the role of plants in the biosphere and human life are described.
IV Block He studies the kingdom of animals and consists of two facilities: single-celled and multicellular animals, which are divided according to a certain plan: the structure, the main processes of vital activity, the role in nature, human life and its economic activity.
III stage. Creating a block - modular structuring of educational material based on the "Tree Tree". Each modular program (MP) is given a name that displays the essence of the topic selected for this and partition.
"Tree of goals" | MP "Diversity of Living Organizations" |
||||||
KDC. | MP "Kingdom prokaryota" | MP "Kingdom Mushrooms" | MP "Kingdom of Plants" | MP "Kingdom Animals" |
|||
IDC | IDC | M 1 - general characteristics prokaryot | M-2. Features of the structure and life activity prokaryot | M-3. Promotion of oxyphotobacteria, features of the organization, role in nature, practical significance | |||
UE-0. Log in to the OCD. | UE-1 Bacteria structure and vital activity | UE-2 Features oxyphotobacterium | |||||
The basis of any modular program is a set of targets (KDC - a complex didactic goal, IDC is an integrating didactic goal). The compilation of the modular program always begins with the allocation of the main scientific ideas of the course, within which the objectives of the study of themes and individual lessons are formulated. Only then the learning content is structured around these ideas into certain blocks. The combination of the objectives of the modular program can be represented as a tree. The trunk of a tree in content corresponds to a separate topic; Stem branches correspond to individual lessons - modular lessons are divided into educational elements or lesson stages. A distinctive feature of the modular technology is that for each educational element their didactic goals are being developed.
The principle of modularity involves building a training course on blocks-modules, inside of which the material is represented as a system of training elements (UE). For each of their UE develop their didactic purposes, without mastering which the common goal will not be achieved.
UE should be no more than 7, but among them are necessary:
- UE-0, aimed at determining the objectives of the learning.
- UE-1, which includes tasks to identify the level of knowledge on the topic and on mastering new material. Sometimes I admit the absence of this UE.
- UE-2, etc. - testing material.
Finishing UE - Summing up:
- evaluation of the degree of achievement of the purpose of the lesson;
- selection of homework, taking into account achievements in the lesson;
- evaluation of work.
IV stage.
Modular learning technology is distinguished by such qualities as:
- flexibility (adaptation to the individual characteristics of the student);
- dynamic (training of types and methods of activity);
- mobility (interconnection, interchangeability and mobility of models inside one topic);
- the ability to conduct modular lessons at different stages of the educational process (study, consolidation, generalization);
- changing the forms of teacher's communication with students.
When drawing up lesson using block modules, I use the plan:
- wording theme lesson;
- determining the objectives of the lesson and the desired learning outcomes;
- breakdown of educational material into separate, logically completed, educational elements;
- selection of the necessary actual material;
- determining the methods of educational activities of students;
- selection of forms and methods of teaching and control.
The principle of modularity involves the integrity and completion, the completeness and logicality of the construction of the units of the educational material in the form of block modules, within which the training material is structured as a system of training elements. From block modules, a biology learning course is constructed.
In modern biology programs, it is possible to distinguish blocks of themes (8-10 hours) and submit several learning modules in them:
I module (1-2 lesson) - oral presentation by the master of the main issues of the topic, disclosure of nodal concepts.
II module (3-5 lessons) - independent and practical work. Pupils on the tasks and under the leadership of the teacher work with various sources of information (textbook, didactic material, reference books, etc.), work the topic of the topic, discuss discussion issues. At this stage, workshops, conferences, travel, games are held.
III module (1-2 lesson) - repetition and generalization of the topic of the topic.
IV module (1-2 lessons) - monitoring knowledge of students throughout the topic.
The combination of concentrated presentation of the main material content of the topic with independent activities of each student separately all together provides certain advantages to such a study of the material. This allows students to clearly determine the general provisions of the topic, submit material in integrity, feel the practical significance of the knowledge studied, to join an independent search and discussion of the results obtained.
The module has an instruction in which, in which the objectives of the assimilation of the modules and each educational element are determined; tasks for performing different levels of complexity; Materials for work; instructions on the form and form of work; Monitoring determining the degree of learning material assimilation (written or oral control of the teacher, self-control, mutual control, etc.).
