Routing
organized learning activities
for middle group No. 3
The date: 17.01.2017
Educational area : "Cognition"
Section: FEMP
Topic: "Cylinder"
Purpose: Pto acquaint children with a geometric body - a cylinder on the basis of a visual-tactile examination.
Tasks:
O.Z .: Teach children to namepropertiescylinder, classify according to various criteria
and correlate the shape of objects with geometric shapes.
R.Z .: Develop cognitive interest in children;
V.Z .: To foster interest in cognitive and research activities, independence, activity.
Vocabulary work : cylinder.
Bilingual component : body - deness.
Equipment: hint pictures, which depict a glass, sausage, hat-cylinder, bankcylindrical, glue stick, 5 pencils for each child, sheets of white paper, cylinders, colored pencils.
Educator: Proskuryakova V.G.
Stagesactivities
Caregiver actions
Children's actions
Motivational
incentive
Guys, look, someone lost their top hat!
But this is not a simple cylinder, but a magic one. Can the cylinder be hugged with fingers or palm?
Guys, since we can hug an object, it means that it has volume.
Where did he come from?
Let's take a look at it.
There is nothing inside.
Maybe we can try to pronounce magic spell?
Finger game "Magic words"
Miracle miracle appear
Show yourself to our children
Door open the magic,
Magic calls with itself!
Guys, after casting a magic spell » in the cylinder, an interesting task has appeared, but a very difficult task - which, we must complete, to draw up a passport for the geometric body "cylinder".
A passport is a document in which we must tell and list everything about the cylinder. This means that in order to compose a "passport" we must learn all the secrets and secrets of a geometric body - a cylinder.
Children listen carefully to the teacher.
Cast a magic spell.
squeeze - unclench fingers
"Spinner» hands,
beat fist on fist, spread arms
"butterfly" fingers.
Organizational
search
Guys, look in our "magic cylinder" there are pictures-tips.
The pictures show a glass, a sausage, a top hat , bank cylindrical, glue stick.
What do you notice in common in these pictures?
Indeed, all objects have a similar shape.
Are these items the same material?
Their size? Color? Appointment?
Guys, objects of this shape are called cylinders. .
CYLINDER:
Friends call me a cylinder.
Looks like an ice cream cone me.
Looks like a column in an old cathedral
It looks like a log and a post in a fence.
Well done boys!
What is the name of this figure?
Can the cylinder be rolled?
Can the cylinder be supplied?
Find cylinders on their tables.
Now pay attention to the pictures in which cylindrical objects are elements: a cannon, a building with columns, a tree, round pillars.
Do you know why cylinder so called?
A very long time ago, when there were no cars yet, people moved heavy objects with the help of tree trunks. Think - how?
Guys, you take five cylinders of the same diameter (pencils).
Imagine that the cube is a very heavy weight that needs to be moved from one end of the table to the other using cylinders . You have seen that the cylinder, it turns out, can roll.
Word « cylinder » translated from Greek - "skating rink", "roller » .
One of its properties is that it can be rolled.
Guys, I suggest find cylindrical objects in a group.
Look at the table, there are different cylinders .
Guys, I propose to find cylinders that are the same for some reason, and name and show the signs of difference.
For example, cylinders , equal in height,
but they can be different in thickness, color, material from which they are made: from paper, plasticine, take plastic, metal, wooden.
Physical education « Zayink and".
One, two, three, four, five,
The bunny began to ride.
Jump zainka much -
He jumped 10 times!
Game: "Passport Office".
This means that with the help of such cylinders it is possible to move the load, since the cylinder has the same circles on both sides. It turns out that the cylinder hides a geometric figure on both sides - a circle. The circle is flat geometric figure... You, of course, remember that a cylinder can be hugged with the fingers of a hand or with a palm, and since we can hug an object, it means that it has volume.
A cylinder is a three-dimensional figure.
I will put the cylinder on the table, and you sit down so that the figure is at eye level.
Guys, what do you see and how can you sketch it?
Now I'm turning cylinder several times, what do you see?
So, if they want to talk about the cylinder , they do it like this:
This is the figure's "passport".
What can you learn from it?
About the height of the cylinder, its thickness.
Guys, if you attach cylinder to rectangle in the center of the cylinder is hidden a geometric figure - a rectangle, and the bases of the cylinder - to the circles, and thus, we made « the passport » its owner.
You have different cylinders on your tables .
Guys, each of you should make up with « the passport » , its cylinder . Apply the cylinder to the center of the sheet, trace the cylinder with a pencil - you get a rectangle, then turn the cylinder and trace the circles with a pencil and paint in the same color as your cylinder.
So the "passports" are ready.
Children look at pictures and name them.
Children's answers.
Children listen to the teacher.
Cylinder.
The cylinder can be rolled.
The cylinder can be supplied.
Children get to know the propertiescylinder.
Children listen carefully to the teacher.
Children call things like a top hat.
Children find cylinders equal in height, but differing in other characteristics and call them.
Children perform movements according to the poetic text.
After all the reasoning, the children come to the conclusion that the cylinder has the same circles on both sides.
Children answer the teacher's questions.
Children draw up a "passport", circle the cylinder and paint the geometric shapes that make up the cylinder.
Reflexive
corrective
- What new have we learned today?
What did you meet?
Do you think we were able to draw up a "passport" of the cylinder and learn everything about the geometric body - the cylinder?
- If yes, then show your green palm, if not, then red.
Answers questions. Evaluate their work.
Expected Result:
Know: geometric body - cylinder.
Have : perception ofclassification of the cylinder according to the features of correlation to the shapes of geometric figures.
Be able to: to name objects similar to a cylinder, to find signs and qualities of a cylinder in a visually-tactile way.
Sections: Technology
Lesson objectives:
- to consolidate knowledge about geometric bodies, skills and abilities to build drawings of polyhedra;
- develop spatial representations and spatial thinking;
- to form a graphic culture.
Lesson type: combined.
Lesson equipment: MIMIO interactive whiteboard, multimedia projector, computers, mimo project for an interactive whiteboard, multimedia presentation, Compass-3D LT program.
DURING THE CLASSES
I. Organizational moment
1. Greetings;
2. Checking the attendance of students;
3. Checking the readiness for the lesson;
4. Completing the classroom journal (and electronic)
II. Repetition of previously learned material
The mimo project is open on the interactive whiteboard
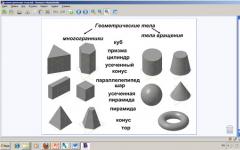
Sheet 1. In your math class, you studied geometric solids. You see several bodies on the screen. Let's remember their names. Students give names to geometric bodies, if there are difficulties, I help. (Fig. 1).
1 - quadrangular prism
2 - truncated cone
3 - triangular prism
4 - cylinder
5 - hexagonal prism
6 - cone
7 - cube
8 - truncated hexagonal pyramid
Sheet 4... Task 2. Geometric bodies and names of geometric bodies are given. We call the student to the board and together with him we drag polyhedrons and bodies of revolution under the names, and then we drag the names of the geometric bodies (Fig. 2).

