(for four-year elementary school)
A.A. Vakhrushev, D.D. Danilov, A.S. Rautian, S.V. Tyrin
I. Explanatory note
The most important tasks of education in primary school (formation of subject and universal action methodsensuring the possibility of continuing education in the main school; education of the ability to learn - ability to self-organization in order to solve educational tasks; individual progress In the main spheres of personal development - emotional, cognitive, self-regulation) are implemented in the process of learning to all subjects. However, each of them has its own specifics.
Reading, Russian and mathematics create a foundation for the development of all other objects at a minimum that they teach children reading, writing and score. The core of rational comprehension of the world has always been a system of sciences, the study of which is the basis of school programs in the main and senior school both by the number of objects and by the number of hours. Thing " The world"On the basis of the skills obtained in the lessons of reading, Russian language and mathematics, teaches children to a holistic integral rational (breathtaking) comprehension of the world, prepares them for mastering the basics of knowledge in the main school, and in relation to the development of the personality, its upbringing plays no less, If not a big role compared to the rest of the subjects.
The subject "The World War" is the foundations of natural and social Sciences. The goal of the course of the surrounding world in elementary school is to understand the personal experience and the teaching children to the rational comprehension of the world.
Unisematic fragmentary knowledge can be used only for the purpose for which they are intended. In a modern rapidly changing world, a lot of unexpected, new tasks, to whom it is impossible to prepare in advance. In an unexpected situation can be useful holistic knowledge system, More than more - the formed ability to constantly systematize the acquired information and detect new connections and relationships. Science is an exemplary example of a knowledge system built on a rational basis.
Acquaintance with the beginning of science gives a disciple key (method) to understanding personal experience, allowing you to make the phenomena of the surrounding world by understandable, familiar and predictable. The subject "The World War" creates the foundation of a significant part of the subjects of the main school: physics, chemistry, biology, geography, social science, history. This is the first and only subject in school, drawing a wide palette of natural and public phenomena. In the future, this material will be studied on various subjects. Therefore, it is within the framework of this subject it is possible to solve problems, for example, ecological education and upbringing.
The specificity of understanding the experience of the modern child is that his experience is extremely wide, but largely virtual, that is, not by direct communication with the world around the world, but indirectly, through the media and primarily television. The role of virtual experience will only increase due to the wide range of computer, the Internet.
Television is not focused on systematic children's education, although it becomes the main "window" into the world around. Therefore, without being able to confront the negative impacts of virtual experience, the school should, if possible, use it for educational purposes and organize the development of the virtual world to schoolchildren. Therefore, the role of the "surrounding world" of the object is very large and there is a need to expand its content, since this item must give answers to a variety of requests for child experience, including virtual.
The understanding of personal experience is also important because it introduces a student to the world a value scale, without which the formation of any target plants is impossible. The subject "The World War" also helps the student in the formation of personal perception, an emotional, appraisal attitude to this world.
II. General characteristics of the educational subject
Acquaintance with the holistic picture of the world and the formation of an appraisal, emotional attitude to the world is the most important lines of the development of the student's personnel of the course of the surrounding world. Modern schoolchildren differ from the peers of fifteen-twenty years ago for curiousness and greater awareness. Unfortunately, these knowledge of children, as a rule, are not systematized and fragmented. The reason is that more objects and phenomena are included in the circle of our communication with which we communicate indirectly. If at the same time small man 5-9 years old knew only those objects and phenomena, which was directly surrounded in the family, in the courtyard, at school, now the situation has radically changed. Thanks to TV, movies, computer and books, the guys may know about diverse phenomena and facts in the distance from their home significantly more than about the surrounding items.
As a result, various schoolchildren have different knowledge and have different questions about the world around. Before the teacher there is a difficult task to build a lesson in such a way that, on the one hand, answer for all questions, guys and satisfy the curiosity of students, and on the other - to ensure the assimilation of the necessary knowledge.
How to learn to achieve both goals. It turns out that there is one way out for this. Actor schoolboy's Education and Education primary classes is an acquaintance with a holistic elementary scientific picture of the world. The meaning of the picture of the picture of the world - with a minimum of reported knowledge to make a person a conscious participant in life. It is very important from the very first steps of the child at school to teach him a holistic look at the world. Then the answer to any question arising from the schoolboy can be easily found, since the guys from the very first steps of the study of the surrounding world are taught to seek the place of each phenomenon of nature and human farms in it.
Himselfing the goal to build a course in which each schoolboy can find answers to the questions that arise from him, we cannot not be aware of the fact that the volume of textbooks are limited. What should be the way out of this position?
To solve the task, a textbook is not suitable, which includes only such specially selected issues that can be accessible and outlined without popularization are presented to younger schoolchildren. After all, with this approach, most of the questions that arise from the guys cannot be answered. As a result, the guys will not be integrated ideas about the world around. This in turn will not allow them to easily perceive new information, as it is difficult to associate with a small number of prevailing ideas and concepts. So, most of their representations will be the result of children's myth-making. These ideas received by the guys in childhood may remain with them for life.
Another situation will develop when using the course to which the integrated course of the surrounding world in the framework of the school 2100 applies to your attention. Schoolchildren introduce wide ideas about the world that form a system covering the whole world. At the same time, the most important concepts ("islands of knowledge") explain only a small part of the world around them, but the closest development zones are made around them allow to respond to most of the questions that arise from the guys. The presentation of a relatively complete picture of the world will make it possible to give the creative research nature to the process of studying the subject, forcing students to ask new and new questions specifying and helping to comprehend their experience.
How to form a holistic picture of the world from a child? It is meaningless to start trying to tell him strangers for him. He may be interested, but will not be able to combine these new knowledge with his experience (knowledge will remain "islets without bridges"). The only way - daily and hourly help the guys to comprehend their experience. A person must learn to understand the world around and understand the price and the meaning of his actions and actions of others. And let the person will not always act in accordance with his knowledge, but to give him the opportunity to live wisely and meaninglessly we must. Regularly explaining his experience, a person tends to understand the world around him. At the same time, it is constantly beginning to arise questions (caused by ignorance "), which require clarification. All this contributes to the emergence of habit (skill) explanations and understanding of their experience. In this case, he can learn how to make any new thing, his own mastering him.
At the same time, it is fundamentally important not to stop at the cold rational analysis of the world. A person is inseparable from those experiences (emotions, feelings, assessments), which he is experiencing in relation to everything that happens around him. Thus, another our goal is to help the student in the formation of personal perception, emotional, appraisal attitude to this world. It was within the framework of this line of development that the objectives of humanistic, environmental, civil and patriotic education are solved. It is the independent definition of a student of his position in the end, it will help him find an answer to the question: "How do we build your life?" In the relationship "Man - Nature", "Man - Society". In the view of the authors, the only human survival strategy in relations with nature is the transition to an environmental economy that will not destroy natural ecosystems, but to embed it in them. In the relationship between people, the main priority is the formation of a civil identity of the tolerant personality - a person who can independently determine its position, is interested and tolerable to treat the positions and interests of other people. Upon reaching these goals, we will be able to hope that our student will be able to take advantage of the picture of the world.
The activity approach is the main way to get knowledge. The inclusion of a holistic picture of the world, accompanied by an explicit expansion of the content, requires significant changes in the didactics of natural science in elementary school.
Traditionally, the basis of learning is the learning of knowledge. Therefore, the main goal of education is to "invest in the head of children." In this case, the content of the course of natural science rate in elementary school is too voluminous. Of course, the whole, even elementary, the picture of the world in elementary school can not be learned, as this is the task of the entire basic school. But we do not apply such a goal. We want to introduce the guys from the picture of the world and teach them to use it to comprehend the peace and ordering their experience. Therefore, the learning process, according to our deep conviction, should be reduced to developing the skill of interpretation of his experience. This is achieved by the fact that the guys in the learning process learn to use the knowledge gained during the fulfillment of specific tasks imitating life situations. The solution of problematic creative productive tasks is the main way of understanding the world. At the same time, various knowledge that schoolchildren can remember and understand, are not the sole purpose of training, and serve only one of its results. After all, sooner or later, these knowledge will be studied in high school. But to get acquainted with a holistic (taking into account the age) the picture of the world later the guys will not be able, as they will study the world separately in class on various subjects.
In this case, we use traditional for schools "schools 2100" the principle of minimax. According to this principle, textbooks contain redundant knowledge that the guys may assign and redundant tasks that students can perform. At the same time, the most important concepts and connections that are ministed in the minimum of content (standard) and the components of a relatively small part of the course must learn all students. Thus, textbooks differ significantly in terms of the material that students may and must be learned.
Within the framework of the historical and social science course, the activity approach is most difficult, since this approach is largely contrary to the tradition of teaching history in school. Often, the discussion from the point of view of science questions either were avoided, or unequivocally interpreted. Attempts to put these questions as problems inevitably came up to the fact that students have a disastrously lacking knowledge to solve them school Course. As a result, the study of history was reduced to the description of events and phenomena, supplemented by an indication of a rigid causal relationship, which suggested during the discussion only a unambiguous issue of the issue (in accordance with the version dominating at that time in science). All these circumstances are extremely hampered by the formation of the ability to use historical experience in modern life. But this is exactly what the implementation of activity-oriented principles is required.
