WEB-TECHNOLOGIES IN THE EDUCATIONAL PROCESS OF THE UNIVERSITY
A.P. Efremov, B.G. Stroganov
Department of Computer Technologies Peoples' Friendship University of Russia st. Miklukho-Maklaya, 6, Moscow, Russia, 117198
The article outlines the basic principles of building a modern educational Internet portal (web-portal), presents its main capabilities in the field of improving the efficiency of the educational process, discusses the issues and problems of its implementation and operation.
Key words: educational process, computer technology, Internet, implementation and operation.
Modern education at the level of secondary and, moreover, higher education is impossible without the use of information technology. The Internet and Intranet, which exist and develop on the basis of web technologies, have the most powerful information and educational resources.
Among the many different software shells designed to enhance the learning process, the most versatile and at the same time easy to learn are informational web resources.
Another important advantage of using information web-resources in the educational process is the fact that their implementation does not require the purchase and installation of special software on users' computers (in computer classes), but only a pre-installed operating system, for example, MS Windows, and the availability standard office suite. In addition, the very development of educational and training web-resources is usually carried out on the basis of free (free) software.
The main place among educational web-resources is certainly occupied by educational web-portals. Such an educational portal is usually called a set of websites united by a common administration system that allows the main users (in our case, teachers and students) to independently exchange educational and organizational information presented in a wide variety of forms: text, drawings (including active animation), sound, video.
Sometimes a learning portal, an education portal, etc. name a set of web-resources sorted in directories by headings. Such an understanding, in our opinion, is more consistent with the definition of a site, rather than a portal.
The main purpose of the educational portal is to transfer part of the educational process from the classrooms to its pages, expanding the capabilities of teachers and students. In this case, overhead costs are significantly reduced.
time for lectures and seminars. The learning process becomes clearer, more diverse and more interesting. Its effectiveness increases in terms of the perception of the material by the listeners.
The first educational portals appeared in Western universities in the mid-1990s. and began to develop rapidly in leading universities from the beginning of the 21st century. (for example, the educational portal of Harvard University - http://www.harvard.edu).
According to their structure, the educational portals of Western universities are built mainly according to a closed scheme, when access to educational materials and the entire organization of the educational process are strictly tied to the individual student. Such a system can be successfully used only if:
a) a high level of computer proficiency among teachers and students (and, of course, the availability of computers themselves for individual use);
b) an extensive university computer network (including WI-FI covering almost all university premises), providing free access at any time for teachers and students to the educational portal and other web resources;
c) a comprehensively developed training program, provided with electronic educational materials and other web-resources (for example, a system of computer knowledge testing);
d) a well-established organization of the electronic educational process.
In our leading universities in the specified period of time, these conditions were practically absent, which led to the creation of open-type educational portals, in which educational web-resources were included in the existing educational process.
One of the first such portals - the RUDN University Educational Portal (UPR) - was developed by us in 2002, patented and installed first on the RUDN Intranet, and then on the Internet (see Fig. 1) at http://web-local. rudn.ru.
From the screenshot of the main page in Fig. Figure 1 shows that UPR is a powerful web resource containing in its shell more than 2000 sites of teachers, more than 3000 sites of taught disciplines, more than 300 sites of departments, faculties (divisions) and specialties. The daily number of visits to the UPR pages exceeds 1,000, and more than 30,000 per month.
However, these figures are typical only for recent years, when the level of computer training of teachers has significantly increased and the requirements of the university management for the use of modern information technologies in the educational process have increased.
Structural features and main capabilities of the UPR. One of the main tasks of a real connection to the educational process of modern information technologies for transferring knowledge is to solve the problem of mastering by the teaching staff the features of working with the web interface of educational portals and other web resources, i.e. daily "online" use of them in the educational process.
Rice. 1. Main page of UPR
It is possible to provide a solution to the problem only under the following conditions:
a) initial computer training of users (teachers and students);
b) the presence of a simple and accessible web-interface of the UPR, which allows the initial user of a personal computer (PC) to post educational and organizational information on its website of the UPR, connect educational electronic materials (EM) to its pages and run educational computer programs (UCP) to test students' knowledge,
c) implementation of free access at any time to educational resources through the computer network of the university and the Internet.
In connection with the above, the structure of the UPR was initially chosen as open, and to view the websites of faculties, departments, teachers, readable disciplines and specialties, it is required to enter one common login and password for all - sh and sh4002 (see Fig. 2-6) . For each hired teacher, a website is automatically created on the UPR (in accordance with the enrollment order).
Rice. 2. Main page of the faculty website
Rice. 3. Main page of the website of the department
Rice. 4. The main page of the teacher's site
Rice. 5. Main page of the discipline site
Rice. 6. Main page of the specialty website
Rice. 7. Search page for sites of teachers, departments, disciplines and specialties
The need to enter a login and password was introduced only for editing and updating the information of the UPR websites by the authors. Each of the listed types of sites could be filled in by the authors independently of each other. At the same time, the DRM has a mechanism that uses user access to the base tables of the common database, thanks to which:
Faculties themselves can connect to themselves the sites of departments, disciplines, specialties related to them;
The departments themselves can connect to themselves the sites of teachers, readable disciplines, specialties;
Teachers can connect to their site the sites of the disciplines they read, UEM from the general base of the university and other information resources of the UPR and the Internet.
These types of sites have a number of service services and a fixed set of menu sections. This approach makes it easier for poorly trained users to edit and update information. In addition, the uniformity of menu sections simplified the search for information in various departments and faculties. However, the internal content of the sections can be designed in a very diverse way, including using HTML markup (see Fig. 3).
A powerful search system allows you to find a teacher's website (see Fig. 7), department, discipline or specialty with one click on the first letters of the name.
Faculties and departments have the opportunity to post news on their websites, information about the structure of education, features of disciplines and specialties, about their teachers, student progress, etc.
The most interesting are the services of communication between teachers and their students and knowledge testing via the Internet. Currently, the UPR is equipped with a common forum, which has forums of faculties and departments as sections. Such a forum can be used both for announcements of faculty and departmental nature, and for communication between students and teachers. In the future, it is planned to organize personal (closed) forums for teachers and, possibly, chats. The use of communication resources of this kind is strongly constrained by the lack of user connection points to the computer network and the Internet.
Teachers have the opportunity to use two computer-based testing systems on their CPR sites. The first of them - Internet testing - is built into the portal system and allows teachers to create tests, open them on the Internet for remote testing of students, receive and process test results (see Fig. 8).
The second, more powerful computer testing system - Mentor-RUDN - exists autonomously with its own server in the RUDN local network (see Fig. 9).
