Features of the Constitution of the Russian Federation
Constitution of the Russian Federation It is the main law of the state that is endowed with the highest legal force and which enshrines and regulates public relations in the field of the legal status of the personality, civil society institutions, the organization of the state, as well as the foundations of the functioning of the public authority.
Essence of the Constitution It is that it is designed to serve the main limiter for the authorities in its relationship with man and society.
Appointment of the Constitution It is to consolidate the foundations of the constitutional system, human rights and citizen, the basics of the organization of the state and the foundations of the public authority.
Note 1.
The Constitution of the Russian Federation is the main law of society and the state. It has the properties of the principal law, and they are due to the fact that the Constitution in the generalized form is enshrined the main results of the economic, political, socio-cultural transformations conducted in the country and the results of the development of the entire legal system.
The constitution as the main law of the state is inherent in the following features:
it regulates the widest sphere of public relations that affect the interests of all citizens;
it finds the fundamental of the political organization of society and the economic structure of the state;
it defines the main directions of judicial activities of the state bodies: legislative and executive;
regulates issues of foreign policy state activities;
she is inherent in a special order of adoption and change.
Legal properties of the Constitution Characteristic features that determine the qualitative originality of this document (Fig. 1).
These signs are as follows:
acts as the main law of the state;
endowed with the highest legal force;
is the core of the entire legal system of the country;
it has stability.
Figure 1. Legal properties of the Constitution
Note 2.
So, the Constitution of the Russian Federation is the main law of the country. It has the highest legal force towards all legal acts. No legal act, which is accepted in the country: Whether the Federal Law, Decree of the President of the Russian Federation, the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation, the court decision, etc., cannot contradict the state's fundamental law, and if it contradicts, the norms of the Constitution have priority importance.
In family legislation, the provisions of Art. 38 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation on the state protection of family, motherhood and childhood, as well as the main responsibilities of parents and children.
So, of the foregoing, it can be concluded that the Constitution of the Russian Federation is the main source of constitutional, as well as all other industries of Russian law. Constitutional norms are mandatory for everyone and are founding.
The main functions and properties of the Constitution
The appointment of the Constitution is manifested in the implementation of constitutional norms. The main functions of the Constitution (Fig. 2) include:
constituent - is that the legality of the state, the constitution attaches political and the political system;
organizational - its essence is that the constitution is enshrined the legal procedure in the country;
ideological - expressed in the ideological basis of policies held by the state;
information - because it is the main source of information about the country that adopted it;
stabilizing - because in the process of adopting constitutional norms, the country's stable development is ensured in a particular direction;
software - it contains provisions that will be really possible in the future and will be widespread.
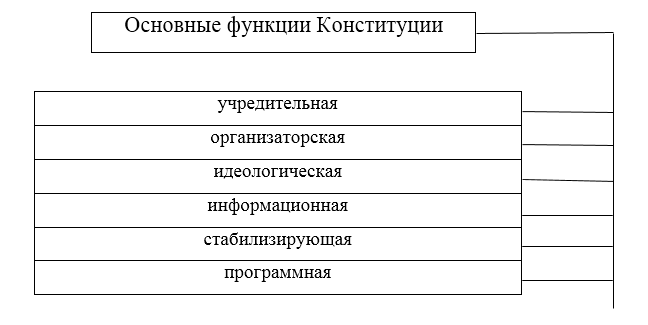
Figure 2. Basic functions of the Constitution of the Russian Federation
The constitution, being the basis of regulatory relations, has the following properties:
- Fundamental character.
- Regulatory.
- Higher legal force.
- Special procedure for adoption.
- Foundation.