We propose not to avoid issues of problems russian history and modernity. These questions you can not finally resolve, in the framework of the school in general, and especially in 3-4 grams. A person who constantly expanding his horizons during his life, comes to solving these problems. Course's task - put In front of the disciples, these questions, since without them a holistic picture of history does not exist. When trying to solve these problems in elementary school, the teacher should pay the attention of children to the fact that to achieve the goal requires a permanent expansion of their knowledge! The purpose of the historical and social science of the environment of the surrounding world is that the student thinks over the problematic issues, so that he is constantly returned to the attempts of their permission.
Thus, in general, students should develop ability to understand and know the world around. Signifyingly apply the knowledge gained to solve educational and vital tasks.
Algorithm of teacher training for lesson. When conducting lessons at our course, teachers are very often faced with the problem of lack of time. The topic of the topic is so extensive that it is not possible to "open" completely together with schoolchildren using the technology of a problem dialogue. There is already a call, and the teacher has not yet explained to the guys all the material. As a result, there is no time for the stage of independent use of knowledge, nor for summing up. The basis of this problem is the desire of a teacher "Open" with students all knowledge. On the contrary, some complex provisions are easier to explain to the teacher himself, leaving lighter "discoveries" for students. It is important that at every lesson at least part of the knowledge of the children "opened" themselves.
The second and main reason for the lack of time is the inability to use the minimax principle. According to this principle, schoolchildren at the lesson can learn a lot of new (maximum), but they must learn only the most important knowledge (minimum).
1st step. At the first stage of preparation for the lesson should be allocated in the contents of the textbook minimum. To do this, it is necessary to open a program and find in the requirements for knowledge and skills by the end of this year of study those related to the topic studied (the list of requirements is also placed in diaries and at the beginning of each section of the textbook). This is the minimum that must learn all students and which will be checked in verification workah at the end of a quarter. The assimilation of these knowledge and skills is ensured not so much at this lesson as in the subsequent lessons in the process of their update. In some lessons, there may not be knowledge and skills relating to a minimum.
Starting from the 2nd class, at the end of the lesson there is a list of concepts that schoolchildren must learn. Some of these concepts dedicated to the font belong to the program minimumThat all schoolchildren should know. It can be indicated by the expression "I need to remember." But the other part of the concepts, facts (it is not highlighted) is not minimal. It can be indicated by the expression "Enough to meet". It includes frequently found surrounded by a child's child, which nevertheless not necessarily know. It is necessary to achieve their understanding in the lesson by all students, but in further lessons it is not necessary to apply them at the stage of actualization. To whom they will seem important, remember them, the rest can forget. BUT B. independent workheld at the end of the topic (once in 3-4 lessons), they are included in the lesson on this topic should be present.
Finally, to the third category of concepts and facts - maximum - These are those in the text of the textbook, but are not placed at the end of the lesson, they are all no longer reflected in the software requirements. They are not only not necessarily to know, but also not necessarily include in the lesson material.
2nd step. At the second stage of preparation for the lesson, revealing the concept of a minimum and maximum, the teacher thinks a problem situation, the main question of the lesson and a small set of the most important issues to find the answer to answer the main question. These basic dialogue issues The teacher includes in its abstract, while simultaneously thinking about the possible answers to children. The developed plan should be told to observe, distracted by the lesson only to the difficulties arising from students when studying the most important knowledge. If the schoolchildren immediately express their versions of the problem (encouraging dialogue), the teacher will not ask all the prepared issues, but will go to the lesson to discuss versions. In general, in our methodology, you need to be pre-ready for the fact that the guys will easily pass the teacher with a thoughtful rut. It is in order for the lesson that the lesson does not lose logic, the teacher writes in his abstract system of the most important issues and tries to follow it.
3rd step. Only in the third stage of preparation for the lesson, the teacher begins to choose and include in the summary of the lesson, those knowledge from the maximum who will be interested in schoolchildren. In the 3-4th grade, you can pre-discuss with the guys, what they want to know. This material is the reserve that the teacher may donate with a shortage of time.
Control of educational results. Any didactics involves control over the learning of knowledge, subject skills and universal training actions. Without knowledge gained by schoolchildren, learning efficiency will be zero. Once again we repeat the knowledge requirements for the classroom on the environment.
First, in our opinion, only those knowledge of students they can enjoy in practice are important. Therefore, first of all, knowledge gained by schoolchildren should allow to describe their observations and explain to the guys their own experience, help respond to questions that arise from them. In fact, the skills of using knowledge are needed, and not the knowledge itself.
Secondly, strong knowledge is important and needed, and the material that has not learned to this lesson. In this regard, we propose to evaluate students in the following two ways:
- The assessment of the learning of knowledge and skills is carried out through the execution of productive tasks in textbooks and workbooks, in independent and final work (1-2 cl.), In verification and test workah (3-4 cl.). Productive tasks require not so much to find a ready-made response in the text, how much to apply the knowledge gained to a specific situation for its explanation. This kind of knowledge of knowledge leads to the construction of a person's adequate reality of a holistic picture of the world understandable for him. Schoolboy who fully fulfilled independently all the necessary tasks in the textbook and working notebook, all the necessary knowledge of the knowledge. At the same time, it will not so much to remember the definition of concepts and the wording of laws, how much will be able to apply them in life. Naturally, such a task may come up with a multitude and add a teacher. But they must meet all the above criteria (first of all, to require creatively applying knowledge) and it is desirable to be associated with any practical activity (write, draw, connect, sculpt, and the like). It is very important that the amount of tasks the teacher determines from the level of knowledge of his students. In any case, there is no need to fulfill all tasks in textbooks and workbooks (minimax principle).
- Assembly assessment of knowledge and skills is carried out through the constant repetition of the most important concepts, laws and rules. At the stage of actualization of knowledge before the start of studying a new material, we offer the teacher to conduct a blitzoprosis of the most important concepts of the course and their relationships that need to be remembered for the correct understanding of the new topic. Especially useful if the guys themselves formulate a list of knowledge necessary to solve the problem. In all textbooks, starting from the 2nd class, at the beginning of each lesson there are questions for actualization of knowledge.
The advantages of such a test of knowledge and skills are that the teacher is constantly aware of those knowledge that children possess. In the case when none of the students can give an answer to the question, schoolchildren under the guidance of the teacher turn to the dictionary. This once again teaches working with him and shows how to do a person if he wants to know anything.
An important role in conducting controls have notebooks for independent and final works (1-2 cl.) and notebooks for verification and test work (3-4 cl.). The level of tasks in textbooks and workbooks is distinguished by its complexity in independent (verification) and final (control) work. Tasks in the textbook and workbook are the most difficult. They include, in accordance with the minimal principle, not only a mandatory minimum (program requirements), which must learn all students, but also the maximum that schoolchildren can learn. At the same time, the tasks of different levels of difficulty are not marked. In contrast to independent (verification) and final (control) works, starting from the 2nd class, the level of complexity (necessary, software or maximum) is marked, which can independently choose students. At the same time, the emphasis of independent (verification) works is made at a mandatory minimum and the most important provisions of the maximum (minimax). And the material of the final (control) works is entirely oriented on the mandatory minimum of knowledge.
Thus, each student must learn each topic by performing a certain amount of tasks in the textbook and the working notebook, coping with the tasks of independent (verification), final (control) works. Positive estimates and marks for the tasks of independent (verification), the final (control) works are a kind of testimony on the topic studied. Each theme for each student must be credited, but the term of receipt of the testing should not be rigidly limited (for example, students should pass all themes until the end of the quarter). It teaches schoolchildren to plan their actions. But schoolchildren must see the results of their work, this role can play:
- table of requirements for the subject in the "Schoolboy Diary". In it, the student (with the help of a teacher) puts his marks for different tasks, demonstrating the development of the relevant skills. For example (2 cl.), Mark for the task: "What substance gives hardness and elasticity to these subjects? (Drawn the ball, inflatable circle, inflatable mattress) "put in the graph of the ability to" explain the differences of solid, liquid and gaseous substances ";
- 2) The student's achievement portfolio is a folder in which originals or copies (paper, digital) performed by a student of tasks are placed, works containing not only the mark (score), but also an assessment (verbal characteristic of its success and advice on improving, eliminating possible flaws) .
The accumulation of these marks and estimates shows the results of promotion in the assimilation of new knowledge and skills by each student, the development of his skills to act.
III. Description of the place of the educational subject in the curriculum
In accordance with the federal basis curriculum, the course "The surrounding world" is studied from 1 to grade 4 to two hours a week. The total learning time is 270 hours. Excursions and practical work occupy a special place. Their required minimum is defined for each section of the program. Excursions include observations, practical work: observations, experiments, measurements, work with ready-made models, independent creation of simple models.
IV. Description of the value orientation of the content of the educational subject
Value of life - recognition of the human life and the existence of living in nature as a whole as the greatest value, as the basis for genuine environmental consciousness.
Nature value It is based on the universal value of life, in a realization of itself as part of the natural world - part of a living and inanimate nature. Love for nature means first of all the careful attitude towards it as a human habitat and survival, as well as the experience of the feeling of beauty, harmony, its perfection, the preservation and increase in its wealth.
Value of man As a reasonable creature, aspiring to good and self-improvement, the importance and need to comply with a healthy lifestyle in the unity of its components: physical, mental and socio-moral health.