Teachers communicate with this system, download tests, receive test results, etc. through the UPR.
TSI-£G Testing on the page of the teacher of the State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Peoples' Friendship University of Russia"
For students
For teachers
Edit Tests
Brief instruction
Rice. 8. Main page of Internet testing of the teacher's site
Rice. 9. The window of the computer testing system "Mentor-RUDN"
It allows you to create intelligent and learning tests, conduct testing using all currently existing multimedia applications, and carry out statistical processing and analysis of test results. Students register once a year in this system, in their group. Each teacher who has his own website on the UPR can prepare tests for his discipline, independently upload them to the server through the UPR, test the students, receive and process the test results, and then publish them for students on his website in the UPR.
The considered systems of computer testing give the teacher a powerful and universal tool for teaching and controlling knowledge.
Organization of user support UPR. In addition to conducting special courses for practical training of teachers in working with ERM, a system of training and user assistance was developed and installed on the portal itself.
The training system includes several tutorials that step by step analyze various aspects of working with the portal and computer-aided testing systems (see Figure 10).
Rice. 10. The window of the program that teaches how to work with the UPR
Assistance to users is also organized through reference, illustrated with drawings electronic materials, located in the "Features" section.
In organizational terms, there is a “hot” telephone line for all users of the DPR and a page for sending letters with questions on various aspects of the work of the DPR.
UPR administration. One of the main advantages of the educational portal under consideration is the independent existence and design by users of all sites (faculties, departments, teachers, disciplines and specialties). Moreover, users themselves establish links between these sites by selecting links - addresses from the corresponding tables of the portal's common database. For example, faculties select links to the websites of their departments, disciplines, specialties from the general database in the relevant sections of their website, and departments choose links to the websites of their teachers, disciplines and specialties. Such a system allows you to transfer all sites to self-service by their users. Otherwise, to maintain such a portal (containing more than 5,000 sites) would require a whole department of employees.
The administration of the UPR in our case consists of:
a) in maintaining and updating the general database of faculties, departments, teachers, disciplines and specialties;
b) in the collection and publication of statistics on the use of CRM;
c) user support (consultations, training);
d) in the constant modernization of the services offered to the user;
e) in the technical support of programs and equipment of the UPR.
In addition to solving the main tasks related to improving the efficiency of the educational process, the UPR is a kind of testing ground where teachers acquire and improve their knowledge and skills in working with a computer and information resources. Students in the process of learning through the ERM master modern electronic web-resources to gain knowledge and skills in their specialties.
LITERATURE
Baikov V.D. Internet: search for information and website promotion. - St. Petersburg: BHV-St. Petersburg, 2000. - S. 197-288.
Solonitsyn Yu., Kholmogorov V. Internet: Encyclopedia. - 3rd ed. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2002.
Ashmanov I., Ivanov A. Optimization and promotion of sites in search engines. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2008.
Wandschneider M. Fundamentals of Web Application Development with PHP and MySQL. - ECOM Publishers, 2008.
Stroganov B.G., Isaikin O.V., Teplov A.V., Burkanova T.I. Educational Web-portal. - M.: Publishing house of RUDN University, 2006.
WEB-TECHNOLOGIES IN EDUCATIONAL PROCESS OF UNIVERSITY
A.P. Efremov, B.G. Stroganov
Chair of Computer Technologies Peoples' Friendship University
Miklukho-Maklaya str., 6, Moscow, Russia, 117198
This article is devoted to main principles of construction of the modern educational Internet a portal, are presented its basic possibilities in the field of increase of efficiency of educational process, are discussed questions and problems of its introduction and operation.
Key words: educational process, computer technologies, the Internet, introduction and operation.
Download:
Preview:
Using Web-Quests technology in the educational process
The last decade has become a period of intensive search for new conceptual ideas in education for school education. However, time and practice have shown that none of these concepts can be considered as the main one, since they are aimed at improving individual components of a complex school education system.
How to achieve the quality of education in practice? The central place in the methodological system is occupied by problem-based and project-based learning, which organically combines all its other components: research activities; pre-profile and profile training; metasubject connections; work with gifted children; extracurricular activities in the subject; preparing students for final examinations.
The Internet has become the leading source of information for students in our time. The indisputable advantage of the World Wide Web is that it is an inexhaustible source of information on any issue. However, as anyone who has tried to find anything there can attest, this procedure is frustrating and requires a significant investment of time and emotion. Sometimes it is like looking for a needle in a haystack.
For this reason, working on projects, setting tasks, and sending students to the Internet for the right information is not at all as easy as it seems at first glance. After all, children and even more so will not be able to find what they need.
One possible solution to this problem involves the use of a structured approach, which gives students the opportunity to use their work more productively when working on projects of various orientations, connecting and combining different information resources in new ways, as well as applying creativity and problem thinking skills. This technology is called "web-quest".
Web-Quests is one of the new areas of project activity, although it is no longer new for the West. The first mention of it refers to the beginning of the 90s of the last century. The developers of the web quest as a learning task are Bernie Dodge and Tom March
A web quest in pedagogy is a problematic task with elements of a role-playing game, for which information resources of the Internet are used.
Most often, a web quest is defined as a project using Internet resources. However, its main feature is the following: instead of forcing students to wander endlessly on the Web in search of the necessary information, the teacher gives them a list of websites that correspond to the subject of the project and the level of knowledge. Of course, children will have to go to these sites to find the information they need, but with a list of resources provided in advance, they won't get lost on the Internet and wander aimlessly instead of doing their project.
The web quest is aimed at developing students' analytical and creative thinking skills; a teacher creating a web quest must have a high level of subject, methodological and infocommunication competence.
A very important feature of web quests is that they are built from a specific set of blocks:
Introduction | designed to capture the interest of students |
The task | describes the final product of the activity |
Process | a step-by-step description of the procedure for what students must do to implement the project; it also provides a list of websites that contain the necessary information |
Grade | this part provides criteria for evaluating student work |
Conclusion | summarizing the results of project activities |
The topics of web quests can be very diverse, problem tasks can differ in the degree of complexity.
The results of the web quest, depending on the material being studied, can be presented in the form of an oral presentation, computer presentation, essay, web page, etc.
B.Dodge describes the following types of tasks for web quests:
retelling | Planning and design | self-knowledge |
Demonstration of understanding of the topic based on the presentation of materials from different sources in a new format: creating a presentation, poster, story. | Development of a plan or project based on given conditions | Any aspects of personality research |
Compilation | Creative task | Analytical problem |
Transformation of the format of information obtained from various sources: the creation of a recipe book, a virtual exhibition, a time capsule, a culture capsule | Creative work in a certain genre - the creation of a play, poem, song, video | Search and systematization of information |
Detective, puzzle, mystery story | Reaching consensus | Grade |
Conclusions based on conflicting facts | Working out a solution to an acute problem | Justification of a certain point of view |
Journalistic investigation | Belief | Scientific research |
Objective presentation of information (separation of opinions and facts) | Winning over opponents or neutrals | The study of various phenomena, discoveries, facts based on unique online sources |
The web-quest technology allows you to fully realize the visibility, multimedia and interactivity of learning.