The module instruction may assume:
Individual independent work of the student;
Partner work in pairs;
Work in the group.
The role of a teacher in modular learning technology is reduced to the following: Development of instructions of modules; Providing individual aid, maintaining the rate of lesson, managing educational and educational activities through modules, clarifying modules in practical work with them, control and correction of learning knowledge, skills and skills.
The technology of modular learning determines the clear structure of the lesson, gives the teacher the opportunity to "see" the whole class, work individually with each student, to assist behind the lagging.
The technology of modular learning is estimated to perform each element. Evaluations accumulate, and the final mark of work is set. The accuracy of control and objectivity of the assessment plays a big role. Get a good assessment is one of the main motivations in the technology of modular learning. The student clearly knows that its work is estimated at each stage and the assessment objectively reflects its efforts and abilities.
Analysis of learning outcomes on block-modular technology allows you to draw the following conclusions:
- The study of biology lays the foundations of natural science thinking, develops careful attitude towards the environment, teaches the ability to lead a healthy lifestyle and forms an ecological culture.
- The purpose of natural science education is to master the ideas of ideas about the nature and dynamics of natural processes, the development of the abilities of independent work with various sources of environmental information.
- The results that students are achieved in the educational process are detected not only through the assessment of the quality of the educational process, but also through the assessment of the conditions. One of the conditions for improving the quality of the educational process can be the block-modular structuring of biology content.
- Block-modular structuring contributes to the consideration of school disciplines as systems through the use of modular learning technology.
- Modular learning technology allows you to present the content of education in the form of complete independent blocks.
- Modular learning technology contributes to a change in the shape of the communication of the teacher and the student.
- Modular learning technology provides students with the maximum amount of time to work independently, which makes it possible to realize yourself in training activities.
- Modular learning technology allows individualizing work with individual disciples.
- With the help of modular learning technology, you can share training material on portions (individual parts).
- Block-modular structuring of the content of natural disciplines makes it possible to improve the quality of student learning and strengthen interest in subjects through the use of non-traditional forms of learning.
Modular lesson number 3.
Topic: multicellular green algae (ullitz, spirohyra, ulva and others). Brown and red algae.
UE - 0 (educational element -0) 2 min.
Integrating goal:
- Expand knowledge about the variety of green multicellular algae.
- The structure and value of brown and red algae.
- Examine the meaning of algae in nature and in human life.
Equipment:
Textbook Book "Biology, bacteria, mushrooms, plants" -25 copies;
-Croscope -15 pieces;
-Micropreparation Green multicellular algae algae.
Tables: "Unicellular and multicellular green algae", an avenous plan with a task - 15 pieces, working notebooks - 25 pieces, a codeoscope, screen, color transparencies: red and brown algae, the right answers to the UE-5 (Task number 1) at the teacher on Transparency.
UE- 1. Input control 8 min.
Purpose: Determine the initial level of knowledge about unicellular green algae.
- Repetition of the previous material on unicellular green algae (oral conversation).
Task number 1. For each full and correct answer to the question, the teacher estimates in 1 point.
- What kind of single-celled algae do you know?
- Among single-celled algae (table on blackboard) Find Chlammedovanda and tell her structure.
- Chlorella is its structure.
- What causes the "bloom" of water.
Task number 2. Write down the numbers of the right judgments. For each correct answer, 1 point (Mach- 3 points).
- All plant-algae growing in water.
- Algae live not only in water, but also on trees.
- Chlorella has no flagella.
- Purecrokok - green single-celled alga.
- Chromatofu in chlammedonads brown.
UE-2 4 min.
Purpose: get an idea of \u200b\u200bmulticellular green algae.
Task number 1. Carefully listen to the teacher's story "Building and meaning of the Ulotrins, spirohyra, seabed salad, ulvy, nitella" and write down the name of multicellular green plants in the notebook. For the listened lecture, place 2 points on the fields.
Purpose: Secure the knowledge obtained by multicellular green algae.
Task number 1: Look under the microscope, the microcreparation of spirohyra, comparing with Figure No. 37 from the textbook and answer the following questions orally.