Value of good - The direction of a person on the development and preservation of life, through compassion and mercy as a manifestation of the highest human ability - love.
Value of truth - This is the value of scientific knowledge as part of the culture of mankind, reason, understanding the essence of being, the universe.
Value of family as the first and most significant for the development of the child's social and educational environment, ensuring the continuity of cultural traditions of the peoples of Russia from generation to generation and thereby the viability of Russian society.
Labor and creativity value As a natural human life, the state of normal human existence.
Value of freedom As freedoms of choosing a person of their thoughts and actions, but freedom, naturally limited by the rules, the rules of society, the member of which is always throughout the social essence is a person.
The value of social solidarity As recognition of human rights and freedoms, the possession of the feelings of justice, mercy, honor, dignity towards themselves and to other people.
Value of citizenship - awareness of a person himself like a member of society, the people, a representative of the country and the state.
Value of patriotism - One of the manifestations of the spiritual maturity of a man, expressed in love for Russia, the people, a small homeland, in a conscious desire to serve the Fatherland.
Value of mankind - awareness of a person himself as part of the world community, for the existence and progress of which the world needs, cooperation of peoples and respect for the diversity of their cultures.
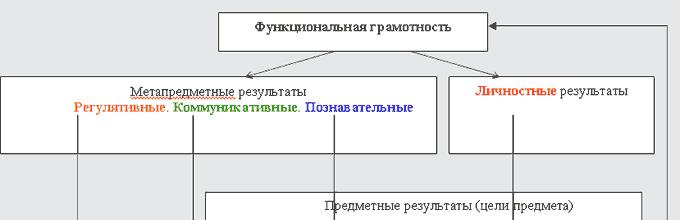
V. Personal, metapredemless and subject results of the learning subject
All results (objectives) of the development of the teaching course form a holistic system together with subject means. Their relationship can be seen in the diagram.

1st grade
Personal results Studying the World Mir Course in the 1st grade is the formation of the following skills:
- Evaluate Life situations (actions of people) from the point of view of generally accepted norms and values: in the proposed situations to celebrate concrete actions that can be assessed as good or bad.
- Explain From the position of universal moral values, why specific deeds can be assessed as good or bad.
- Alone define and express
- to make a choicewhich act to make.
The means of achieving these results is educational material and the tasks of the textbook providing the 2nd Development Line - the ability to define their attitude to the world.
MetaPronsMet results The study of the "Arrible World" course in the 1st grade is the formation of the following universal educational actions (Wood).
Regulatory Wood:
- Define and formulate The purpose of the activity in the lesson with the help of a teacher.
- Try The sequence of actions in the lesson.
- To study express Your assumption (version) based on working with a textbook illustration.
- To study work According to the proposed teacher plan.
- To study differ The task is true of incorrect.
- Learn together with the teacher and other students to give emotional evaluation class activity in class.
Cognitive Wood:
- differ New from the already known with the help of a teacher.
- Do preliminary selection of sources of information: navigate In the textbook (on the reversal, in the table of contents, in the dictionary).
- Make new knowledge: find answers Issues using a textbook, your own life experience and information obtained in the lesson.
- draw out As a result of the joint work of the whole class.
- Recycle the information obtained: compare and group Items and their images.
- detail retell Small texts, call their topic.
The means of forming these actions is the training material and the tasks of the textbook, providing the 1st Development Line - the ability to explain the world.
Communicative Wood:
- register His idea in oral and written speech (at the level of supply or small text).
- Listen and understand Speech of others.
- Expressively to read and retell text.
The median of the formation of these actions is the technology of a problem dialogue (encouraging and loving dialogue).
Subject results Studying the World Course in the 1st grade is the formation of the following skills.
- call surrounding objects and their relationships;
- explain how people help each other to live;
- call live and non-residential natural wealth and their role in human life;
- call the main features of each year of the year.
- evaluate the correctness of behavior in everyday life (communication rules, rules of the Obzh, traffic).
2nd class
Personal results Studying the World Miring Course in the 2nd grade is the formation of the following skills:
- Evaluate Life situations (actions of people) from the point of view of generally accepted norms and values: in the proposed situations to celebrate concrete actions that can estimate Like good or bad.
- Explain
- Alone define and express The simplest common rules for all people (the foundations of universal moral values).
- In the proposed situations, relying on common for all simple rules of behavior, to make a choicewhich act to make.
MetaPronsMet results Studying the "Arrible World" course in the 2nd grade is the formation of the following universal training actions.
Regulatory Wood:
- Define The purpose of the activity in the lesson with the help of a teacher and independently.
- Learn together with the teacher to detect and formulate training Together with the teacher (for this, a number of lessons are specifically provided in the textbook).
- To study to plan learning activities in the lesson.
- Express His version, try to offer the way it is verified (based on productive tasks in the textbook).
- Working on the proposed plan, use Required means (textbook, simplest devices and tools).
The means of forming these actions is the technology of a problem dialogue at the stage of studying a new material.
- Define The success of the fulfillment of your task in the dialogue with the teacher.
The means of forming these actions is the technology of assessing educational achievements (learning success).
Cognitive Wood:
- Navigate in your knowledge system: understandWhat is needed for more information (knowledge) to solve the learning task one step.
- Do preliminary selection Sources of information to solve the learning task.
- Make new knowledge: find The necessary information both in the textbook and in the dictionaries proposed by the teacher and encyclopedias (in the 2nd class textbook for this, a special "encyclopedia within the textbook" is provided).
- Extract new knowledge: to extract information presented in different forms (text, table, circuit, illustration, etc.).
- Recycle the information obtained: observe and make independent conclusions.
Communicative Wood:
- Convey your position to others: register His idea in oral and written speech (at the level of one sentence or small text).
- Listen and understand Speech of others.
- Expressively to read and retell text.
- Join In a conversation in class and in life.
The means of the formation of these actions is the technology of problem dialogue (encouraging and liner dialogue) and productive reading technology.
- Together to negotiate about the rules of communication and behavior at school and follow them.
- Learn to perform various roles in the group (leader, artist, criticism).
The means of forming these actions is the work in small groups (in methodical recommendations This version of the lessons is given).
Subject results Studying the World Course in the 2nd grade is the formation of the following skills.
The 1st line of development is to be able to explain the world:
- explain the differences in solid, liquid and gaseous substances;
- explain the effect of attraction of land;
- associate events on earth with the location and movement of the Sun and the Earth;
- watch the weather and describe it;
- be able to determine the sides of the light through the Sun and the compass;
- use the globe and cards, find and show parts of light, mainland and oceans on them;
- call the main natural zones and their features.
2nd Development Line - to be able to determine your attitude to the world:
- evaluate the correct behavior of people in nature;
- respectively refer to other peoples living on Earth.
3-4th grades
Personal results Studying the World Miring Course in the 3-4th grade is the formation of the following skills:
- Evaluate Life situations (actions of people) from the point of view of generally accepted norms and values: to learn from separating actions from the person himself.
- Explain From the position of universal moral values, why concrete simple actions can be assessed as good or bad.
- Alone define and express The simplest common rules for all people (the foundations of universal moral values).
- In the proposed situations, relying on the common rules for all to make a choicewhich act to make.
The means of achieving these results serves the training material and the tasks of the textbook, aimed at the 2nd Development Line - the ability to define their attitude to the world.
MetaPronsMet results Studying the World Course in the 3rd grade is the formation of the following universal training actions:
Regulatory Wood:
- Self formulate the objectives of the lesson after prior discussion.
- Together with the teacher, to detect and formulate a learning problem.
- To make a plan to solve the problem (tasks) together with the teacher.
- Working according to plan, to check its actions with the goal and, if necessary, correct errors with the help of a teacher.
The means of forming these actions is the technology of a problem dialogue at the stage of studying a new material.
- In the dialogue with the teacher, develop the evaluation criteria and determine the degree of success of the fulfillment of its work and the work of all, based on the existing criteria.
The means of forming these actions is the technology of assessing educational achievements (learning success).
Cognitive Wood:
- Navigate in your knowledge system: independently supposeWhat information is needed to solve the learning task one step.
- Take away Sources of information among the dictionaries proposed by the teacher, encyclopedia, reference books necessary for solving the learning task.
- Make new knowledge: extract Information presented in different forms (text, table, circuit, illustration, etc.).
- Recycle the information obtained: compare and group Facts and phenomena; Determine the reasons for phenomena, events.
- Recycle the information obtained: draw out Based on summarizing knowledge.
- Convert information from one form to another: make up plain plan educational and scientific text.
- Convert information from one form to another: present information In the form of text, tables, schemes.
The means of forming these actions is the training material and tasks of the textbook, aimed at the 1st Development Line - the ability to explain the world.
Communicative Wood:
- To convey your position to others: register Its thoughts in oral and written speech taking into account their educational and life speech situations.
- To convey your position to others: express your point of view and try her justify, leading arguments.
- Listen to others, try to take another point of view, be ready to change your point of view.
The means of the formation of these actions is the technology of a problem dialogue (encouraging and loving dialogue).
- Read out loud to yourself textbooks and at the same time: to conduct "dialogue with the author" (predict the future reading; put questions for the text and search for answers; check yourself); separating new ones; allocate to make plan.
The means of forming these actions is the technology of productive reading.
- Contract people: performing various roles in the group, cooperate in a joint solution (tasks).
