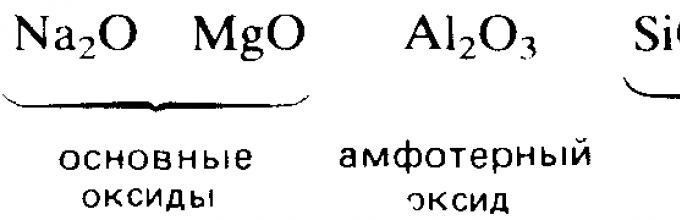Hydrogen compounds of nonmetals. Regularities in changes in their properties in connection with the position of chemical elements in the periodic table of D. I. Mendeleev.
Hydrides. In compounds with non-metals, hydrogen exhibits an oxidation state of +1. Since the ionization energy of hydrogen is very high, its chemical bond with nonmetals is not ionic, but polar-covalent. The most electronegative p-elements on the right side of the periods, such as sulfur and chlorine, react with hydrogen to form covalent hydrides, which have acidic properties and the strength of these acids increases as the size of the atom of the nonmetal attached to the hydrogen increases. Exceptions are methane CH 4, which is a neutral compound, as well as ammonia NH 3, which has basic properties. Hydrogen compounds of nonmetals are highly soluble in water and form acids with the same formulas.
More electronegative p-elements, such as aluminum, silicon and phosphorus, do not react with hydrogen when heated.
Ticket number 14.
Higher oxides of chemical elements of the third period. Regularities in changes in their properties in connection with the position of chemical elements in the periodic table of D. I. Mendeleev. Characteristic chemical properties of oxides: basic, amphoteric, acidic.
The reactivity of elements in interaction with oxygen, generally speaking, decreases as one moves to the right along each period. For example, in the 3rd period, two s-metals, sodium and magnesium, and two p-elements, aluminum and phosphorus, react violently with oxygen to form oxides. In the same period, the elements silicon and sulfur are only able to react slowly with oxygen. Chlorine and argon, located at the right end of the period, do not react with oxygen at all.
Electropositive s-metals form ionic oxides, such as sodium oxide Na 2 O and magnesium oxide MgO. The oxides of elements located in the middle and right parts of the period are predominantly covalent compounds, such as oxides of nitrogen and sulfur.
The acid-base character of the oxides also changes from basic in oxides of elements on the left side of the period to amphoteric in oxides of elements in the middle part of the period and then to acidic in oxides of elements on the right side of the period. For example, s-metals usually form oxides that dissolve in water to form alkaline solutions:
Molecular oxides of p-elements, such as carbon dioxide and sulfur trioxide, usually have acidic properties. The natural change in basic properties with the transition to acidic properties is clearly manifested in oxides of elements of the 3rd period.

Ticket number 15.
Acids, their classification and chemical properties based on the concept of electrolytic dissociation. Features of the properties of concentrated sulfuric acid using the example of interaction with copper.
An acid is a complex substance, the dissociation of which produces only one type of cations - hydrogen ions.
Classification of acids.

Hydrochloric acid is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride gas in water.
Chemical properties. Acids change the color of indicators: litmus turns red, methyl orange turns yellow.
When reacting with bases, salt and water are formed (neutralization reaction). Both water-soluble and water-insoluble bases react:

When reacting with basic oxides are formed with:

Acids react with metals, located in range of voltages to hydrogen, which releases hydrogen gas and forms a salt:

Strong acids react with salts of weak acids, displacing weak acids from their salts:
Obtaining acids. Many acids can be obtained by reacting acid oxides with water:


Concentrated sulfuric acid at ordinary temperatures it does not affect many metals. For this reason, for example, anhydrous sulfuric acid, unlike its solutions, can be stored in iron containers.
But concentrated sulfuric acid attacks almost all metals when heated. In this case, salts of sulfuric acid are formed, but hydrogen is not released, but other substances are produced, such as sulfur dioxide.
Thus, when concentrated sulfuric acid is heated with copper, the sulfuric acid first oxidizes the copper to copper oxide, and is itself reduced to sulfurous acid, which immediately decomposes into sulfur dioxide and water:

The resulting copper oxide reacts with excess sulfuric acid to form salt and water:
Thus, copper oxide is an intermediate substance in this reaction. Adding these equations, we get the final reaction equation, which includes only the starting and final substances:

The test is designed in four versions. Each option includes two parts. The first part contains 14 tasks with a choice of answers (basic level of complexity), the second part contains two tasks (B1 and B2) with a short answer (increased level of complexity). Recommended for 9th grade students as current control, as well as for preparation for the Unified State Exam.