- The shape of the chromatofor at the spirohyra, compare with chromatophore in chlamdomonada.
- What do you know multicellular green algae?
Task number 2: For each of the proposed organisms, select the appropriate characteristics and record.
For this task MAX -3 score.
Name department
1) single-celled green algae;
2) multicellular green algae.
- External structure
1) the body is a thin, nicycle layer;
2) the body of the oblong shape, on the pointed end of two flashes;
3) resembles a marine salad about 30 cm long and the thickness of only 2 cells;
4) The body of the spherical shape, without flagella.
Habitat.
5) in flow and fresh reservoirs;
6) in the seas and oceans.
UE-4 6 min.
Purpose: learn brown and red algae.
Task number 1: Read the article "Brown and Red Algae" from paragraph 12 pp. 58-59.
Rate your work in 1 point.
Task number 2: Look on the screen (codeoscope and colored transparencies) a variety of red and brown algae, accompanied by a teacher's explanation.
UE-5 10 min
Purpose: study the meaning of algae in the nature and life of a person.
After the specified time, the teacher provides the correct answers on the screen (color transparencies and a codecope).
Correct errors and expose themselves points for this task -max - 5 points
UE-6 homework and summing up lesson 2 minutes.
Paragraph 12 p. 57-61 Task in working notebooks - 40,41.42 and an individual creative task - to make a crossword puzzle on the topic "Algae".
If you earned:
14-16 points rating "5";
- 12-13 points rating "4";
- 11-8 points rating "2".
If you have less than 8 points, do not despair and study again the new material.
Topic №3 Kingdom - Plants - 8 hours |
|||||||||||||||||||
Variety and value of plants |
Singlelet nitchables. Green hydrogen-leb, lab. Slave №6 |
Multi Algae: Green, Brown, Red |
Lichens |
nicky, horsetails |
Vote |
seed |
|||||||||||||
Ivanova Masha |
|||||||||||||||||||
Boyko Nadia |
|||||||||||||||||||
Cargo Veronica |
|||||||||||||||||||
Kucha Alena |
|||||||||||||||||||
Kaputin Vitya |
|||||||||||||||||||
Ivanina Angela |
|||||||||||||||||||
Karimov Angela |
|||||||||||||||||||
Nagina Dasha |
|||||||||||||||||||
Karnukhov Vitya |
|||||||||||||||||||
Kravchenko Olya |
|||||||||||||||||||
Sazonova Nastya. |
|||||||||||||||||||
Cucumbers Denis |
|||||||||||||||||||
Chernyshev Zhenya |
|||||||||||||||||||
Astashev Andrey |
|||||||||||||||||||
Musin Robert. |
|||||||||||||||||||
Bugakov Sasha |
|||||||||||||||||||
Terentyev Pavel |
|||||||||||||||||||
Samime Garey Igor |
|||||||||||||||||||
Mamokova Light |
|||||||||||||||||||
Baguezhev Arthur |
|||||||||||||||||||
Simonyan Suzana |
|||||||||||||||||||
Mukasheva Alua |
|||||||||||||||||||
Modular lesson №4
Topic: Mammals detachments: Pardon-painted nonpospeps.
UE -0 ( Educational Element) 2 min
Integrating goal:
a) expand knowledge about the variety of mammals;
b) to show on the example of ungulates features of their structure due to food;
c) the practical importance of animals for humans.
Equipment: Tutorial V.V. Latushin, V.A. Shapkin - 25 pieces, an aiming plan of a modular-rating lesson - 15 pieces, screen, diaperoctor, diapositive (troops of cetaceous, proboscis and predatory, man-and non-parqual animals), a codeoscope, color transparencies, a computer, a dish-tutor.
UE-1 Input Control 7 min.
Purpose: Determine the initial level of knowledge about the mammalian class.
- Write down in the notebook date, the name of the topic and the purpose of the lesson.
- Repetition of the previous material in the class of mammals.
Task 1: Oral for each right answer Teacher puts 1 point.
- Why is the class named mammals?
- By the range on the screen, find out the animal, to which class it is also a brief description of the detachment.
Five ranges are proposed, for example: (seal, elephant, wolf, bear, taway).
Purpose: get an idea of \u200b\u200bthe onboard and non-parqual animals.