- Visibility includes various types of demonstrations, presentations, videos, display of graphic material in any quantity.
- Multimedia adds to traditional teaching methods the use of sound, video, animation effects.
- Interactivity combines all of the above and allows you to influence the virtual objects of the information environment, helps to introduce elements of student-centered learning, provides students with the opportunity to fully reveal their abilities.
The use of this technology in the learning process makes it possible to:
- to increase the interest of students in the study of the academic discipline;
- increase learning motivation;
- use various types of information for perception (text, graphic, video and sound);
- visualize a variety of situational tasks, etc.;
- educate the information culture of students.
What problems can this technology be used to solve?
1. Acquire basic knowledge of the discipline, section or topic of the course.
2. Systematize the acquired knowledge.
3. Build self-control skills.
4. Form motivation for learning in general.
5. Provide educational and methodological assistance to students in independent work on educational material.
The teacher, developing and using quests in the educational process, has the ability to:
- it is easy to spread your experience, your model of teaching a particular academic discipline to other teachers, since a quest created once can be used repeatedly;
- implement different teaching methods simultaneously for different categories of students, thereby individualizing the learning process;
- reduce the amount of material presented through the use of demonstration modeling;
- to practice various skills and abilities of trainees using a PC as a simulator;
- carry out constant and continuous monitoring of the process of mastering knowledge;
- reduce the amount of routine work, thereby freeing up time for creative work and individual work with students;
- to make more effective independent work of students, which becomes both controlled and managed.
With the use of quests, the student gets the opportunity to:
- to work at the optimal pace for him;
The work of the branch under modern conditions of web technologies.
“... it is very important to learn how to use all the new technologies.
This is the number one task not only for students, but also for teachers.
All training should be focused on
use of modern technologies”.
YES. Medvedev
One of the necessary conditions for effective training of students in the field of secondary and higher professional education is the use of modern electronic learning tools.
Working with modern electronic learning tools, students can influence their own learning process, adjusting it to their individual abilities and preferences. They study exactly the material that interests them, repeat the study as many times as they need, which contributes to more effective perception. The use of high-quality multimedia tools makes it possible to make the learning process flexible in relation to social and cultural differences between students, their individual styles and pace of learning, their interests.
One of the directions of the process of informatization of educational institutions is the interaction of teachers with students in virtual methodological communities. One of the most frequently used information resources is methodological materials posted by a teacher on the website of an educational organization.
Web technologies greatly increase the possibilities of telecommunications both in terms of access to new sources of knowledge and in terms of organizing and supporting new types of educational activities. Web technologies provide the following didactic opportunities:
1. Presentation and transfer of educational, methodological and reference information:
transfer of educational, methodological, scientific and reference information in text, graphic, sound and video formats;
visualization and reproduction of educational and methodological information in various formats (text, graphics, animation, sound, video);
organization of consultations, communication with the teacher, with fellow students (forum, chat, sending messages, e-mail, etc.);
the possibility of interactivity with the help of multimedia information specially created for these purposes and operational feedback;
the possibility of prompt submission of reports on the results of control and evaluation activities.
2. Storage and processing of educational, methodological and reference information:
free search for educational, methodological and reference information on any network computer and computers connected to it through gateways of other networks;
access to educational software and documentation from huge file archives (given that most of the information is distributed free of charge);
the ability to store and reserve information of any kind (static, dynamic, text, graphic, visual, sound, video);
processing and editing (reconstruction) of educational, methodological and reference information using a text or graphic editor;
systematization of information in own electronic file cabinets and databases;
3. Designing the educational process:
the possibility of organizing electronic teleconferencing (audio and videoconferencing), including in real time;
exchange of information simultaneously with a large number of users on a specific topic in the mode of teleconferences;
use of modern software for solving educational and methodological problems of the educational process;
the opportunity to organize various kinds of joint research work of students, teachers, students, researchers from various universities, schools, scientific and educational centers in different regions or even different countries;
the opportunity to organize a network of distance learning and advanced training of teaching staff (organization of a distance learning center based on computer telecommunications in order to obtain an additional specialty).
the possibility of organizing network communities;
organization of a collective electronic encyclopedia (Wikipedia), a collective electronic textbook (Wiki technology);
access to the catalogs of hundreds of the world's best libraries;
access to global databases and knowledge bases;
operational control of the assimilation of knowledge, skills and abilities;
the possibility of organizing individual and collective educational activities;
activation of cognitive activity;
motivation for independent learning activities;
the possibility of self-education, self-development, self-esteem, self-regulation;
formation and development of creative skills.
Let us single out some didactic possibilities of an educational Web resource developed and supported by the didactic possibilities of Web technologies:
preparation and editing of an educational Web resource directly in the network educational space using a simple text editor;
storage of an educational Web resource in the network Web space;
free search for an educational Web resource in the network educational space;
use of software and peripheral devices of remote web-computers (computers connected to the network educational space) to run training programs, simulators on them, and conduct appropriate calculations;
interactivity of the educational Web-resource due to specially created multimedia support and operational feedback;
the possibility of prompt and adaptive conduct of control and evaluation activities;
remote use of an educational Web resource in order to support the educational process or improve qualifications.
Currently, hypertext systems are quite widely used in various fields, in view of the special advantages that hypertext gives us. In the field of education, the following advantages of hypertext systems can be distinguished:
can be used for automated learning. It allows the student to view not only a large group of elements, but also to study the mechanism of formation of associative links;
makes it possible to navigate large databases. Regardless of the volume, the system can provide access to the necessary information, offer a search strategy built taking into account the interests of a particular user;
serves as a means of supporting intellectual activity, tk. gives a hint about the relationships of each aspect or concept, which provides easier access to information arrays;
practically does not limit the scope and direction of educational activities;
organizes information according to semantic criteria, due to which the effect of an objective information environment arises.
the study of material built on the principle of hypertext is convenient for perception and has a positive effect on memorizing the main material;
gives the user a "live", dynamic system in which there are different possibilities, and at the same time allow him to both be independent in this system and actively act;
the ability to choose your own learning path dictated by the cognitive interests of the student, due to the designed independent navigation;
allows you to personalize the learning process.