Download:
Preview:
TEST on the topic “Periodic law and periodic system
Chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev"
Option #1
A1. A sulfur atom has the same number of electrons in its outer level and the charge of its nucleus, respectively.
1) 4 and +16 2) 6 and +32 3) 6 and +16 4) 4 and +32
A2. Arsenic and arsenic atoms have a similar structure of the outer electron layer.
Aluminum→silicon→phosphorus→sulfur
Highest oxidation state
A4. Attraction of electrons from the outer layer to the nucleus increases in series
2) increasing the force of attraction of valence electrons to the nucleus
3) decrease in electronegativity
A6. In order of increasing non-metallic properties, they are located
A7. The largest radius of an atom
1) bromine 2) zinc 3) calcium 4) germanium
A8. Has the greatest restorative activity
1) Si 2) P 3) S 4) C1
A9. The highest oxide composition EO is formed by all elements
1) Group IV A 2) Group IIA 3) Period IV 4) Period II
A10. By the period number you can determine
1) the number of electrons on the outer level of the atom 3) the charge of the atomic nucleus
2) the number of all electrons in an atom 4) the number of energy levels in an atom
A11. How many energy levels are there in a scandium atom?
1) 1 2) 2 3) 3 4) 4
A. The metallic and reducing properties of elements in the main subgroups increase with increasing nuclear charge.
B . As the nuclear charge increases, the basic properties of oxides and hydroxides increase.
IN 1.
AT 2.
Option No. 2
1) Ca 2+ 2) Al 3+ 3) Na + 4) F ─
A2. Silicon atoms and
1) phosphorus 2) selenium 3) germanium 4) vanadium
A3. In the series of chemical elements:
aluminum→silicon→phosphorus→sulfur atomic radius
1) increases 3) does not change
2) decreases 4) first increases and then decreases
increases in series
A5. In the series Be-B-C-N occurs
1) increasing the radius of atoms
4) reduction in the number of valence electrons
1) only A is true 2) only B is true 3) both judgments are correct 4) both judgments are incorrect
1) A1 2) Mg 3) Na 4) Si
IN 1.
1) the charges of atomic nuclei decrease
2) the number of electrons in the outer electronic layer increases
3) electronegativity decreases
4) the radius of atoms decreases
5) metallic properties are enhanced
AT 2.
Option No. 3
A1. The number of valence electrons in a strontium atom is
1) 2 2) 3 3) 4 4) 38
A2. What determines the place of a chemical element in D.I. Mendeleev’s periodic table?
1) the number of electrons on the outer level of the atom 3) the charge of the atomic nucleus
2) the number of neutrons in the nucleus 4) the mass of the atom
A3. The pair of elements that have the most similar chemical properties is
1) Ca and K 2) Na and K 3) B and C 4) C and O
A4. In which series are the chemical elements arranged in descending order of their atomic radii?
1) N, C, B 2) N, P, As 3) Na, Mg, K 4) Si, C, N
A5. Has the greatest restorative activity
1) Si 2) P 3) S 4) C1
A6. Formula of the higher oxide formed by an element of the fourth group
1) EO 2 2) E 2 O 3 3) EO 3 4) E 2 O 5
A7. In the series of chemical elements Si─ P ─ S
1) the number of valence electrons in atoms increases
2) the number of valence electrons in atoms decreases
3) electronegativity decreases
4) atomic radii increase
A8. Attraction of electrons from the outer layer to the nucleus increases in series
1) Si-P-N 2) S-P-As 3) Na-K-Rb 4) Si-Ca-K
A. Elements of the main subgroup have the same number of electrons in the outer level
B. In the main subgroups, the reducing ability increases with decreasing atomic radius
1) only A is true 2) only B is true 3) both judgments are correct 4) both judgments are incorrect
A10. The highest oxidation state in the series of chemical elements is chlorine-bromine-iodine
1) increases 2) does not change 3) decreases 4) changes periodically
A11. In which series are the chemical elements arranged in order of increasing metallic properties?