- Learn respect to the position of the other, try to negotiate.
The means of forming these actions is the work in small groups.
Subject results Studying the World Miring Course in 3rd grade is the formation of the following skills.
Part 1. Inhabitants of the Earth
The 1st Development Line is to be able to explain the world.
- give examples of bodies and substances, solid bodies, liquids and gases, energy actions;
- give examples of relationships between alive and inanimate nature;
- explain the value of the cycle of substances in the nature and life of a person;
- give examples of living organisms of different "professions";
- list the features of coniferous and flowering plants;
- animals (insects, spiders, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, animals), mushrooms.
2nd Development Line - to be able to determine your attitude to the world:
- prove the need for a careful relationship of people to living organisms.
Part 2. My Fatherland
The 1st line of development is to be able to explain the world:
- learn about the lives of people from historical text, cards and draw conclusions;
- distinguishing objects and orders created by people (culture), from what is created by nature;
- explain what society is, the state, history, democracy;
- by year to determine the age, place of events in the past;
- distinguish from each other times of ancient Russia, Moscow state, Russian Empire, Soviet Russia and the USSR, modern Russia. Recognize modern coat of arms, flag, anthem of Russia, show the border and capital on the map.
2nd Development Line - to be able to determine your attitude to the world:
- learn to explain your attitude towards relatives and friends, to the past and true native country.
Subject results Studying the "Arrible World" course in the 4th grade is the formation of the following skills.
Part 1. Man and Nature
The 1st line of development is to be able to explain the world:
- explain the role of the main organs and systems of organs in the human body;
- apply knowledge about your body in life (for the preparation of the time mode, rules of behavior, etc.);
- call the main properties of air as gas, water as fluids and minerals as solid bodies;
- explain how a person uses the properties of air, water, essential minerals;
- explain what is the main difference of person from animals;
- finding contradictions between nature and human economy, to propose ways to eliminate them.
2nd Development Line - to be able to determine your attitude to the world:
- evaluate what is useful for health, and what is harmful;
- prove the need for a careful attitude towards living organisms.
Part 2. Man and humanity
The 1st line of development is to be able to explain the world:
- according to the behavior of people, find out what they have Emotions (experiences), what they have character traits;
- distinguish from each other different epochs (times) in the history of mankind;
- explain the differences between people of modern mankind: distinguish citizens different states; nationality of man from his race; Believers of different religions and atheists.
2nd Development Line - to be able to determine your attitude to the world:
- explain what interests unite you with your relatives, friends, fellow countrymen, citizens of your country, which unites all people on earth in one mankind;
- notice and explain what actions of people contradict human conscience, rules of behavior (morality and law), human rights and the rights of the child. Offer that you yourself can do to correct visible violations.
1st grade. "I and the world around" (66 h)
As we understand each other (9 h) Schoolboy, his duties. School. Hand and index finger - the simplest way to communicate. Hand. Index finger, its role in the showing of items. Speech is the main way to communicate people. Use the word for the name of the subject, the feature, actions. Items that can not show your finger (distant, fabulous, objects in the future).
Use of sharing knowledge between people. Transfer and accumulation of life experience - the basis of people's welfare. Source of life experience: own experience, knowledge of other people, books.
The concepts of "right", "left", "in the middle", "for", "before", "front", "back", "forward", "back", "left", "right", "above", " Below "," top "," bottom ". "Earlier" and "later."
How we learn that in front of us (4 hours) Objects and their signs. Signs common with other objects and peculiar. Discernment of items on features. Comparison of the signs of this subject with others. Properties of objects, their parts and actions with them allow you to distinguish between objects. Combine objects. Signs of combinations: subjects as signs; Objects with specific features.
How do you recognize the world (4 h) Man's senses. Eyes - organ of view, ears - organ of hearing, nose - body sentence, language - body of taste, leather - organ of touch. Memory is a repository of experience. Mind. Help parents and teachers to children in recognizing the world. The book keeps the knowledge and experience of people. Encyclopedia.
Your family and your friends (7 h) Your family and its composition. Mutual assistance in the family. The role in the family of each of its member, "profession" family members. Your family help. What qualities should family have.
Rules of safe behavior in the house. Dangerous and poisonous substances. How to behave in the kitchen, in the bath. Terms of use of electrical appliances. Rules of fire safety. Caution with relationships with other people's unfamiliar people.
Friend and friends. Communication as the interaction of people, exchange of thoughts, knowledge, feelings, impact on each other. The value of communication in a person's life. Ability to communicate. The role of polite words in communication. Smile and her role. Expression of greetings and farewell, gratitude, requests, apologies, refusal, disagreement. How to listen to the interlocutor. Miracles of communication (hearing, conversation, music, drawings, dancing, etc.). Types of communication in humans and animals, their similarity.
What surrounds us (10 hours) City and its features. Residential area: houses, streets, parks. Urban transport. The mutual assistance of people of different professions is the basis of the life of the city. Traveling around the city: residential areas, factories and factories, business and science Center Cities, recreation area. Village, his features. Life of people in villages and villages. Growing plants in vegetables, gardens and fields, dilution of pets. Rules of safe behavior on the street. Traffic light. Road signs.
The relationship of people of different professions in the process of bread production. Fabulous hero Kolobok and his journey. Human farm. The role of natural wealth. Mining from underground storerooms. Production of things at factories and factories. Agricultural plants and animals, their help person. Agriculture: crop production and animal husbandry. Service sector. Transport.
The dependence of a person from nature. Live natural wealth: animals and plants. Non-resident natural wealth: air, soil, water, stocks of underground pantry. Nature Forces - Wind, Sunlight, River Flow. The role of natural wealth in human farm. Careful attitude towards natural wealth. Solid, liquid and gaseous bodies, their display in Russian. Three water states: solid (ice, snow), liquid (water), gaseous (pairs).
Excursion "Safe Run to School."
Live inhabitants of the planet (9 h) Plants, mushrooms, animals, people - living organisms. Growth, breathing, nutrition, reproduction - properties of living organisms. Mortality of living organisms. Careful attitude towards living inhabitants of the Earth.
Plant and animal similarity: breathing, food, growth, development, reproduction. Plants feed all the inhabitants of the Earth and saturate air oxygen. Plants - "Kormaltsy". Animals are more often moving, looking for prey, eat food. Their "Profession" - "Etheries". The protection of living organisms in nature is the most important concern for a person. Pysticity of plants (flowering and non-flowered plants). Mushrooms. Animal manifold. The connection of the living organisms of different "professions" with each other. Their fitness for their place of life.
Cultural plants and domestic animals - our friends. Man's care about them. Dogs - man's helpers. Origin and breed dogs. Indoor plants - aliens from different countries. Plant care (regular watering, light). Rural house and its inhabitants - animals, their use by man. Caring for domestic animals. Cultural plants. Garden, garden and field plants are human breadwinners. Fruits and vegetables. Edible parts of plants.
Man, like an animal: breathes, feeds and gives birth to cubs. The similarity of man with animals. Acquaintance with the appointment of various parts of the human body. Man is a reasonable creature. Production of things. Acts peculiar to a reasonable creature. Caring for nature.
Ecology is a science on how to live in a world with nature, without violating its laws. Rules of behavior in nature. Question of students to sponder: what can and what can not be done in nature. Careful attitude towards the environment.
Why and why (2 h) Sequence of events and its causes. Cause and investigation.
Seasons (12 hours) Fall. Signs of autumn: cooling, short day, leaf fall, ice on puddles. Coloring leaves. Preparation of animals by winter.
Winter. Signs of winter. Weather in winter. Snow, snowflake, icicle, frosty patterns. Animals and plants in winter. Help animals.
Spring. Signs of spring: ice-frequency, melting of snow, breaking leaves, arrive of birds, beginning of flowering plants, nesting birds. Flowers - primroses. Birds and their nests.
Summer. Signs of summer: a long day, short night, bright sun, thunderstorm (thunder, zipper). Folk signs. All living brings offspring, ripening fruits. Mushrooms. Traveling water. Rules of behavior in a thunderstorm. Near and logo animals.
Excursion to the park "Autumn Nature".
Excursion to the park "Winter Nature".
Excursion to the park "Spring Nature".
The watch at the discretion of the teacher is 4 h.
2nd class. "Our Planet Earth" (68 h)
Introduction (4 hours) Common words - concepts. Live and ne. nature. Things. Substance. Solid bodies, liquids and gases, their properties. Air - a mixture of gases. Water - liquid. Loda is a solid body. Change of states of substances.
Earth and Sun (16 hours) Determining the day and year time on the Sun and the Moon. Determination of directions on the sun and the polar star. The main sides of the horizon: East - the direction at the sunrise, the West - the direction for the sunset, the north - the direction to the polar star, the south - direction in the sun at noon. Compass and use to them. Practical work with a compass. Moon phases change. Production of sunshine.
Form of the Earth. Skyline. Proof of the shag-like form of the Earth: expansion of the horizon with a rise in height, round-the-world travels, moon eclipse, space flight.
Practical work With a globe. Globe - model of the Earth. Movement of globe and land. Equator, pole, hemisphere. Meridians and parallels.
Universe or space. Planets and stars - celestial bodies. Stars - Self-dried celestial bodies. Constellations. Planets shine reflected light. Planet Earth. Sun - Star. Planets of the solar system. Movement of planets in orbits around the sun. The Moon is the Earth's satellite. Solar eclipse. Air color.