We conclude that all bodies are divided into polyhedrons and bodies of revolution.
We turn on the presentation "Geometric Solids" ( application ). The presentation contains 17 slides. You can use the presentation in several lessons, it contains additional material (slides 14-17). From slide 8 there is a hyperlink to Presentation 2 (cube sweeps). Presentation 2 contains 1 slide, which shows 11 cube unfolded (they are links to videos). The lesson used an interactive whiteboard MIMIO, and students work on computers (doing practical work).
Slide 2. All geometric bodies are divided into polyhedrons and bodies of revolution. Polyhedra: prism and pyramid. Bodies of revolution: cylinder, cone, ball, torus. Students trace the diagram into a workbook.
III. Explanation of the new material
Slide 3.Consider a pyramid. We write down the definition of the pyramid. The top of the pyramid is the common top of all faces, denoted by the letter S. The height of the pyramid is the perpendicular, lowered from the top of the pyramid (Fig. 3).

Slide 4.Correct pyramid. If the base of the pyramid is a regular polygon, and the height drops to the center of the base, then the pyramid is correct.
In a regular pyramid, all side edges are equal, all side edges are equal isosceles triangles.
The height of the triangle of the side face of a regular pyramid is called - apothem of the right pyramid.
Slide 5. Animation of building a regular hexagonal pyramid with the designation of its main elements (Fig. 4).