Task 1: Listen to the teacher's story about the detachment of man-fate animals
a) tender
b) ruminants, using color tables and diaposition, write to the notebook of representatives of mannial animals (look at the board circuit number 1)
For the listened story and record in the notebook, estimate in 2 points.
UE-3 3 min.
Purpose: consolidate the knowledge gained on the detachment of manflock.
Task number 1: View drawings of representatives of man-fate animals on the textbook "Zoology in tables, drawings and schemes" p. 253 and perform work.
Insert the missed words.
For each correct answer 1 point.
Caban is a home ancestor ________________
Elk is the largest type of family ________________
At the guinestiles on the legs ________________ Number of fingers.
max 3 points
UE-4 6 min.
Purpose: learn nonposable animals
Task№1: Read from X 34 Article of the detachment of nonposable families tapir, horses, rhinos, using drawings from the textbook and drawings "Zoology in tables and drawings" p. 254
After reading, relevant in 3 points.
UE-5 13 min.
Purpose: consolidate knowledge, on a wooden and non-parunning animal.
Task number 1: 5 min.
View the disk episode is zoology tutor using a computer, a codecope and a screen.
For a viewed episode, estimate in 2 points.
Task number 2: 4 min.
Test work. Decide, correctly or wrong, a particular judgment.
- The bristles in the boar protects the skin from damage to dry branches of trees and shrubs.
- Kabana has a complex stomach.
- Turning guinea animals include: goat, giraffe, bison, deer, etc.
For this task, estimate in 2 points.
Task№3: 4 min
Perform test work. Choose the indexes of the correct answers.
For this task Max 3 points.
1. Parquers have on their feet:
a) 4 fingers;
b) 2 fingers;
c) Some types of 2, while others are 4 fingers.
2. The horns are available:
a) in many man-fated;
b) in many man-fate and few doctile;
c) in many mannocardoons and many non-parlance.
3. A complex stomach consisting of four departments have:
a) all herbivore mammals;
b) only large herbivore mammals;
c) Only ruminants are mannocardines.
Check out the correctness of your answers and put points on the fields, the teacher offers the correct answers on the screen (codeoscope, colored transparencies)
UE-6 Reflection 3 min.
- What value for you personally have the knowledge gained today at the lesson, the first five answers are estimated at 1 point.
Homework Paragraph 34. Write a message about the onboard and nonposable, listed in the Red Book.
Note:
17-15 points rating "5";
- 14-12 points rating "4";
- 11-8 points rating "3";
- Less than 8 points rating "2".
If less than 8 points, do not be mistaken and read the material again.
Mammalian class or animals |
||||||||||||||
Tits: single-pass. and soupbed |
Fittings: rodents, haresay. |
Tits: Catto-shaped. and etc. |
Fittings: Parquers. and non-paruncop. |
Detachment: Primates |
Generalization by mammal. |
|||||||||
The amount of points |
The amount of points |
The amount of points |
The amount of points |
The amount of points |
The amount of points |
The amount of points |
||||||||
1. Gorozhankin Yaroslav |
||||||||||||||
2. Adygizalova Nammin |
||||||||||||||
3. Burak Irina |
||||||||||||||
4. Boyko Masha |
||||||||||||||
5. Vasilyeva Olesya |
||||||||||||||
6. Gebgard Vitya |
||||||||||||||
7. Danilenko Ksenia |
||||||||||||||
8. Coskin Marina |
||||||||||||||
9. Koktko Roxalana |
||||||||||||||
10. Karimova Angela |
||||||||||||||
11. Kovaleva Anya. |
||||||||||||||
12. Ignatieva Katya |
||||||||||||||
13. Mikhalyuk Julia |
||||||||||||||
14. Polishchuk Daria |
||||||||||||||
15. Popkov Nadia |
||||||||||||||
16. Romanish Julia |
||||||||||||||
17. Strizhkova Natasha |
||||||||||||||
18. Surovetsky Alina |
||||||||||||||
19. Naumenko Katya |
||||||||||||||
20. Tumanina Ksyusha |
||||||||||||||
21. Fernuk Aleksey |
||||||||||||||
22. Shapina Yana. |
||||||||||||||