Force of gravity. All items are attracted to each other, large massive objects attract the stronger - the law world full gravity. Effect of earthly attraction on our life. Weightlessness.
The change of night and day. The main source of light on the ground is the sun. Rotation of the Earth around its axis - the reason for changing the day and night. The commensuity of the rhythm of human life by day. Daily regime. Practical work with a globe.
Change of seasons. Nature life varies by season. Sun height over the horizon in different seasons of the year. Change the angle of inclination of sunlight during the year. The appeal of the Earth around the Sun is the reason for changing the seasons of the year. The axis of the Earth is directed to the polar star. Thanks to the inclination of the axis, the Earth turns to the Sun, then its northern hemispheres (summer of the northern hemisphere), then the southern (winter of the northern hemisphere). The land retains heat solar rays.
Cold, moderate and hot light belts and their location on earth and relative to sunlight. Polar circle, tropic. Cold Belt - Long Winter and Short Summer, Moderate Belt - Winter and Summer Alternation, Hot Belt - "Eternal Summer".
The atmosphere is an air envelope. Weather and its signs. Temperature, its measurement. Thermometer. Practical work with a thermometer. Cloudy. Sedips: rain, snow, hail. Wind and cause of its formation. The climate is a naturally repeated weather state during the year. The diary of the weather observation. Signs of good and bad weather.
What is depicted on the globe and map. Globe and map (8 h) Plan and map - image of the earth on the plane. View of scale. Conditional signs.
Globe is a reduced earth model. Card hemispheres.
Conditional designations for the map and the globe. Height and depth on land map and globe. Practical work with a map.
Mainland is a large land of sushi, surrounded by water. Eurasia, Africa, Australia, North America, South America and Antarctica - continents. Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, America and Antarctica - parts of the world. Northern Arctic, Atlantic, Quiet and Indian Oceans.
Form of the earth's surface (7 hours) Rivers - a permanent water flow from precipitation, dropped on the surface of the sushi. Source, river, mouth (Delta). Left and right bank. Water collection. Circulation of water in nature. Why does the water in the river ends? Why in the river so much water? Why do rivers flow not only during rain? How do rivers and streams change the earth's surface? River valley. The most important rivers of the world and their location on the map. Mountain and plain rivers. Lakes are natural reservoirs with standing water. Flowing and faceless lakes. Large lakes. The deepest lake is Baikal. The Caspian Sea is the biggest lake.
Plains - smooth or weak-headed sushi sections. Plains and lowlands. Swamps. Mountains - raising the earth's surface. Nature of Plains and Mountains. Rocks. Minerals. The most important plains, mountains and vertices and their location on the map. How mountains were formed: underground force raises the mountains, and the weathered destroys. How the mountains turn into plains. Weathering. Mountains and volcanoes. Volcanoes and eruptions. Earthquakes - the result of the displacement of the Earth's layers.
Peninsula - Sushi sections, outstanding in the ocean. The most important peninsula and their location on the map. Islands - small areas of sushi separated by seas and oceans from the mainland. The most important islands of the globe and their location on the map. The seas are large reservoirs with salty water, located along the edges of the oceans and ishing sushi. Properties of the seas: All seats are connected to each other, the water level in all seas is the same, the water in the seas is salty. The most important seas of the world and their location on the map. The inhabitants of the seas. Coral reefs and inhabiting their organisms.
Excursion "Forms of the earth's surface" (in spring).
Earth - Our Common House (11 h) The habitat of living organisms. Food links. Ecosystem - joint living organisms and that section of the land on which they live. Plants - "Kormaltsy". Animals - "Etheries". Mushrooms, microbes, rainworms are "garbers." Consumers and garbers give nutrients to plants. The relationship of all living beings in the ecosystem. Their mutual fitness. Createness of substances.
Natural zones - land areas with similar natural conditions that receive a similar amount of solar heat and light and replacing in a certain order from the pole to the equator.
Natural zones of cold belt. Ice deserts and their inhabitants. Tundra. Stern climate: long polar night and a short summer day. Eternal Frost. Landscape tundras. Animal I. vegetable world. The location of the tundra on the globe. Red Book.
Temperate zone. The woods. Change seasons. Evergreen coniferous and deciduous trees. Leaf Fall and its role in the seasonal climate. Animal and vegetable world. Location of forests on the globe. How forests replace each other.
Steppe. Dry climate steppes. Open landscape. Animal and vegetable world. Location on the globe. Desert. Hot dry climate. Desert landscape. Animal and vegetable world. Device of living organisms to the dry climate of the desert. The location of the desert on the globe.
The fragile nature of steppes and deserts, the need to save it. Arid zones of hot belt. Tropical desert zone and its inhabitants. Oasis. Steppe of hot belt - Savannah. Evergreen forest. Hot wet climate of rainforest. Animal and vegetable world. The location of evergreed forests on the globe.
The mountains. Cooking with the rise in the mountains: the sun heats no air, but the ground. Elementary ideas about high-altitude lower. Mountain plants and animals. Natural catastrophes in the mountains.
Adaptation of people to life in various natural conditions. Human races. Elementary human needs: food and clothing. Collecting food (fruits, berries, mushrooms, roots) and wildlife hunt - the most ancient human classes. Farming and cattle breeding. Agriculture - the occupation of the residents of plains and lowlands. Cattle breeding is the occupation of the inhabitants of the desert and the mountains. Cities - place of residence of many people employed in industry. Countries and inhabiting their peoples. Map of countries and cities - political map. Large countries and the city of the world and their location.
Excursion "Acquaintance with the nature of its natural zone." Safe travel rules.
Parts of Light (10 h) Europe. Countries and cities of Europe (United Kingdom, France, Italy, Germany, Ukraine, Denmark, Sweden). Alps - Mountains of Europe. Objects around us and their homeland. Heroes of children's fairy tales from European countries.
Asia. The largest part of the world. Natural conditions Asia. Asian countries and peoples (Japan, China, India). Asia is the birthplace of more than half of humanity. Objects around us and their homeland.
Africa. Natural conditions of Africa: hot climate. Peoples of Africa: Negros and Arabs. African countries: Egypt. Sahara Desert. Natural areas of Africa. Objects around us and their homeland. African animals. How to protect yourself from sunlight.
America. Indians are indigenous residents of America. Moderate and hot climate. Natural zones of North America. North America is the second homeland industry. Countries (USA, Canada) and Cities. Objects around us and their homeland. Natural zones of South America and their inhabitants. South America is the birthplace of the smallest birds, the biggest snakes, butterflies and beetles, the hardest and the easiest tree. The opening of America by Vikings and Columbus.
Australia. Climate and Natural Areas of Australia. Australia is the birthplace of Kangaroo and other animals with a bag. Antarctica is the coldest mainland on Earth. Self low temperatures. Glaciers. Life in Antarctica exists only along the edge of the coast. The development of the southern pole. The largest cycle of water. Why in Antarctica is colder than in the Arctic.
Russia. The biggest country in the world. Nature of our country. The main rivers, lakes, plains, mountains, islands, peninsula and the sea of \u200b\u200bRussia. Natural wealth of our country. People are the main wealth of our country. Ancient masters - the pride of Russia. Architectural monuments of our country. Nature and sights of their edge.
Our little planet Earth (3 hours) Impact growth modern man In nature: accumulation of garbage, climate change, creation of artificial lakes and deserts. The need for protection and careful attitude towards nature. Rules of behavior in the apartment, allowing to maintain nature.
The watch at the discretion of the teacher - 5 h.
3rd grade. Section 1: "Earth Residents" (34 h)
Substance and energy (4 hours) Natural and artificial bodies. The substance is what all objects and bodies consist in nature. The substance consists of particles. Molecules - the smallest particles of the substance. Clean substances, mixtures. Three states of matter: solid bodies, liquids and gases, the location of particles in them. Transformation of substances. Why plasticine is soft, and glass is solid. Why ice is lighter than water.
Energy is a source of movement. Mature manifestation of energy. Electricity, sunlight, falling water - phenomena due to energy. Turning energy on the example of life of people. Fuses of energy. Transformation of energy and heat isolating.
The shell of the planet, covered by life (5 hours) Air, water and stone shell. The spread of living organisms. Live sheath of land - biosphere. Life is common in the field of mutual penetration of the atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere.
The most important condition for people's life is the order of the world. The stability of conditions is a consequence of the cycle of substances in nature. Life is a member of the cycle of substances.
Participants of the cycle of substances. Plants - manufacturers, their role in providing food and oxygen. Animals - consumers, their role in limiting the number of plants. Mushrooms and bacteria are destroyers, their role in converting dead organisms into mineral nutrients for plants.
The flow of a substance going through a living organism (nutrition, breathing). Metabolism. The use of absorbed substances for life, growth, self-renewal, reproduction. Burning and breathing.
The role of the sun as a source of energy. Sun energy stock by living organisms.
Environmental system (9 h) A large cycle in the biosphere connects all ecosystems among themselves. The ecosystem is the unity of the living and inanimate nature, in which the community of living organisms of different "professions" can jointly maintain the cycle of substances. Community. Live and non-residential components of the ecosystem. Power chains. Soil is the unity of the living and non-living. Soil fertility. How is the soil formed?