Slide 6... We write down the definition of a prism in a notebook. A prism is a polyhedron with two bases (equal, parallel polygons), and the side faces of a parallelogram. The prism can be quadrangular, pentagonal, hexagonal, etc. The prism is named after the figure lying at the base. Animation of building a regular hexagonal prism with the designation of its main elements (Fig. 5).

Slide 7.A regular prism is a straight prism with a regular polygon at its base. The parallelepiped is a regular quadrangular prism (Fig. 6).

Slide 8.A cube is a parallelepiped, all the faces of which are squares (Fig. 7).

(Additional material: the slide has a hyperlink to the presentation with cube sweeps, 11 different sweeps in total).
Slide 9.To write down the definition of a cylinder, a body of revolution is a cylinder formed by rotating a rectangle around an axis passing through one of its sides. Cylinder retrieval animation (Fig. 8).

Slide 10.A cone is a body of revolution formed by the rotation of a right-angled triangle around an axis passing through one of its legs (Fig. 9).

Slide 11.A truncated cone is a body of revolution formed by the rotation of a rectangular trapezoid around an axis passing through its height (Fig. 10).

Slide 12.A ball is a body of revolution formed by the rotation of a circle around an axis passing through its diameter (Fig. 11).

Slide 13.A torus is a body of revolution formed by the rotation of a circle around an axis parallel to the diameter of the circle (Fig. 12).

Students write down the definitions of geometric bodies in a notebook.
IV. Practical work "Building a drawing of the correct prism"
Switching to the mimio project
Sheet 7... A triangular regular prism is given. At the base is a regular triangle. Prism height \u003d 70mm and base side \u003d 40mm. We consider the prism (the direction of the main view is shown by the arrow), we define the flat figures, which we will see in the front, top and left views. We take out the images of the views and place them on the drawing field (Fig. 13).

Students independently draw a regular hexagonal prism in the "Compass - 3D" program. Prism dimensions: height - 60 mm, diameter of the circumscribed circle around the base - 50 mm.
Building a drawing from a top view (Fig. 14).

Then a front view is built (Fig. 15).

Then a left view is built and dimensions are applied (Fig. 16).

Works are checked and saved on computers by students.
V. Additional material on the topic
Slide 14... Regular truncated pyramid (Fig. 17).

Slide 15.A pyramid truncated by an inclined plane (Fig. 18).

Slide 16.Development of a regular triangular pyramid (Fig. 19).

Slide 17.Unfolded parallelepiped (Fig. 20).