Literature:
1. Voladad S.N. Studying the methods of presenting information in the course of informatics: (On the example of hypertext representations of educational material on trigonometry): Diss. ... cand. ped. Sciences: 13.00.02. - M., 2000. - 152 p.
2. Dronov V.P. Information and educational environment of the XXI century. Bulletin of education. - M., - 2009. - No. 15. - pp. 44-52.
3. Zenkina S.V. Pedagogical foundations for the orientation of the information and communication environment to new educational results: Diss. ... Dr. ped. Sciences. – Moscow, 2007
4. Kuznetsova A.A. Fundamentals of the general theory and methods of teaching informatics. - M .: Binom Publishing House, 2010, - 207 p.
5. Nimatulaev M.M. "Designing a modern information educational environment based on the didactic capabilities of web technologies" (article in a scientific collection of articles)
Web technologies in education. Distance learning systems on the Internet
Introduction
Distance learning can be considered any form of education in which the teacher and students are separated in time and space. For example, correspondence and television courses are forms of distance learning. The advent of the Internet and Web-technologies has given new opportunities in the development of distance learning, and today quite often the term "distance" is used in relation to "online" learning. But, in fact, online learning is a form of distance learning.
A distance learning system via the Internet or an Online Learning System (OLS) can be defined as a set of software and hardware tools, methods and organizational measures that make it possible to ensure the delivery of educational information to students via public computer networks, as well as to test the knowledge gained within the framework of a course of study by a specific listener, student, learner.
The use of Online Learning Systems (OLS) has certain benefits: such systems allow more students to be involved in the learning process and make it more accessible both in terms of the cost of education and in terms of the geographical remoteness of teachers and students.
Among the main advantages of SOO are the following:
- the opportunity for students to choose a convenient place and time for training;
- the possibility of obtaining access to training courses for persons who cannot get this access offline for certain reasons (there is no possibility to interrupt work, geographical distance from the educational institution, illness, etc.);
- reduction in training costs - there is no need to make long trips for individuals, and for organizations - to send employees on business trips.
The LMS (Distance Education Systems) market can be divided into the following sectors:
- corporate;
- DL in the system of higher and secondary education;
- DO in state and local government.
According to some studies, the US online learning market is already over $10 billion. Moreover, according to research company International Data Corp. (IDC), the US corporate online learning market is set to grow by more than 50% to reach $18 billion in 2005. While the global IT learning market (both offline and online) will grow by 13% per annum from $22 billion in 2000 to nearly $41 billion in 2005
According to the Gartner Group, the enterprise e-learning market was worth about $2.1 billion in 2001. Gartner predicts a 100% annual growth rate (CAGR) for this market over five years to reach $33.4 billion. by 2005
Functionality of Online Learning Systems
Key Features of the Online Learning System :
As a set of training materials, in some cases, video cassettes (or CDs, DVDs) with a recording of basic lecture courses may be sent. And further interaction within the framework of the training course is carried out via the Internet.
Ways of presenting information
The main ways of presenting information within the framework of the RBS:
- Text
- Graphics
- 3D graphics
- Animation, Flash animation
- Audio
- Video
The implementation of video courses on the Internet is possible if there are powerful telecommunication capabilities and, most likely, this type of training in Russia may be in demand in rare cases for corporate systems.
Other ways of presenting information on the Internet have already become quite traditional. In this case, of course, it is necessary to take into account the specifics of a particular course of study and the bandwidth of the channels of specific users.
Typical Structure of an Online Learning System
In its most general form, the architecture of Web content management systems can be represented as follows:
Rice. 1. Architecture of Web content management systems
As a rule, this technology is based on a three-tier client/server architecture. This architecture splits the data processing between the client, the application server and the data store.
Typical Structure of the Online Learning System Portal
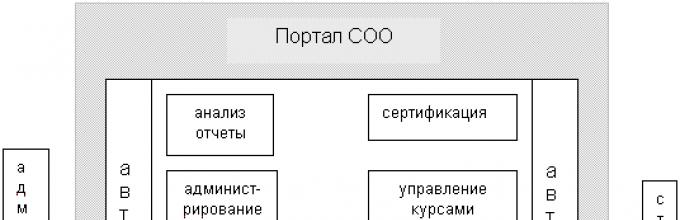
For the most part, online learning systems are built on the basis of a portal scheme. In general, such a structure looks like this:

Rice. 2. Structure of the Online Learning System Portal
Forms of distance learning via the Internet
Online (synchronous, scheduled) lectures, seminars suggest the following scheme of work: by the appointed time, students come to the site, where they register, after which the lesson begins. The lesson is led by the teacher, answering the questions of the "listeners" online - either in a chat or using sound applications. It is possible to use teleconferencing technologies, but this imposes certain requirements on the bandwidth of communication channels.
Offline classes (asynchronous, on-demand) are as follows: students come to the site at a convenient time for them and use pre-prepared materials - presentations, flash presentations, videos, perform prepared tasks, can ask questions to teachers by e-mail or in a conference, forum.
One of the problems that arise in online learning is the problem of user authentication when checking knowledge. How to check that exactly the person who entered introduced himself answers the test questions on his own?
- You can solve this problem by issuing a certificate stating that the student has "completed an online training course". This somewhat reduces the level of such a certificate, but removes responsibility from the educational institution, the center.
- In the case of corporate training, the company can appoint inspectors and pass the exam in a computer class.
- In cases where the course is focused on obtaining the knowledge necessary for the employee himself to perform his official duties, the issue of authentication is not acute.
LMS business models. Main market participants
Business models
The commercial provision of Internet-based distance learning services can be implemented within the following business models.
1. Development and supply of technologies and software and hardware solutions for creating online learning systems.
2. Lease of software and hardware systems and network resources for deployment of remote learning systems (ASP).
3. Provision of commercial services for access to training courses developed and maintained by specialized companies and educational institutions, training centers, universities, etc.
4. Consulting services for the "translation" of existing "offline" courses to the online environment, the preparation of course content, as well as the deployment of a distance learning system and the organization of the distance learning process.
Various combinations of the above models and alliances of companies operating within a particular business model are also possible.
Main market participants
FOREIGN COMPANIES DEVELOPERS AND DLS SERVICE PROVIDERS
SmartForce provides solutions for creating training courses.
Flash demo by SmartForce:
SmartForce e-Learning Platform Suites
To simplify the integration of LEO platforms and provide flexibility in functionality and performance according to the business needs of the enterprise, SmartForce has developed five software packages that can be configured and built to form an enterprise e-learning platform.
- LEARNING MANAGEMENT SUITE. Allows you to manage resources and track student completion of curriculums.
- CONTENT MANAGEMENT SUITE. Provides interactive content creation, deployment, and management.