1) Br- Se- K 2) Mg- Al- Si 3) N- Li- C 4) S- Cl – P
A12. In order of increasing non-metallic properties, they are located
1) S-Se 2) Se-Br 3) Br-I 4) I-Te
A13. Hydroxide has the strongest basic properties
1) KOH 2) NaOH 3) RbOH 4) CsOH
A14. Acidic properties are most pronounced in
1) Br 2 O 7 2) SeO 3 3) As 2 O 5 4) GeO 2
IN 1. In the series of chemical elements Na ─ Mg─ A1:
1) the charges of atomic nuclei decrease
2) the number of electrons in the outer electronic layer increases
3) electronegativity decreases
4) the radius of atoms decreases
5) metallic properties are enhanced
AT 2. In the series of chemical elements F─ Br ─ I:
1) all elements have the highest oxidation state equal to the group number
2) non-metallic properties weaken
3) the highest oxidation state increases
4) the radius of atoms increases
5) form volatile hydrogen compounds with the general formula NE
Option No. 4
A1. The number of electrons in an argon atom is equal to the number of electrons in an ion
1) Mg 2+ 2) Al 3+ 3) Na + 4) C1 ─
A2. The sulfur atoms and
1) phosphorus 2) selenium 3) germanium 4) vanadium
A3. In the series of chemical elements:
aluminum→silicon→phosphorus→sulfur atomic radius
1) increases 3) does not change
2) decreases 4) first increases and then decreases
A4. Ability to donate electrons increases in series
1) Si-P-S 2) S-P-Cl 3) Na-K-Rb 4) Ca-K-Na
A5. In the series Be-B-C-N occurs
1) reduction in the number of valence electrons
2) decreasing the force of attraction of valence electrons to the nucleus
3) increase in electronegativity
4) increasing the radius of atoms
A6. Metallic properties are enhanced in a row
1) Mg-Ca-Ba 2) Na-Mg-Al 3) K-Ca-Fe 4) Se-Ca-Mg
A7. The greatest amount of energy must be expended to remove an electron from an atom.
1) sulfur 2) silicon 3) calcium 4) arsenic
A. In the main subgroup, with increasing nuclear charge, the acidic properties of hydroxides weaken.
B . As the nuclear charge increases, the nonmetallic properties of the elements increase.
1) only A is true 2) only B is true 3) both judgments are correct 4) both judgments are incorrect
A9. Hydroxide has the strongest basic properties
1) phosphorus 2) calcium 3) magnesium 4) barium
A10. The element exhibiting the most pronounced metallic properties
1) A1 2) Mg 3) Na 4) Si
A11. In the series B→C→N→O, oxidizing properties
1) weaken 2) strengthen 3) do not change 4) change periodically
A12. In the main subgroups with increasing atomic number, the metallic properties of the element
1) intensify 2) weaken 3) do not change 4) change periodically
A13. In the series Na→K→Rb→Cs, the ability of metals to donate electrons
1) weakens 2) strengthens 3) does not change 4) changes periodically
A14. An element whose atom has four electrons in its outer shell
1) beryllium 2) titanium 3) germanium 4) phosphorus
IN 1. In the series of chemical elements Li ─ Be ─ B:
1) the charges of atomic nuclei decrease
2) the number of electrons in the outer electronic layer increases
3) electronegativity decreases
4) the radius of atoms decreases
5) metallic properties are enhanced
AT 2. The elements of the 3rd period are characterized by
1) decrease in atomic radius with increasing nuclear charge
2) the same number of valence electrons
3) the same number of electronic levels in atoms
4) increase in the acidic nature of higher hydroxides formed by these elements
5) the same state of aggregation under normal conditions
Answers:
options |
||||
Exercise | ||||
1) (2 points). Atomic nuclei were discovered:
A.D. Mendeleev. W. J. Thomson.
B.E. Rutherford. G.D. Chadwig.
2) (2 points). The period number in the Periodic System is determined by:
A). The charge of the nucleus of an atom.
B). The number of electrons in the outer layer of an atom.
IN). The number of electron layers in an atom.
G). The number of electrons in an atom.
3*) (2 points). The shape of electron orbitals is characterized by:
A). Main quantum number.
B). Magnetic quantum number.
IN). Orbital quantum number.
G). Spin quantum number.