Marina Golovina
Passport of the project "The World of Geometric Figures"
Project passport
Topic: "The World of Geometric Shapes"
Participants: Educator, children, parents.
Implementation period: April 2016
Implementation base: MBDOU "Kindergarten number 16" Iskorka "
Relevance of the problem:
In the process of studying the program for the formation of elementary mathematical concepts with children of the 2nd junior group, I noted that children find it difficult to distinguish objects by shape and find geometric shapes in the environment. Therefore, I developed the project "The World of Geometric Figures" with the aim of forming geometric representations, since it is an important section of mental education, has a wide significance in all the cognitive activity of a child.
Characteristics of the project
Project type: Complex
A type: Cognitive and play
Duration: Short
Problem.
Due to age characteristics, children have insufficiently formed mathematical concepts, namely, the knowledge of geometric shapes and the ability to find them in the environment.
Purpose: To form in children of primary preschool age knowledge about geometric shapes.
Tasks.
Educational:
Improve the ability of children to compare two shapes in color and shape, to select according to the shape.
To form the ability to recognize geometric shapes and find them in objects of the environment.
Strengthen the ability to distinguish and name a circle, square, triangle, rectangle, oval.
Developing:
Logical thinking and coherent speech, attention, memory;
Spatial orientation, numeracy, motor skills;
Observation, ability to compare and analyze;
Ability to generalize, classify, highlight the main thing.
Educational:
To foster feelings of cooperation, accuracy, independence.
Estimated results
Children should have the ability to recognize and name geometric shapes in the environment, in a drawing, to correctly find a given figure in a set of geometric shapes. Find similarities and differences in geometric shapes.
Project Products
Album of geometric shapes.
Exhibitions of drawings, applications.
Mechanisms of the project
1. Innovation.
2. Pedagogical assistance and support in organizing joint activities of children and parents.
3. Joint creative activity with parents.
Resource support of the project
1. It is carried out through improving the joint activities of all project participants; educator, children, parents.
2. Use of various forms of work with information material.
3. Updating the developmental environment.
Event plan
1. Interaction with children.
Cognitive development
Acquaintance with geometric shapes, circle, square, rectangle, triangle, oval. Examination of the figure by the tactile-motor way. Acquaintance with figures of different sizes. Classification of objects on the basis of shape, creation of images based on characteristic features. Finding the necessary figures by the method of visual correlation. Developing in children the ability to reproduce the relative position of figures in space, the development of the ability to compose an image from individual geometric figures. Formation of the ability to find a geometric figure of a certain color and size.
Speech development
Formation of the ability to listen carefully, observe, form the ability for dialogical speech, teach to answer questions with words and sentences, enrich vocabulary, teach to distinguish and name geometric shapes familiar to them in a variety of settings, according to the teacher's word.
Didactic game "Wonderful basket": acquaintance of children with vegetables by their shape, color.
Laying out the Christmas tree from triangles, examining the Christmas tree and its decorations (fix the shape of the Christmas tree and its decorations).
Arouse the desire to tell with the teacher r. n. from. "Turnip", "Kolobok", "Teremok", activate verbs.
Acquaintance with the nursery rhyme, playing the game based on the text "Cucumber, cucumber".
To enrich and activate the speech of N. Pikulev's children, "The cat was blowing a balloon."
The development of intonation speech, memory Russian folk call "Sun-bucket".
Improving the ability to listen to poetry, provide children with the opportunity to finish words, phrases. Lyrics by A. Barto "Truck", "Ship".
Improving the ability to listen to a story without visual accompaniment. The story of J. Thaits "Train".
Development of vocabulary, outlook, the ability to name the color, size of objects, promoting the development of speech as a means of communication. Compilation of the story "The driver is driving a truck."
Artistic and aesthetic development.
Formation of interest in the aesthetic side of the surrounding reality, satisfaction of children's needs for self-expression in acquaintance with geometric shapes, through the development of productive activities of children (drawing, modeling, application).
Drawing.
Formation of interest in drawing, the ability to draw round, oval shapes. “My cheerful, ringing ball”, “Apple with a leaf”, “Vegetables”, “Colored balls”.
Developing the ability to draw horizontal and vertical lines connecting them. "Festive Christmas tree", "Truck", "Birdhouse".
Modeling.
Consolidation of the ability to sculpt round objects, development of children's interest in the result of their work. "Apples", "Kolobok", "Tumblers", "Beads".
Formation of the ability to sculpt elongated objects, tapering to one end, slightly pulling and narrowing the end with your fingers. "Big and small carrots."