- COMPETENCY SUITE. Links a set of skills and business roles to corporate strategies and goals.
- COLLABORATION SUITE. Forms a learning platform with learning resources.
- CUSTOMIZATION SUITE. Delivers corporate training content to the "right people at the right time"
DigitalThink is a provider of e-learning solutions for businesses that are tailored to a company's strategic business goals, provide an engaging learning environment, and include management tools and measurement of return on investment (ROI).
- E-Learning Catalog includes more than 3,000 hours of courses. Course topics: IT, management, sales, e-skills, financial services, HR, etc.
- E-Learning Platform- scalable, open DigitalThink E-Learning platform - the basis of e-learning solutions for business. The E-Learning platform supports user experience and provides administrators with management and analysis tools. The open protocol enables seamless integration with other applications in the enterprise.
- E-Learning Services- DigitalThink combines the experience of understanding the business goals of customers with the experience of creating educational projects. Services range from curriculum design to implementation and maintenance.
E-Learning DigitalThink technology is a fully maintained, outsourced Web environment that supports collaboration with educators and provides ROI tracking and reporting. E-Learning DigitalThink technologies are based on open architecture, e-learning environment and learning management system (LMS).
The company offers the eLearning Studio software package, which includes software products previously released by the company:
- Authorware 6 is a program designed to develop an application in the field of education;
- Flash 5 is a program designed to develop flash animations;
- Dreamweaver 4 is a program designed to work with the publication of materials on the Web.
The eLearning Studio package contains a set of tools for developing e-learning applications. Although these tools are adapted for creating e-learning applications, the product is still a tool (high-level language) for creating a demo video, the principles of which are not much different from the principles for creating flash videos intended for any other needs.
Creation of a distance learning system with controls for courses and students, etc. using Macromedia eLearning Studio will require the involvement of programmers and the use of additional solutions.
In general, Macromedia's product is suitable for creating interactive presentations using sound animation, etc. based on flash technologies. Companies such as Cisco (http://www.cisco.com/mm/quickstart/launcher.htm) use this package in their training courses.
The full eLearning Studio package is $2999, the Authorware 5.x upgrade is $899, the Authorware 3.x and 4.x is $1099, and the standalone Authorware 6 is $2699.
The updated Authorware 6 product features one-button publishing to Web and CD-ROM, drag-and-drop synchronization for various types of media, and support for MP3 audio streaming.
Interwise offers an Enterprise Communications Platform (ECP) solution. The solution is centrally managed by the Interwise Communications Center application, an application implemented as an Internet portal that allows personalized access and login to the five main ECP applications.
The Enterprise Communications Platform includes the following components.
IBM offers a Lotus LearningSpace 5.0 solution as well as ASP services. The solution consists of the following sets of applications and technologies.
- Mindspan Planning- a system designed for the initial analysis of the level of the student, the development of a strategy for his training and methods.
- Mindspan Design- a system designed to create a structure of courses, a certification system and analyze the results of training in a company; it is possible to integrate the solution with existing enterprise resource management systems.
- Mindspan content- a system designed to create and post content; Microsoft PowerPoint and Lotus Freelance Graphics applications can be used.
- Mindspan Technologies– a solution consisting of the Lotus LearningSpace platform, Learning Management System called TEDS , and Lotus LearningSpace Forum 3.01 ; the solution allows you to use Domino applications available at the enterprise, as well as Authoring Tool Suites that provide support for various content, including those created using Macromedia's Web Learning Studio. TEDS - provides integration of the Lotus LearningSpace platform with mail systems, personnel and financial management systems, and as well as skills management and testing/certification systems.
The main client application is Live Virtual Classroom.
The company offers a Blackboard 5 solution as well as ASP services for enterprises and educational institutions.
The Blackboard 5 solution consists of three main applications:
- Blackboard Learning System- enterprise course management system;
- Blackboard Community Portal System- a unifying portal that provides access to resources, course administration, communication tools, schedules, etc. for the relevant categories of users;
- Blackboard Transaction System- an Internet system that provides identification of students, provision of access and management of tuition payments, etc.
The Blackboard Learning System consists of the applications:
- course management- the course management system itself, which provides content management (personal information, course elements and documents, academic Web resources, publisher-provided digital material), communication tools (forums, chats, etc.), tests, surveys, exams; as well as providing various additional controls for teachers.
- Blackboard Building Blocks architecture for interoperability and customization- a component that integrates various types of content and commercial applications with the Blackboard platform, as well as contains various utilities and applications for students and teachers.
- Advanced integration and system management- a system that provides integration of the Blackboard solution with various information systems (student information system (SIS)) or back office (ERP) systems of the enterprise.
The solution is compatible with Microsoft .Net., allows you to place course materials in Microsoft Office, Adobe Acrobat PDF, HTML formats, various graphics, audio and video formats, as well as animations (Flash, Shockwave, Authorware).
Docent offers the Docent Enterprise solution for in-company training. The company has experience in implementing solutions at enterprises in various industries (energy, finance, pharmaceuticals, telecommunications).
The solution consists of the following applications: Docent Learning Management Server (LMS), Docent Outliner, Docent Content Delivery Server (CDS), and Docent Mobile.
The solution is a portal and allows you to conduct live classes (on a schedule), classes on demand, certification, student learning planning. There is a system for charging fees for courses (billing, i.e. providing the opportunity to organize paid training outside the enterprise), administration functions for the portal, course materials and the educational process, as well as enterprise personnel management, including referral to courses, etc.
The Docent Outliner application is designed to publish course materials.
This solution is one of the most used solutions for DO.
You can get acquainted with the Demo version.
It should be noted that at present Docent solutions are being actively implemented by various companies.
Centra develops e-learning solutions and offers turnkey solutions based on its developments. The main activity of the company is focused on the development of corporate training for enterprises.
The company offers a solution for corporate training of enterprise personnel.
The solution consists of the following components.
- virtual classroom provided by the product Centra Symposium 5.0, which is intended for conducting live classes, conferences and similar events among the staff, partners and customers of the company, as well as for training on products and sales. Up to 250 users can participate simultaneously and in real time. Various functions are available, such as: hand raise, voice over IP, video conferencing (for example, broadcasting the speaker to users), support for multiple speakers, text chat, recording live classes for later use, etc. The solution requires the user to have Internet browser through which the client application is loaded directly.
- web conferencing is provided by Centra Conference 5.0, which is designed for live Web conferencing for a small number of participants. The principle of operation of Centra Conference 5.0 is similar to the principle of operation of the previous application, with the difference that the Centra Conference 5.0 product is more focused on a small number of participants: "simultaneous statements" of several people are possible; there is no leader, in connection with which all participants have equal opportunities, etc.