4) (2 points). A pair of elements that have a similar structure of the external and pre-external energy levels:
A). S and Cl. B). Be and B. B). Kr and Xe. G). Mo and Se.
5) (2 points). The p-element is:
A). Scandium. B). Barium. IN). Arsenic. G). Helium.
6) (2 points). Electronic configuration …3d104s2 corresponds to the element:
A). Calcium. B). Krypton. IN). Cadmium. G). Zinc.
7) (2 points). An amphoteric hydroxide is a substance whose formula is:
A). Zn(OH)2. B). Mg(OH)2. IN). Ca(OH)2. G). Cr(OH)2.
8) (2 points). A series of elements arranged in order of increasing metallic properties:
A). Mg-Ca-Zn. B). Al-Mg-Ca. IN). Sr-Rb-K. G).Ge-Si-Sb.
9) (2 points). The element E with the electronic formula 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p1 forms a higher oxide corresponding to the formula:
A). E2O. B). E2O3. IN). EO2. G). EO3.
10) (2 points) An isotope of iron, the nucleus of which contains 22 neutrons, is denoted by:
A). 40/20Ca. B). 42/20Ca. IN). 44/20Ca. G). 48/20Ca.
11) (9 points). Match.
A).1s22s22p63s23p1 1). Aluminum.
B).1s22s22p63s2 2). Potassium.
B).1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p4 3). Selenium.
D).1s22s22p63s23p64s1 4). Magnesium.
Higher oxide formula.
1.E2O 2.E2O3 3.EO 4.EO3.
Higher hydroxide formula
1.EON 2. E(OH)2 3. E(OH)3 4.H2EO4.
12) (3 points). Based on their position in the Periodic Table, arrange the elements: Germanium, Arsenic, Sulfur, Phosphorus - in descending order of oxidizing properties. Explain your answer.
13) (6 points). How and why do metallic properties change in the Periodic Table?
A). Within the period.
B). Within the main subgroup.
14).(7 points). Create an electronic formula for an element with atomic number 30 in the Periodic Table. Draw a conclusion about whether this element is a metal or a non-metal. Write down the formulas of its higher oxide and hydroxide, indicate their nature.
15) (5 points). What chemical properties are characteristic of the oxide of an element of the 3rd period, the main subgroup of group VI of the Periodic table? Confirm your answer by writing the reaction equations.
A1. Chemical signnitrogen element:
A)
Al b) N c) Na
d) O
A2. Item name
with the sign Fe:
A) Copper
b) Iron c) Gold d) Aluminum
A3. Complex substance
- This …
A) carbon dioxide b) copper c)
hydrogen d) oxygen
A4. The substance has the highest relative molecular weight
With formula:
A) H2S b) SO2 c) K2S d) CuS
A5.
Element of the third period of the main subgroup of group II
Periodic table of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev is...
A) Aluminum b) Beryllium c) magnesium d) calcium
A6. Designation of an isotope whose nucleus contains 8 protons and
8 neutrons:
A) 168О b) 178О c) 188О d) 198О
A7. An atom of a chemical element whose electron shell contains
16 electrons:
A) Oxygen b) Sulfur
c) Chlorine
d) Sodium
A8. An atom contains two electronic layers (energy levels):
A) Bora
b) Potassium c) Aluminum d) Magnesium
A9. A pair of chemical elements having at the external energy level
4 electrons each:
A) P and C b) Si and Ca c) N and P d) C and Si
A11. Information about
number of energy (electronic) levels
An atom of an element gives:
A) period number b) group number c)
atomic number d) relative atomic mass
A10. Least electronegative
element (from those listed):
A) Nitrogen
b) Hydrogen c) Chlorine d) Phosphorus
A12.Chemical
element having 20е;20р11;20n01
A) Mg
b) Na c) Ve d) Ca
IN 1. Atom or ion
having the following distribution of electrons over energy levels 2e8e:
A) Ne
b) Ca+2 c) Mg+2 d) Na+
AT 2. Select
chemical elements arranged in order of decreasing metallic properties:
A) Li, F, Na, O b) Li, Na, O, F
c) F, Na, O, Li d) F, O, Na, Li
AT 3. Potassium ions and
chlorine have:
A) the same nuclear charge
B) the same relative
molecular weight
B) the same total number
electrons
D) the same number of electrons per
external energy level
C1. Write down the diagrams
the formation of compounds consisting of atoms of chemical elements:
A)
hydrogen and fluorine b) magnesium and chlorine
Define the type
chemical bond in them
C2. You write
compounds with a covalent polar bond: O2, Li, H2Se, K2O, BaCl2,
Fe, J2, FeS, HJ, SO3,
S, ZnO
relate? Why?