The ability to roll with straight and circular movements of the hands, the ability to pull back with fingers, round the ends, smooth the surface. "Cucumber and beets".
Application.
Formation of the ability to choose large and small objects of a round shape, consolidation of the idea of \u200b\u200b\\ u200b \\ u200bthe difference in objects in size, the difference in objects in shape. "Big and small balls", "Balls are rolling along the path", "Canning fruit".
Ability to compare a circle and a square. "Balls and Cubes".
The ability to convey the image of a toy similar to a triangle, placing the details in decreasing order of magnitude. "Pyramid".
Formation of the ability to depict an object consisting of several parts, observing a certain sequence. Consolidation of knowledge about shape and size. "Truck", "Flag", "Birdhouse", "House".
Social and communicative development
The mastery by children of initial ideas of a social nature and the inclusion of children in the system of relationships. Introduction to the elementary generally accepted norms and rules of relationships with peers and adults.
Role-playing games
Contribute to story-based collective games. Acquaintance of children with the attributes of games (classification of dishes, their shape, knowledge of furniture and its shape, cabinet - rectangular, table - square). “The doll Vera has a new wardrobe”, “The dolls are having dinner”, “The birthday of the doll Katie”, “Serves the table”.
Building games
Consolidation of the ability to combine a single plot of the game with building material. Formation of skills of joint play and enrichment of the game plot. Development to transfer familiar actions with building material into play situations. "Let's Build a Fence", "A House for a Matryoshka", "A Truck Carries Loads", "Let's Arrange a Room for a Doll", "A Tower for a Princess".
Didactic games
Acquaintance with geometric shapes, consolidation of knowledge about the form. Formation of children's ability to assemble a picture from separate parts, consolidation of knowledge of colors. “Assemble the picture”, “Lay out the Christmas tree from triangles”, “Geometric cubes”, “Mosaic from geometric figures”, “Put a geometric figure on a column”. "Fascinating Geometry", "Mathematical Lotto".
Theatrical games
Involving children in an improvisation game, developing intonation and speech skills, encouraging expressive onomatopoeia, developing the ability to play roles in collective improvisation. Table theater "Repka", "Teremok", "Kolobok". Puppet theater "Three bears", "Zayushkina hut".
Work
Development of labor activity, education of a value attitude towards one's own work, the work of other people and its results.
Game situation; "Let's set the table for dolls."
Fulfillment of errands: bring a toy (triangular, square, round, oval, rectangular, put the doll on a chair, put a book on the table.
Caring for indoor plants (wipe the dust from the leaves, the leaves are round, oval).
Observing the work of the janitor, tools (wheelbarrow, shovel, the work of the driver (parts of the car: the cab is rectangular, the wheels, the steering wheel are round).
Physical development.
Development of physical qualities (speed, strength, flexibility, coordination). Accumulation and enrichment of children's motor experience, mastering basic movements.
Formation of the need for physical activity in children:
1. "Turnip" - rolling the ball with both hands.
2. "My cheerful ringing ball" - throwing the ball over the tape.
3. "Sun" - opening and closing the circle.
Outdoor games
The development of motor activity, the formation of the ability to navigate in space. "Find your house", "Run to what I call", "The sun and the rain."
Round dance games
Strengthening the ability to lead a round dance, the ability to act on a signal. "Mice lead a round dance", "Carousel", "Loaf", "Blow up the bubble", "Smooth circle", "Circle-circle".
2. Interaction with parents.
Making geometric shapes from various materials.
Album creation.
3. Joint activities of parents and children.
Selection of illustrations and poetic material about geometric shapes.
4. Joint activities with children and parents.
Conversations, consultations on the design of the album.
Stage 1 - preparatory
Purpose: Creation of conditions for the implementation of the project.
GCD development related to the main theme of the project.
Acquaintance of parents with project activities, determination of the range of issues where parents can provide assistance during the project.
Collaboration with the music director.
Collaboration with a physical education instructor.
Didactic games.
Role-playing games, construction games, round dance games.
Visual aids with geometric shapes.
Stage 2 - main
Working with three questions.
Preparation and implementation of GCD on the topic.
Diagnostics at the beginning of the project.
With a musical director, dancing in a circle, round dances, acquaintance with musical instruments in their form (balalaika, triangle, box, cymbals, drum).
With a physical education instructor - rolling the ball with two hands "Turnip". Throwing the ball over the tape - "My jolly ringing ball." Opening and closing the circle - "Sun".
Didactic games: “Laying out the Christmas tree from triangles”, “Geometric cubes”, “Fascinating geometry”, “Mathematical lotto”.