Lake ecosystem. Small single-celled and large algae. Daphnia and cyclops - favorite food of aquarium fish. Large and river fish. Bacteria and their role in waste recycling. Gradual lake overgrowth.
Swamp - overgrown lake. Swamp plants. Sphagnum and its role in absorption of excess water. Bolden berries and consumers. Animals swamp. Not fully closed savage swamp. Peat and accumulation of deadly organic. The gradual self-suping of the swamp.
Ecosystem meadows. Meadow plants: cereals and dissemination. Dernovina and its role in preserving and creating relief. Animals meadows. Rainy worms and bacteria, their role in soil fertility. Meadow ingrowth forest.
Forest ecosystem. Trees are the main forest plants. Wood. Trees are powerful pumps (movement of water with mineral salts in the trunk). Forest shrubs. Forest herbs. The value of forest animals. Animals not only participate in the cycle of substances, but also regulate it. The spread of plant seeds (birch, oak, raspberry, etc.). Forest mushrooms and bacteria and their role in closing the substance cycle.
The role of water and wind in the destruction of mountains, soil flushing. The role of life in preserving a living shell. Changing ecosystems and restoration of a closed cycle of substances. Life cures the wounds of the biosphere. Unestation of the fire, abandoned field (deposits). How to help nature cure her wounds?
Field - artificial ecological system. Cultural plants, plantal on the fields. The dependence of the cycle of substances on the fields from human activity. Plowing fields. Field fertilizer. The inability of cultural plants to protection - mass reproduction of weeds and pests. Animal fields. Present and future struggle with weeds and pests.
Aquarium is a small artificial ecosystem. Non-fat (sand, stones, water) and live components of the aquarium. Algae, wraps and fish, bacteria. The relationship of all living and non-living components in the aquarium. Possible errors of a beginner aquarist.
Excursion "Inhabitants of the lake, meadow, forests."
Live participants cycle of substances (10 hours) Plants and their role on Earth. Stem, leaf, root - the main organs of flowering plants. Flower - breeding organ. Seed and his role. Fetus. Variety of plants: coniferous, flowering, mosses, horships, planes, ferns, algae. Plants consist of individual cells. Chlorophyll and his role.
Animals and their role on Earth. Simple animals. Division of labor between different parts multicellular organism. Worms. The role of muscles with active movement. The occurrence of the head and tail, back and bug. Mollusks. Mollusc shells as a house and muscle support.
The appearance of solid covers - protection against predators. The outer skeleton of arthropods - the "lats" of the knight. Insects and varieties. Insect development. Cracks, spiders and their features.
The emergence of the spine - the inner skeleton. Fish - vertebral animals adapted to life in water. Fish manifold. Animal output on land. Life on the border of water and sushi and the structure of amphibians: Lightweight - respiratory organs, naked skin and the development of tadpoles in water. Reptiles - land animals with non-permanent body temperature. Beasts and birds are animals with a constant body temperature. Birds and their fixtures to flight. Pen. Departure and sedentary birds. Beasts. Wool. Caring for the offspring in animals and birds. Brain and senses.
Careful handling of wild animals. Pet behaviors.
Mushrooms are wood destroyers. Mycelium. Yeast and their role in the manufacture of bread. Edible and poisonous, spongy and lamellar mushrooms. Commonwealth of mushroom and tree. Lichens.
Bacteria - Universal Destroyers of Substances. Bacteria are the simplest, ancient and smallest living beings. Difficulties of observation of bacteria. Traces of life bacteria are visible everywhere. Bacteria -Freight participants of all cycles.
Using people cycle for their needs. The destruction of the cycle of substances and the threat of the well-being of people. Nature does not have time to restore stocks. Nature does not have time to recycle garbage. Examples of environmental disorders in the biosphere. Life in harmony with nature is the only strategy for humanity. Reserves and national parks.
Excursion in Zoo or botanical Garden, local history museum, the theme of the "diversity of plants and animals".
The repetition of the material passed is 4 hours.
Watch at the choice of teacher - 2.
3rd grade. Section 2: "My Fatherland" (34 hours).
Your relatives and your homeland in the stream of time (4 hours) Pedigree person. Generation ancestors. Pedigree tree. Surname, name and patronymic - communication times.
The idea of \u200b\u200bthe "River of Time". Historical account time. Century (century) and era - time reference point. Adopted in the modern Church of the Christian Era. Primary ideas about Christianity - one of the most common religions in the world.
Our homeland (house, city or village, native land, country). Society in which we live. The image of the state. Government. Laws are mandatory for all rules of behavior established by the state. My homeland, My Fatherland - Russia!
The story of my homeland. History - science about the past of mankind. Historical sources. The image of the centuries-old history of Russia.
The times of ancient Russia. IX - XIII century (5 hours) Ancient residents of Russian expanses. The life of Slavic tribes.
Creature Old Russian state. Kiev is the capital of the great princes of ancient Russia. The adoption of Christianity at Prince Vladimir Svyatoslavich.
"Ancient Rus is a country of cities." Cities - Centers of Culture Ancient Russia. The idea of \u200b\u200bculture as all the achievements of humanity. Cultural wealth of ancient Russia. Temple in the life of the ancient Russian city. Monasteries. Chronicles and handwritten books. Slavic ABC - Cyrillic.
Protecting Russian Earth. Raids steppes-nomads. Bogatyr outposts. The fragmentation of Russian lands. Fighting European knights. "Battle on the Ice". Alexander Nevskiy.
The ruin and death of ancient Russia. Mongolian invasion. State Golden Horde. Primary ideas about Islamic religion. Russian land under the rule of the Golden Horde.
The times of the Moscow state. XIV - XVII century (4 h) The time of creating a Moscow state is the time of the struggle of cruelty and mercy. Kulikovsky battle. Dmitry Donskaya. Sergius of Radonezh. "Trinity" Andrei Rublev. Exemption from the Ordane Iga. Association of Russian principalities in the Russian state.
Great Sovereign Ivan III. State coat of arms of Russia - double-headed eagle. Moscow State is the heir of ancient Russia. Earth and people of the Moscow state. Classes and life of rural residents - peasants. Boyars and nobles. City of the Moscow state. Capital State - Moscow.
Moscow Kremlin is a monument of the Moscow state, the "Heart of Moscow and all Russia". Cathedrals of the Moscow Kremlin. The image of the king of Ivan the Terrible. St. Basil's Cathedral. Troubled time - the threat of collapse of the Moscow state. People's militia of Kuzma Minin and Dmitry Pozharsky. The liberation of Moscow and the salvation of the Fatherland.
The times of the Russian Empire. XVIII - early XX century (5 hours) Transformation of Russia by Peter Great - the first Russian emperor. Victory B. hard war With Sweden. The exit of Russia to the sea. New capital - St. Petersburg. Commission of Russia to European culture. New Empire Symbols: State Flag (White-Blue-Red), Naval Andreevsky Flag.
Power and people of the Russian Empire. The image of Catherine II. Great Russian commander A.V. Suvorov. The power of the emperor and officials. Representation of serfdom.
Patriotic War 1812 - the threat to the existence of Russia. Borodino battle. The unity of the people in the face of the enemy. M.I. Kutuzov.
Achievements of Russian culture at the time of the Empire. Mikhailo Lomonosov - "Our First University". Alexander Sergeevich Pushkin is the creator of the Russian literary language. Best works Russian architecture and painting.
The Board of Alexander II is the time of change in the Russian Empire. Abolition of serfdom. The rapid development of the updated empire.
The times of Soviet Russia and the USSR. 1917 - 1991 (4 h) The life of workers and peasants at the beginning of the 20th century. People and power. Nicholas II. Revolution 1917 V.I. Lenin and Bolsheviks. Civil War in Russia. Disintegration of the Empire and the formation of the Soviet Union.
The purpose of the Soviet state is the construction of a fair society. Symbols of the USSR: Red flag, coat of arms. The power of the Soviets and the Communist Party. Attempt to build a fair society. Board I.V. Stalin.
The Second World and Great Patriotic War. Victory over fascism. Heroes of the Great Patriotic War.
Development of the Soviet Union after World War II. Achievements of science and technology in the USSR, the development of space. Changes in the life of people. The need for change in the country.
Modern Russia (8 h) Transformation of the USSR in the CIS. The largest state of the CIS - Russia. Modern Russia is the heiress of the ancient Russia, the Moscow state, the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. Restoring government symbols. The concept of citizenship. The constitution is the main law of the state. Rights and obligations of citizens.
What is democracy? Presentations on the electoral system.
State power in Russia. The idea of \u200b\u200bthe power of the legislative and executive. The President is the head of state, which is elected by the people. Government. State Duma is a meeting of the representatives elected people, which creates laws.
Russia is the common house of many nations. Languages \u200b\u200band customs of the peoples of Russia. Unity and equality of all nations of Russia.
The Russian Federation is a state created by the Union of Territories. Council of the Federation. Russians are all citizens of the Russian Federation.
The property of Russian culture - library, museums, theaters. Our most important task is to preserve and multiply the cultural wealth of Russia. State holidays of modern Russia (the origin and tradition of the celebration).
4th grade. Section 1: "Man and Nature" (34 h)
Man and its structure (14 hours) Human device. The main systems of human body organs and their role in the life of the body.