2) Write the chemical formulas of the higher oxides of the elements Mg and S. What oxides (basic, acidic or amphoteric) do they belong to? Why?
3) Write the chemical formulas of the higher oxides of the elements Ca and Cl. What oxides (basic, acidic or amphoteric) are they? Why?
4) Write the chemical formulas of the higher oxides of the elements K and N. What oxides (basic, acidic or amphoteric) do they belong to? Why?
5) Write the chemical formulas of higher oxides of the elements Si and Li. What oxides (basic, acidic or amphoteric) are they? Why?
Option 2. PART A. Multiple choice test items. ^1.(2 points). Electronic formula of an atom of an element of the main subgroup of group IV, period 3Periodic table: A. 1s22s22p2. B. 1s22s22p63s23p4. V. 1s22s22p63s23p2. G. 1s22s22p63s23p6. ^2.(2 points). The higher oxide and hydroxide of an element of the main subgroup of group V of the Periodic Table correspond to the general formulas: A. E02 and H2EO3. B. E03 and N2EO4. B. E2O5 and NEO3. G. E2O7 and NEO4. ^3.(2 points). Oxidizing properties weaken in a number of elements: A. P-N-O-F. B. C1-S-P-As. B. Br-C1-F-I. G. V-S-N-R. 4.(2 points). The electronic formula Is22s22p63s2 corresponds to a particle whose designation is: A.S0. B.A13+. B.S4+. G, Si0. 5.(2 points). A covalent polar bond is formed in a compound whose formula is: A. PH3. B. Nal. B. 02. D. S02 6.(2 points). The valence and oxidation state of nitrogen in nitric acid are respectively equal: A. Five and +5. B. Four and +5. B. Three and +5. D. Three and + 3. 7. (2 points). The atomic crystal lattice has: A. Ozone. B. Diamond. B. Oxygen. G. Hydrogen. 8.(2 points). Acid properties in a series of compounds whose formulas are N2O5 - P2O5 - As2O5: ^ A. Change periodically. B. Do not change. B. Intensify. D. Weaken. 9.(2 points). The simple substance sulfur interacts with each of the substances of the series: A. HC1, Na, 02. B. K, Zn, Na2SO4. B. Mg, 02, H2. G. A1, N20, 02.10. (2 points). The transformation scheme C-4 → C+4 corresponds to the equation: A. CH4 + O2 = C + 2H2O. B. C + O2 = CO2. B. CH4 + 2O2 = CO2 + 2H2O. ^ G. CO2 + C = 2CO. PART B. Free-response questions. 11. (10 points). Write the reaction equations with which you can carry out the following transformations: NH3 ← N2 → NO → NO2 → HNO3. Indicate the types of chemical reactions. 12.(4 points). Which gas will occupy the larger volume (n.v.): 100 g of carbon dioxide or 5 g of hydrogen? Support your answer with calculations. ^ 13.(4 points). In which compound will the covalent bond be more polar: methane or silane? Give a reasoned answer. 14.(6 points). Arrange the coefficients in the reaction scheme P + H2SO4(KOH.) → H3PO4 + SO2 + H2O using the electronic balance method. Specify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent. 15. (6 points). 13 g of zinc were placed in the acid obtained by dissolving 11.2 liters of hydrogen chloride gas (HC) in water. Calculate the volume of gas released during this process (no.).
1. Which simple substance - formed from elements No. 11, No. 12 or No. 13 - has the most pronounced metallic properties? Why? Write the formulas of the hydroxides of these elements and indicate their nature.
2. Identify the most typical metal and non-metal of the 4th period. Justify your answer.
A typical metal of the fourth period is K, a non-metal is Kr (metallicity increases from right to left across the period). Typical metals contain 1-2 electrons in their outer energy level (potassium has 1), and non-metals have more than 4 (krypton has 8).
3. Which simple substance - formed by element No. 14, No. 15 or No. 16 - has the most pronounced non-metallic properties? Why? Write the formulas of acids corresponding to the higher oxides of these elements. 