Role-playing games: "Vera's doll has a new wardrobe", "Setting the table", "Katya's doll's birthday".
Construction games: "A house for a nesting doll", "Let's arrange a room for a doll", "A truck is carrying loads", "Let's build a fence."
Exhibition of drawings, applications.
Stage 3 - final
Summing up the results of the development of the project by children.
Diagnostics of children at the end of the project.
Album design of children's works.
Design of the album "Parade of Geometric Figures".
Used Books:
1. N. M. Krylova "Kindergarten - a house of joy"
2. V. P. Novikova "Mathematics in kindergarten",
3. E. V. Kolesnikova "Mathematics for preschoolers 3-4 years old",
4. L. S. Metlina "Mathematics in kindergarten",
5. E. V. Serbina "Mathematics for Kids",
6. V. G. Zhitomirsky, L. N. Shevrin "Geometry for kids",
7. E. V. Kotova, S. V. Kuznetsova, T. A. Romanova "244 exercises for little geniuses."
Mathematics
FEMP lesson in the middle group
"Let's help the Tsar to find the Princess"
Prepared by: G. M. Efremova,
educator of the I quarter of the MBDOU category
D / s No. 80 "Rechenka", Naberezhnye Chelny
Software content:
- Teach by comparing subjects in length, width. Indicate the comparison results with the appropriate words.
- Continue to develop children's ability to navigate a piece of paper (find right, left, top, bottom corners, middle) To consolidate knowledge of the number series, numbers of the next and previous. To consolidate knowledge of geometric bodies, to be able to classify them.
- To develop the ability to listen and hear each other.
Material for the lesson :
Sheet of paper, geometric shapes
Strips of different lengths, different colors
Numbers from 0 to 8
Volumetric geometric bodies
- "cave"
- "passports" of geometric bodies
Doll princess
Musical hammer, metallophone, tape recorder
Pointer, easel.
LESSON PROCESS
Introductory part:
Once upon a time there was a king. And he had a beautiful daughter. Once the king went about his business, and the princess was left alone at home. She went out into the garden for a walk. Suddenly a strong wind swooped down, picked up the princess and carried her to the distant kingdom, to the thirtieth state. The king returned, sees no princess. He was saddened, sat down and did not know how to help his grief.
Guys, let's help the king, let's go to his daughter - the princess. And you will not be afraid of difficulties. Then close your eyes and we will be transported into a fairy tale.
"Hold on tightly to the hands - immediately find yourself in a fairy tale!"
Here we are in a fairy tale. There are many different tasks awaiting us on the way, which we must complete.
First task. Go to the tables, sit on the chairs. Look, I have a map. Look at her carefully. And now I will remove it, and you must draw up the same map.
What's in the top right corner?
What's on the left?
Where are the triangle and square?
What's in the middle?
Who will tell you about the whole map?
We have coped with this task. Now you can move on.
There are several roads before us, which one to choose?
On the short one you will go - you will get to the koshcheya, you will go along the long one - you will find the princess!
There are tracks on the table, what are they? (different in color, length).
Let's compare, find the shortest, the longest. What can you say about the green carpet? How can you measure the tracks? Spread them out from longest to shortest. I'll check now, I won't say who did the right thing and who I pat on the head, goth and did the job correctly.
(Close your eyes)
Now let's get on our horses, let's fly faster! Clink-clink-clink. We arrived in the forest.
What grows in the forest?
What kind of trees are there?
And what are the trunks of the trees? (thick, thin)
Look at the fallen trees on our way. Let's get off our horses and step over them. And here a trickle runs. And what are the streams (wide, narrow, shallow, deep)... Let's jump over the brook.
Oh, it seems we got lost, got into a maze. We can get out of the maze if we make a magic note. You have numbers on your table. They need to be arranged in order.
Count from 1 to 8.
Count in reverse order
Name the neighbors numbers 5, 7.
What is the number before 4, after 2, etc.
Look, I also built a digital segment (1, 2, 4, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8) , (What is wrong).
Coped with this task. Well done!
Oh guys, some kind of cave. And in it lives a forest monster - Shur Ale. He will not let us go further. What to do? (fill up the cave with stones).
But we have no stones. How can you close the entrance to the cave? We have geometric bodies.
Look, here there are passports of geometric bodies. I will show them to you, and you will quietly name them and slowly lay the entrance to the cave. We speak quietly while Shur Ale fell asleep. So they closed the entrance to the cave.
Guys, come over to me. We went to the door. It seems to me that someone is behind her, but the door will open if we guess how many times the clock has struck. 2, 3, 4 (hammer knocking, counting by ear).
A metallophone sounds, the door opens. There is a princess sitting there. The princess thanks the children that they were not afraid of difficulties. Asks which task was difficult, which one you liked more.
Guys, how can you tell the king that we have found his daughter, the princess? (letter, telegram, advertisement in the newspaper, in the program "Wait for me")