- web meetings provided by the product Centra eMeeting 5.0, which is designed for personal meetings and presentations. In general, this product is similar to the previous one, but it adds organizer and meeting management features. To work with the application, it is enough to have a thin client.
- Centra Knowledge Center- organizational and managing the training program and personal settings application. Also intended for content management, etc. administrator or course author, includes a course catalog.
In addition, among the developments of the company there is a content creation system - Knowledge Composer Pro, and its variety - Knowledge Composer for PowerPoint, which is based on the Microsoft PowerPoint program.
Note that all services offered by the company are provided both in the form of boxed solutions and in the form of ASP-services.
It is also worth noting that Centra solutions are currently being actively promoted, and an increasing number of companies are implementing and using them in their business.
9 HP: e-learning-on-tap
Hewlett-Packard offers the HP virtual classroom solution, which is a hosted service that allows an instructor to provide real-time online training (http://www.hpe-learning.com/store/about_services.asp).
As part of this service, a "Virtual Classroom" is rented for a while, in which "classes" take place between the teacher and students. "Virtual classroom" is a set of software tools that allows you to create online courses and organize interactive interaction between a teacher and students (presentation, lecture, chat, etc.). To conduct classes, you only need an Internet connection and a browser, all the necessary software is downloaded from the HP website automatically.
Payment can be made on an hourly basis at an average of $23 per listener per hour. There are other forms of payment, including for services to provide "hot" support and advice.
Pricing examples based on $23 per user per hour:
10.Pathlore Learning Management System
(http://www.pathlore.com/products_services/lms_datasheet.html)
The company offers the Pathlore Learning Management System (LMS) solution.
The solution consists of the following blocks:
- Global Learning- the main portal with a customizable interface; with the help of the portal training planning is carried out, access to the catalog of courses is provided, etc.;
- Administration Center– course management program and training plan;
- content center- a program for managing "objects" of content, posting information on courses and tests;
- Design Center- a block for creating and managing the interaction (interface) of courses, while no additional programming is required;
- System Center is a back office management program that includes functions such as monitoring connections to the system.
The company offers a ready-made (boxed) product or the development of a training system that takes into account the specific requirements of the enterprise (without the provision of ASP services). The demo version of the LMS "Prometheus" can be found at http://www.prometeus.ru/products/sdo/enter.asp
The Prometheus system has a modular architecture that allows you to expand, upgrade and scale the system as needed. The system consists of the following modules.
- Sample Web Site- a set of HTML pages that provide information about the training center, the list of courses and disciplines, the list of tutors on the Internet or LAN (Intranet) of the organization.
- Workstation "Administrator". The module ensures that the administrator performs his official duties. Responsibilities include: system management, differentiation of access rights to its components, registration of new tutors and organizers. The user can work from any client computer connected to the network.
- AWP "Organizer". The module ensures that the organizer fulfills his official duties. Responsibilities include: formation of groups of students, registration of students, control over tuition fees and distribution of educational materials. The user can work from any client computer connected to the network.
- ARM "Tutor". The module ensures that the tutor performs his official duties. Responsibilities include: advising students, monitoring their progress, testing, putting marks in a grade book, generating reports for management. The user can work from any client computer connected to the network.
- AWP "Listener". The module provides the student with all the necessary tools for successful study of the course. The listener can communicate with the tutor and classmates, study electronic versions of courses, perform laboratory work, take tests, work on mistakes. The user can work from any client computer connected to the network.
- Tracking module. The module records in the database all calls to information materials located on the Web server of the training center, providing reporting on who, when and what they read or viewed.
- Module "Course". The module provides access to the courses by students, tutors, organizers and administrators. For each user, the list of courses is generated dynamically based on their group membership.
- Module "Registration". The module registers new listeners in the system and enters information about them into the database.
- Module "Test". The module generates a unique test task for each listener. Saves the answers to the questions in the database, analyzes them and calculates the score. Generates a detailed test attempt report and stores it on the server for later analysis.
- Test Designer module. The module allows you to interactively create new tests, expand and modify existing ones, or import a test from a text file. The user can work from any client computer connected to the network.
- Module "Accounting". The module provides control over the receipt of payments and distribution of training materials.
- Module "Reports". The module generates a variety of reports on the activities of the educational institution.
- Course Designer module. The module allows you to create offline e-learning courses with their subsequent placement on the server of the training center. It is a separate program that is installed on the local computer. This computer does not need to be connected to the network.
2. Cognitive Technologies(www.cognitive.ru).
The company offers a ready-made (boxed) product - LMS "ST Course", as well as ASP services - "ASP-Course".
The company "City-Info" developed the LMS "Intraznaniye". The Intraknowledge system is positioned as a corporate employee knowledge management system and includes three main modules:
The system has a Web interface. Data on the results of testing employees is stored centrally and is always available for viewing by authorized persons (employees of the personnel department, heads of departments, top managers, etc.).
The demo version of the system can be found at http://intraznanie.gorod.ru.
The company "Informproekt" has developed the "Batisfera" system, which offers opportunities for distance education for educational institutions.
The Bathysphere system consists of two blocks.
Teaching block "TUTOR" allows you to create educational material of any type and form, namely: lectures, homework, laboratory work, tests, tests, interactive tests, exams, electronic textbooks.
When creating work, the teacher can strictly regulate the time for performing the corresponding test work and establish the procedure for admission to each subsequent task. TUTOR includes modules:
- EDITOR - an editor that generates educational material (with the ability to use sound and video fragments);
- REPORTS - a program for systematizing the reports of students who completed the educational task;
- SKINMAKER is a general-purpose software tool that allows you to easily change the basic design of the program, taking into account the tasks and aesthetic preferences of the user.
Second block - READER- designed for students, it allows:
- listen to a lecture;
- perform laboratory, control work, homework;
- pass the test and exam online;
- enter the results obtained by the student during the testing process (test, exam, etc.) into a text file, send it by e-mail or print it.
The demo version of the LMS "Bathysphere" can be found at http://www.baty.ru/demo.html.
How to build distance courses
The most common "way" to create a distance learning system, which can now be found on the Web, is the translation of educational materials into HTML-form and posting them on the Web sites of educational institutions. Of course, this is an important stage, but the design of educational material in the Web form and the opening of access to it via the Internet does not introduce any innovations into the learning process itself. Translating a physics textbook into an HTML structure and making it possible to read it does not mean creating a distance learning course in physics.
Learning involves not just reading the educational material, but its active comprehension and application of the acquired knowledge in practice.