Leather. The structure of the skin. The skin and its role in protection against cold and heat, external influences, microbes (bacteria). The impermanence of conditions in the external environment and the constancy of the conditions inside the body. Potting and its role in maintaining body temperature. Hygiene rules. Tan and sunlight protection. Corn - protection against abrasion of the skin. The skin is the sense organ. Sensitivity of the fingers. Patterns on the palms and fingers.
Movement of man. Inner skeleton, its advantages and disadvantages. Continuous growth of bones. Bones and their strength. Joints. Mobility in the spine and shoulder joint. Fractures, dislocations. How to give first aid? Muscles - body drivers and his skeleton. Muscles and joint. Muscle functions: reduction and relaxation. Physical fatigue of a person.
Digestion. Digestive organs. Teeth and chewing. Roth and language. Harness, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver. Rules of healthy nutrition. Digestion and its role in transforming food into a universal source of energy and building material, common to all living beings: proteins, carbohydrates and fats.
Options and their role in the removal of harmful substances and excess water from cells. Kidney, bladder. What is urine?
Respiratory organs: nasal cavity, throat, trachea, bronchi, lungs. Hygiene breathing. How do we breathe? How do we speak? Sneeze and cough. Tracheit, bronchitis, inflammation of lungs.
Circle circles. Heart - pump. Arteries, veins and capillaries. Arterial and venous blood. Pulse. Blood pressure.
Blood and its transport function inside the body. Transfer of nutrients and oxygen to all body cells. Blood and its red color. Why doesn't all blood flow from a person? Fearless defenders in human blood.
Brain - control body. Nervous system: brain and nerves. The function of the nervous system is fast and accurate transmission of control signals from the brain to organs and informative information about the state of the organs to the brain. Head I. spinal cord. Nerves - "Wires" of the nervous system. Control of breathing, heartbeat, food digestion. Hemisphere - Samea main part Brain man. Our feelings. Thinking. The glands of the internal secretion and the production of hormones, diverted blood throughout the body. Humor of fear and danger and its action.
Sense organs. Eyes - organs of vision. Crystal. Retina. Perception in light and in the dark. Perception through the eyes of movement. Protection of vision. The nose is the sense of smell. Ear - an organ of hearing. Language - body of taste. Leather is the touch body. Equilibrium body. Pain - a danger signal. The specificity of sensitive cells and the absence of the specifics of the signal on the nerves.
Reproduction is the property of living organisms. Embryo - Mother's Organ. Embryo nutrition and breathing. Birth. The dependence of the child from the mother. A person will not be born, but become.
Injuries. Microbes are causative agents. Bacteria and viruses. What causes flu and how is it transmitted? What is a cold? Why core, windmill and scarletina are sick once? Protection of the body. High temperature, its causes. Blood cells - germ eaters. Vaccinations and their role in saving us from diseases. Medicine wins terrible ailments. Diseases modern society. Physical culture is a necessary element of the culture of a civilized person.
Origin of man (2 h) Man's ancestors - man-like monkeys and their features. Well-developed hand, eyesight and complex brain. B2-like movement, vertical body formulation, exemption of hands from movement functions and highly planted head. Long period of childhood and training. The basis of the survival of our ancestors is to predict the behavior of enemies and food objects in space and time and collective action. Man and his mind. Speech.
Primitive herd as a prototype of human society. Monkey and the oldest people of our planet. Manufacturing tools of labor. Storage of guns and the manufacture of their future - the main background of the progress of technology. Use of fire and breeding fire. Collective hunting for large animals. Division of labor. Long learning children and later their mature. Origin of family. The appearance of a man is reasonable.
Man-made nature (10 hours) Taming and dilution of domestic animals, breeding cultivated plants. Breed and varieties. Artificial selection. Livestock and crop production, their role in human farm. Plowing, crop rotation, fertilizer, watering, the use of greenhouses and pesticides allow you to increase the harvest.
The invention of the lever and its use for the manufacture of tools. Inclined plane and wheel and their use by man. Wedge, block, gate.
Water, its properties (takes the shape of a vessel, pushing force, fluidity, incompressible, the ability to dissolve). Change the properties of water when heated and cooling. Reporting vessels - water supply device. Filtration. The device of the simplest steam engine, hydraulic press and jack.
The air, its composition and properties (expanding when heated, does not conduct heat, low density, elasticity). Balloon. Does the air pushing force?
Mountain breeds and minerals, their use by man. Properties of rocks and minerals (constant shape, strength, hardness). Production of bricks, cement, concrete, glass. Precious and diverse stones.
Metals, their properties (hardness, plasticity are expanded when heated, heat and electricity), mining and use. Bronze, iron and its alloys. Metal processing methods. The use of various metals.
Peat, stone coal, oil and natural gas - fossil fuel, its origin. Steam engine. Internal combustion engine, rocket engine.
Electricity in nature. Use of electricity by man. Magnets, their features.
Sound, its properties (height of sound and its connection with vibration). Communication and musical instruments. Light, its properties (distribution in a straight line, refraction, absorption).
Modern technologies in the service of a person. Production of synthetic materials. Artificial satellite And flight into space. The invention of computers, robots and laser and their role in the life of a modern person.
Assigning the farm of our ancestors. Producing economy. Creating an artificial ecosystem. Violation of the cycle of substances in the biosphere: accumulation of production and livelihood waste, pollution ambient. Our land becomes more and more unexpected and stranger. Ecological economy of the future person.
The repetition of the material passed is 5 hours.
Hours of choosing teacher - 3 hours
4th grade. Section 2: "Man and humanity" (34 hours)
Man and his inner world (9 h) Man - Child of Nature and Society. "Mowgli" - a man outside human communication. Training and education in the development of man.
The main qualities of the personality. Character. Character features as sustainable personality manifestations.
Emotions. Expression of emotions. Emotional states. Mood. Anxiety. Self-esteem - or what you see yourself. Self-esteem and estimation: you are about yourself, you about others, others about you.
Relationships with others and to others: sympathy and antipathy. Communication and its types (speech and neust). Mimica - "facial expressions" and pantomime - "Language of movements". Moral standards.
Man and Society (4 h) Society as interconnection of people. Conflict. Causes and types of conflicts. Methods for resolving conflicts.
The rules for the behavior of people in society. Conscience. Morality and right.
Circles of communication and social groups. Humanity is the greatest social group.
Human rights in society. Crimes against personality. Rights of the child. Protection of the rights of the child.
Picture world History mankind (6 hours) The World History of Humanity is the emergence and change of human society from the appearance of the first people to the present day. The picture of the world history of mankind is a change of several epochs - "times." The image of the development of society as an image of changes in the technique, the forms of society, the rules of morality.
The primitive world (1 million years - 5 thousand years ago) - the time of the emergence of a person and its settlement on the planet. Ancient world (3 thousand BC - V century new era) - the time of the first civilizations - new types of societies. The Middle Ages (V-XV century) is the time of changing some civilizations by others and the distribution of the area of \u200b\u200bcivilizations on the planet. New Time (XV-XIX century) - the era of the rapid development of European civilization, harsh changes in the life of people. The newest time (XX century) - the era of heavy tests for humanity and creating the foundations of the worldwide human (universal) civilization.
Man and Multidious Humanity (5 h) One humanity consists of different races and different nations of the Earth. Races of mankind. Peoples, their main differences. Nationality of man. Human rights to develop their folk culture, equality of representatives of different races and peoples.
One humanity consists of citizens of different states. The diversity of the states of the planet. Monarchies and republics. Democratic and non-democratic states. Human rights to participate in government management, freedom of speech.
One humanity consists of believers, adherents of various religions and atheists. Faith (idea of \u200b\u200bthe gods) and atheism (disbelief in God). Human right to freedom of conscience (choose any religion or be an atheist).
The religions of the world - religion that spread to many peoples of the world and became part of the global universal culture.
Man and one humanity (4 hours) The image of the "world economy" uniting all of humanity. Human labor activity. Property, income, wages. Exchange and money. The relationship of states and peoples of the planet in the field of production and trade.
Modern humanity unite common tasks development of culture and sports. Universal cultural achievements and values, the problem of their preservation and development. Modern Olympic movement, value for modern humanity. Almost all states of the planet are included in the United Nations. UN objects, principles of construction, practical work for the benefit of all mankind. One of the main documents of the UN is the Declaration of Human Rights.
All of humanity unites global (universal) problems of modernity, which threaten the very existence of humanity.
Summarizing repetition - 2 h.
The path of mankind in the XXI century. The future depends on each of us!
The clock on the selection of the teacher is 4 h.
VII. Thematic planning and main activities of students
VIII. Material and technical support of the educational process
Primary education is significantly different from all subsequent stages of education, during which systematic courses are being studied. In this regard, the equipment of the educational process at this educational stage has its own characteristics, determined by both the specifics of learning and raising younger students in general and the specifics of the "surrounding world" in particular.
In primary school, the foundations are laid for the subsequent study of systematic courses of physics, chemistry, biology, geography, history and social studies. The course "The World War" contains elementary, accessible to the perception of students of the younger school age information about living and inanimate nature; man, his biological nature and social essence; society, his history and culture. The main task of the "surrounding world" course in elementary school is the formation of a holistic picture of the natural and social world with all the diversity of its phenomena, the formation of the presentation of the place and role of man in him, the development of an emotional-value attitude towards him. Therefore, the principle of clarity is one of the leading principles of training in elementary school, since it is obvious that it is the basis of the formation of ideas about the objects of nature and the culture of human society.