4. An element with a constant valence of two is located in the 4th period. Its oxide and hydroxide are basic in nature. What element is this? What is the structure of its atom? Write the formulas for the oxide and hydroxide of this chemical element.
Ca. Atomic structure: 20 electrons, 20 protons, 20 neutrons. Core charge +20. There are two electrons in the outer energy level. CaO – calcium oxide, Ca(OH)₂ – calcium hydroxide.
5. Indicate the serial number, the charge of the nucleus and calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in volumes of: a) potassium (41K); b) beryllium (9Be); c) magnesium (24Mg); d) calcium (42Ca); e) aluminum (27Al); e) titanium (48Ti); g) vanadium (51V); h) iron (56Fe). 
6. How does the composition of the isotope nuclei differ: a) 63Cu and 65Cu; b) 107Ag and 109Ag? Give a reasoned answer based on calculations. 
7. Calculate the molar masses of substances whose formulas are ₂SO, NO₃, O. Write the formulas of similar compounds containing the H isotope and calculate their molar masses. 
8. How many molecules of sulfur oxide (IV) of different masses can be formed by the interaction of isotopes 16O, 17O, 18O and 32S? Write down formulas for all molecules and calculate their molar masses. 
9. Write the electronic formulas of the atoms: a) sulfur and sodium; b) argon and potassium; c) calcium and chlorine; d) neon and aluminum; e) silicon and bromine; e) arsenic and carbon. 
10. Based on the theory of atomic structure, explain the reasons for the periodicity of changes in the properties of elements and their compounds. Support your answer with specific examples.
The properties of simple substances and compounds of elements repeat periodically because the electronic configurations of atoms repeat periodically. Thus, the atoms Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba have the same structure of the outer electron shell; it contains 2 electrons. These elements easily give them up, exhibiting reducing properties and an oxidation state of +2.
11. How to explain, based on the theory of atomic structure, the sharp transition from inert gases to alkali metals?
In noble gases, the outer energy level is complete; after adding another electron to it, another energy level is filled, which becomes external. One electron in the outer energy level is a characteristic of alkali metals.
12. Determine the place of elements in the periodic table using the electronic formulas of their atoms: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2; 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6; 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2. Make up formulas of oxides and hydroxides and acids corresponding to these elements.

13. Based on their position on the periodic table, characterize the elements potassium, bromine, and aluminum. 
14. The oxide of an element (3rd period metal) has a molecular weight of 102. Identify the element and draw a diagram of the structure of its atom. Write the formulas of the oxide and hydroxide of this element and indicate their nature. 
15. Calculate the mass (n.s.): a) 8.96 liters of a gaseous compound of fluorine with hydrogen; b) 13.44 liters of a gaseous compound of phosphorus with hydrogen; c) 17.92 liters of a gaseous compound of sulfur and hydrogen. 
16. Elements A and B belong to the same period. A simple substance formed by elements A reacts violently with water. A simple substance formed by element B is a heavy, toxic, red-brown liquid with an unpleasant odor. What elements are we talking about?
Br – element B (Br₂ is a heavy toxic red-brown liquid). K – element A, reacts violently with water. Ca - also interacts with water, but not as violently as K.
17. The substance used as a mineral fertilizer consists of two elements - A and B. The simple substance corresponding to element A is an alkali metal. Element A belongs to the same period as the element that forms the only non-metal that is liquid under ordinary conditions. Element B is in group VIIA, its atoms are part of table salt. Identify elements A and B and write: a) electronic formulas of their atoms; b) the formula of the substance formed during their interaction.
18. Elements X and Y are in the 2nd period. A simple substance formed by element X reacts with water to release hydrogen. The molecular mass of the hydrogen compound of element Y is 20. Identify these elements and write: a) electronic formulas of their atoms; b) the equation of interaction of simple substances formed by these elements; c) the equation for the reaction of the hydroxide of element X with the volatile hydrogen compound of element Y.
19. What chemical properties does the element with atomic number 34 have? Which element is its properties most similar to? give a reasoned answer based on the positions of the elements in the periodic table. 
20. Find in the periodic table an element located in the 4th period, 5th row and exhibiting a valence of six when combined with oxygen. What is its valence when combined with hydrogen? Write the formulas of these compounds.
Se. SeO₃ – selenium oxide (VI), H₂Se (valency of selenium in combination with hydrogen – II).