The "activity" of comprehension is quite often expressed in the fact that students ask questions to the teacher, and LMS should provide for such an opportunity. In addition, the material itself must be constructed in such a way as to "provoke" questions. But at the same time, there should be a teacher on the "other end of the line" who can answer the question in real time for synchronous course, or at least quickly enough - for asynchronous.
The "application" of knowledge can be implemented in the form of answers to a simple test or the performance of more complex tasks. In both cases, the results of the test or task must be checked either automatically or, again, by the teacher.
Thus, the main differences between an online training course and a presentation or a Web site are not just the provision of access to information, but involvement in interactive interaction with knowledge control and the accumulation of information about the learning process of students. The accumulation of information about the learning process and the courses taken is especially important in the case of a corporate distance learning system - personnel departments and managers receive very important information about the training activity of employees and the progress of their training.
We can offer the following simplified scheme for organizing an online training course.
- Sequential movement along the course: until the first point is passed, it is impossible to go to the second point (the movement can be organized within individual topics). If the topic has already been completed and passed, arbitrary admission to individual items is possible.
- Checking knowledge before moving on to the next item (in the form of simple questions with multiple answers) with fixing the fact of passing and the result.
- Issuing assignments to students with verification of performance and grading.
- Conducting a dialogue with the trainee - the "questions and answers" function.
What kind of specialists should be involved in creating an online learning course and what skills should they have?
Some thoughts on this subject are given in article by Patti Shank, teaching technology consultant at the University of Colorado Denver. An abridged translation of the article can be found.
Based on these considerations, the course development team should consist of three groups of specialists:
- Distance learning (DL)- training, in which all or most of the training procedures are carried out using modern information and telecommunication technologies with the territorial disunity of the teacher and students.
- Remote education– education implemented through distance learning.
- Distance learning technology(educational process) - a set of methods and means of teaching and administering educational procedures that ensure the conduct of the educational process at a distance based on the use of modern information and telecommunication technologies.
- Case technology- a type of distance learning technology based on the use of sets (cases) of textual, audiovisual and multimedia educational materials and their distribution for self-study by students when organizing regular consultations with tutors in a traditional or remote way.
- TV technology- a type of distance learning technology based on the use of television systems to deliver educational and methodological materials to students and organize regular consultations with teachers - tutors.
- network technology- a type of distance learning technology based on the use of telecommunication networks to provide students with educational and methodological materials and interactive interaction between a teacher, an administrator and a student.
- DO system- an educational system that provides knowledge through distance learning technologies. Includes: staff of the administration and technical specialists, faculty, educational materials and products, teaching methods and means of delivering knowledge to students (corresponding to one or more types of distance learning technologies), united organizationally, methodically and technically for the purpose of conducting distance learning .
- Establishment of the DL system- an educational institution or an association of educational institutions that ensures the functioning of the DL system.
- Distance Learning Center(center of distance education), Center for distance education - a separate subdivision, representative office or branch of an institution of the system of distance education, which provides administrative, educational, methodological, informational and technical support for the educational process.
Resource Center DO- an educational organization or its division that creates its own, and also distributes borrowed educational materials for distance learning.
- Full Scale Distance Education- distance education, based on the passage of a full cycle of education of the appropriate level and profile with the issuance to the student of an appropriate document on education (diploma).
- Organization of full-scale distance education- an educational organization that has teaching, methodological, technological, technical and administrative potential, allowing remotely with the proper quality and in full of the state standard to provide full-scale distance education.
- Training center (shared use center) organizations of full-scale distance education - a structural subdivision of the organization of full-scale distance education in the form of a branch or representative office, located in a certain geographical point, having educational premises, equipment and means of communication, administrative and educational support staff, allowing for the residents of this geographical point to conduct an educational process carried out basic educational institution on distance technology.
Individual distance learning- distance learning at the place of residence (location) of the student, who has the necessary hardware and software to provide telecommunications and training.
- Database of educational materials (for distance learning)- a set of educational and methodological materials (textbooks, manuals, guidelines, etc.) intended for distance education and presented in a form that provides access to them by participants in the process of distance education.
- Information and educational environment of DO(IOS DO) - a set of educational materials, means of their development, storage, transmission and access to them, used in distance learning technologies.
- virtual audience- a lot of remote from each other workplaces, united by data transmission channels and used within the framework of distance learning technology by students to perform the same educational procedures in terms of content, with the possibility of interactive interaction with each other and the teacher.
- Remote Access Lab- a subdivision of an educational organization equipped with real educational and research equipment with remote access to it via telecommunication channels.
- Virtual Lab DO- a remote access laboratory, in which real teaching and research equipment has been replaced by mathematical modeling tools.
- Tools DO- software and information support used to present educational materials in the information and educational environment of distance learning.
- Educational and methodological support of DO- a base of educational materials, a system for managing this base, methods of distance learning, tests, recommendations on distance learning technology, taking into account didactic and psychological aspects.
- DO software- system and application programs and software systems used in one form or another of distance learning, including tool environments for creating training programs and software systems.
Technical support to- used in the information and educational environment of distance learning computing, telecommunications, satellite, television, peripheral, multiplying, office and other equipment, as well as data transmission channels.
- Organizational support of DO– forms of organization of the educational process with the use of distance learning technology, as well as recommendations for their use, in accordance with local and federal legislation.
- Regulatory support of DO- legal documents of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation (licensing, attestation and accreditation norms and rules, legislative acts, standards, orders, instructions, etc.), as well as internal regulatory documents of organizations providing distance learning, regulating the preparation and conduct of the educational process on the basis of distance learning learning technologies.
- Staffing for subsidiaries- staffing tables, job descriptions, faculty involved in the conduct of distance education and in the development and replenishment of the base of educational materials in an educational institution of a distance type.
- Extraterritorial faculty- professors and teachers of an institution of the DL system living in different places, united organizationally and methodically by means of telecommunications and leading the educational process in the educational centers of this organization on the basis of agreements concluded with them.
- Tutor- a methodologist, teacher or consultant-mentor, who is part of the teaching staff of the distance learning system, providing methodological and organizational assistance to students in the framework of a specific distance learning program.
With the development of globalization processes, new goals are set for higher education - the training of professional personnel capable of working effectively in the changing conditions of the global market. Modern higher education is distinguished by a number of features and requires certain changes in the content and organization of education. The main factor stimulating change is the rapidly increasing flow of information. This growth is happening at such a pace that the old methods and the education system itself can no longer cope with it. A simple increase in the amount of knowledge being mastered leads to an excessive increase in the teaching load, adversely affects the health of students, but does not give the desired results. With such a rate of change, knowledge is updated so quickly that by the time students finish their studies at the university, the knowledge acquired by students has time to become obsolete.
Many experts believe that in connection with the processes taking place in the world, it is necessary to radically transform higher education, taking into account the current level of information technology development.
The basis of a full-fledged education is the interaction between people - teachers and students, as well as between the students themselves. Information technologies are precisely the means that can make this communication extremely effective.
Information technology does not replace human communication - it simply solves certain problems, thus making it possible to concentrate on conceptual ideas. The use of such technologies has ample opportunities. So, students can view the curricula in advance, get acquainted with the content of the courses. Thanks to this, communication with the teacher can become much more meaningful. On the other hand, students can listen to lectures in advance, study the necessary material using, for example, the Internet, and then, already prepared, come to a lecture to do exactly what they were there for: exchange ideas, discuss various points of view, etc. As the results of research show, such transformations in the process of teaching students lead to an increase in the quality of the knowledge gained.
One of the fundamental ideas of the development of the Internet has recently become the concept of Web 2.0. The term Web 2.0 has been used for a relatively long time, but in its modern sense it originated at the Web 2.0 conference (http://www.web2con.com) which was organized in October 2004. In the proceedings of this conference, Tim O'Reilly published the first and most popular article, which was the first to explain the meaning of this term, and also clearly demonstrated the differences between the first and second generation networks. The use of the term Web 2.0 is mainly associated with the so-called social services and networks, which magically allow you to unite people into social groups, quickly search for like-minded people and the necessary information. However, without the skillful leadership of the group and the desire to share information by its members, as well as without some additional tools, it will most likely not be possible to achieve these goals. In fact, all the so-called social services only allow you to publish your materials on the Web, including multimedia ones, as well as draw attention to them using various techniques, such as organizing by topic, creating communities of interest. himself or holding various contests among users. Such a complex of services is commonly called Web 2.0 technologies. As a rule, the publishing system in such services is quite rigid and is optimized for a specific type of content: short notes, photos, sound or video recordings. However, this simplification allows you to use these services without programming knowledge or the ability to write HTML documents. As a result, these services can be used not only by IT professionals, which was the reason for a significant expansion of their audience. In fact, it is the availability of services that distinguishes them from complex Web 1.x publishing systems.
Another significant difference in Web 2.0 is the active use of presence services, which allow you to determine where the user is and how best to deliver information to him. Such services make it possible to conduct dialogues in almost real time, which greatly increases the intensity of user communication. In fact, ease of use and status of presence is a qualitative change in Web 2.0 compared to previously used technologies. Areas of use
As far as learning is concerned, Web 2.0 technologies make it possible to organize it via the Internet. However, one separate service is usually not enough for this: reference information can be stored on an encyclopedia site like Wikipedia, illustrative material in photo archives, filmed video and audio lessons on sites like YouTube, blog sites such as LiveJournal can be used to communicate with students. . However, one of the highlights of Web 2.0 lies in the possibility of effective communication. The technology of creating and developing communities, which distinguishes Web 2.0, allows the teacher to communicate with several students in real time via instant messaging or by issuing assignments through online diaries. Among the social services there are also calendars that allow you to organize the planning of classes. In general, before starting training in the Web 2.0 format, the teacher needs to collect all the necessary data on various services and link them with a network of cross-references. As already mentioned, these services are fragmented and require efforts to synchronize them. At the same time, there are specialized distance education systems that have all the same functions. However, it turns out that such systems are quite difficult to use and require certain qualifications from teachers. Meanwhile, Web 2.0 services are optimized for users with minimal skills.
The concept of Web 2.0 means a change in the principles of operation of conventional software products. The widespread use of special interfaces leads to the fact that familiar applications start working through the browser. This means that everyone can work exclusively with web applications - an online text editor, spreadsheet processor, organizer, bookmark storage service, file storage tools, listening to music. As a result, complete user mobility is achieved - it is enough to have access to the Network, and you can work with the Network in the same way as with a regular computer with applications installed on it. In this case, all applications will be available through the browser, and the user only needs the operating system, the browser itself, and access to the Internet.
The next point that the creators of the Web 2.0 concept focus on is the redistribution of the previously existing roles of the content creator and its consumer. This separation of duties in Web 2.0 is gradually being erased, and content consumers, that is, Internet users, are gradually becoming full-fledged participants in the process of its creation.
In education, Web 2.0 is primarily access to learning tools through a browser. In addition, a number of other additional tools appear that implement the principle of Web 2.0 - this is the use of RSS and podcasting in education. Courses in the form of podcasts allow the student to listen to lectures not only at the computer, but also at any free time, even outside the home.
A distinctive feature of new technologies is also the independent formation and change of educational content by students. Educators working in the field of distance learning have noted that when using tools such as wiki technology and blogs, students move from discussing prescribed topics among themselves to discussing a wider range of topics with experts around the world. Other technological innovations implemented in Web 2.0 are associated with an increase in network bandwidth and the widespread use of multimedia - video and audio materials. Audiobooks, which can be listened to on an iPod or mp3 player, as well as lectures in the form of podcasts, are already being fully used. Mobility and a large amount of content that can be placed on modern media will help increase students' awareness and erudition.
Thus, the concept of Web 2.0 in education provides for the following functionalities in education: rss feeds for subscribing to news, online lectures in the form of podcasts, a wiki environment for creating joint projects, the use of teachers' blogs and students to form educational content when studying certain courses.
In this case, the concept of Web 2.0 provides an opportunity to exchange knowledge not only from a teacher to students, but also between students and from students to teachers. This circumstance forms a high-quality educational environment, since it becomes possible, when studying the course, to ask a question not only to the teacher, but to other experts in the field under study.
Web 2.0 technologies make it possible to significantly increase the accessibility of training programs, introduce cataloging and ratings, and much more for one simple goal - to increase the accessibility and quality of education. A training course can be created as a compilation of educational material from various authors with a catalog of courses with a clear and transparent rating, so that the student has the opportunity to choose a particular one from all courses, for example, in macroeconomics and, after listening to the course , contribute to the overall ranking.
BIBLIOGRAPHY:
1. Tim O'Reilly. What is Web 2.0. http:// www. computerra.ru/think/234100/
2. Nikolai Karev. Web 2.0 - revolution or farce? opendocument
3.Roman Dots. Educational program on Web 2.0. http://www.i2r.ru/static/512/out_23422.shtml
Bibliographic link
Gnedenko V.V., Tyutyaev A.V. The use of Web 2.0 technologies in education // International Journal of Applied and Fundamental Research. - 2009. - No. 3. - P. 82-0;URL: https://applied-research.ru/ru/article/view?id=12 (date of access: 01.02.2020). We bring to your attention the journals published by the publishing house "Academy of Natural History"