In this regard, the main role is played by learning tools. visual aids:
- natural living benefits - houseplants; Animals contained in aquarium or corner of wildlife;
- herbarium; insect collections; wet preparations; Stuffed and skeletons of representatives of various systematic groups; microsperats;
- collections of rocks, minerals, minerals;
- fine visual benefits - tables; Moilazzi human torso and individual organs, etc.;
- geographical and historical cards;
- itemsrepresenting the life of a traditional and modern family, its farms, everyday, holiday life and much more from the life of society.
Another means of clarity is the equipment for multimedia demonstrations (a computer, media projector, DVD projector, video recorder and others) and fighters of the surrounding world (photo and video camera). It is due to the Internet and a single collection of digital educational resources (for example, http://school-collection.edu.ru/) allows you to provide a visual image to the overwhelming majority of the course "Environment".
The use of a variety of learning tools in their combination allows you to form the correct ideas about the objects under study - their size, form, color; On the meaning of the phenomena and events of the historical and cultural life of the country and the world, etc.
Along with the principle of clarity in the study of the "Enough Mir" course in elementary school, the principle of objectivity plays an important role, according to which students exercise various actions with the objects studied. In the course of such activities, schoolchildren form practical skills and skills, a conscious absorption of the material being studied is ensured.
The "Arrive Mir" course provides for a significant number of laboratory and practical work that model the phenomena of the natural and social world. Based on this, the second important requirement for the equipment of the educational process in elementary school when studying the world around the world is that among the training facilities must be presented instruments, dishes, tools for practical work, as well as diverse distribution material.
Handout For practical I. laboratory work Must include herbarium, seeds and fruits of plants, collections of minerals and minerals, bones, casual fish, bird feathers, diverse artifacts of the world of culture, etc.
In the course of studying the "Around World" course, younger students are mastered at the level accessible to them methods of knowledge of nature and society, including observation, measurement, experiment. For this, the educational process should be equipped with the necessary measuring instruments: weights, thermometers, centimeter rules, mins.
In primary school, students begin to form cognitive interests, cognitive motivation. At this age, most schoolchildren are expressed in the study of nature, their own organism, human relationships, so the study of the "surrounding world" course, rich in information about living and inanimate nature, human body, his inner world, various sides of public life, should stimulate the formation of sustainable cognitive interest, its further development. This is largely promoted by the activity, practical oriented nature of the content of the "Arrive Mir" course, as well as the use of a variety of learning tools during its study. These include primarily set of encyclopedias for younger studentsthat allows you to organize the search for children interested in children. In addition, an important role belongs to excursions provided for by the program "The Overview World", therefore, the equipment of the educational process should be included sightseeing equipment, including folding loupes, compasses, binoculars, garden scoops, roulettes etc. For excursions in the classroom it is useful to have a set of popular illustrated identifies of objects of nature (minerals, plants, animals, etc.). To visit local lore, artistic, ethnographic, memorial museums, it is important to have special guidebooksdesigned for interactive excursions for one or another exposure.
IX. Obzh in the course "Enough Peace"
As part of the 2004 basic plan, the material on the OBZH is included in other items, in particular to the world around (mainly). Since it is minimized, then it is automatically studied in the framework of the "surrounding world". Nevertheless, local attempts are made in different regions. From the point of view of the federal center it is not required, but the region has the right to independence. As a result, for example, in new methodological recommendations for preschoolers, we made double thematic planning: on OM and OBZH.
This article presents material for 3 class students surrounding the world for which is provided in the form of simplified ecosystem models. The concept of society of people, its structure and importance in the life of each person is also considered. On the simple examples There is a process of explaining the surrounding world. This is the main task of this material.
The concept of ecosystems
In order for the 3 class schoolchildr, it is better to understand what is a planet Earth, it is necessary to clearly demonstrate the globe model. Our planet has an outer shell, which is called an atmosphere. All living organisms on Earth breathe atmospheric air. The atmosphere protects the Earth from overheating, from the radiation of cosmic rays.
The earth has a water shell is a hydrosphere. The hydrosphere form underwater water, rivers, the sea, the oceans of the globe.
Lithosphere forms a solid shell of the Earth. Susha, mountains, land belong to the lithosphere.
All living organisms living on Earth live in the biosphere. The biosphere is on the border of all other three spheres.
All living organisms on Earth live in an air, water and terrestrial environment. In order for the cycle of substances in nature, it is not stopped, all living organisms cannot do without each other. All organisms on functions (or still you can compare the functions of organisms with professions) are divided into manufacturers, consumers and destroyers. Manufacturers are plants and trees, consumers are mostly all animals, but destroyers include bacteria, mushrooms and worms. Manufacturers, consumers and destroyers cannot live on earth without air, water, soil and rocks. Consequently, all the above elements can be divided into two large groups: live and non-fat nature. Thus, you can imagine the world around us - this is a living and non-fat nature.

The concept of society. His structure
For a student of 3 classes to determine the concept of society, it should be brought as an example of his own family, which (in the main mass) consists of members: father, mother, grandmother, grandfather, brothers, sisters. Family (group of people) is an elementary or main cell of society. All members of society interact with each other. Thus, also society is the world around. The whole society is holding on four components. These constituents are parliament, hospital, church, prison. The world around us is a certain structure that was formed in ancient times, and its base is preserved today.
The concept of economics
Let's lay out those things that are necessary for a person for life. Such things are called needs. What can we attribute to the needs of a person? This is a need for food, in vacation, in clothes, in work, in maintaining health, in transport, safe. This list can be continued for a long time. The needs of humanity are different in purpose and meaning.
Needs can be informative (theater, books, television), physiological (hunger, sleep), material (apartment, computer, car, cottage). Much gives us nature - it is the heat of the sun, the air, water, the crop of the earth. And love, communication, friendship is all we all get, communicating with each other. And all the material benefits is something that can not be in nature (at home, cars, clothes) - gives us the economy. Translated from Greek - "Housekeeping". Here in such a simple explanation for students of 3 classes around the world will look simple and understandable.

Conclusion
In conclusion, I would like to say that, despite the scale and complexity, the world around us is a rather fragile structure, appreciate, and most importantly, take it for future generations is the main task of adults before children. But at the same time, at the stage of training at the younger generation, it is necessary to form an appropriate system of values.
The world around the world.
What is the world around.
Lesson number 1.
Topic: What is the world around.
Formation organization (type of lesson): lesson with elements of research and gaming activity.
Type of lesson: Introductory lesson, dating lesson with a new training subject.
Objectives lesson:
The assimilation of the initial ideas about the educational subject "surrounding the world", about objects of living and inanimate nature.
Creating conditions for the formation and development of mental functions, abilities, motivational installations, creative research thinking through involvement in active educational and research activities
The formation of moral and volitional qualities, the ability to control their behavior in the training situations.
Basic concepts: The world around: the world of nature, the world of things, the world of people.
Meta-reported links: the world around us.
Resources: Workbooks student, textbooks, color pencils, 3 pictures of the city, underwater and girls at the pond; Carriages and objects of nature, things, people.
Planned learning result, incl. Wood formation:
To have ideas about the world around the world, about objects of living and inanimate nature, give exemplary answers to the question: "Why do you need to study the world around?",
Know the distinctive features of objects of alive and inanimate nature.
Be able to conduct simple observations, to compare objects of living and inanimate nature, give answers in the form of a small proposal for uncomplicated teacher issues or fairy-tale character, be able to execute teacher instructions.
To be able to cooperate with comrades in the simplest role-playing games and conduct simple dialogues.
1. Chinarily Wood: Formation of interest in a new subject, determining the need to study the world in which you live;
2. Regulatory Wood: organization of the workplace according to the instructions of the teacher; If possible, assess their work and the work of the comrade; Determine the task plan under the guidance of the teacher.
3. Required Wood: navigate the textbook and workbook; Compare items, objects: find a common and distinction; Group items, objects based on essential features; Play listened, identify theme lesson; draw conclusions under the guidance of the teacher.
4. Communicative Wood: participate in the dialogue in the lesson, to answer the questions of the teacher, to formulate the question of the question of interest; Listen and understand the speech of others.
7.Feflexia. Personal Wood
Formulated Wood
Teacher's activities
Activity student
1. The organizational moment
Communicative Woods
The teacher welcomes children, with a smile takes their greetings and with the help of a small respiratory exercise removes the possible tension. Prepare children
TEACHER. Good morning, children! Let's get together to work together to the lesson - we will raise your hands up, take a deep breath, carrying hands a few seconds above, and then sharply put them down, make a small tilt forward and deep exhalation. And now everyone will sit up as it will be comfortable to work in the lesson.
Children happily welcome teachers, make a breathing exercise and are seated in their workplaces. At the same time occupy a convenient but acceptable posture
2. Actualization of reference knowledge.
Personal Wood
Speech workout. The teacher involves learning into a dialogue.
-How do you think who will be an assistant to you at the lesson?
Riddle-tip.
Here is the very first assistant:
He and smart, he and faithful
On the lesson on the desk will be lying
Polystai, he will tell everything!
-How is our tutorial called?
This is the name and the subject we will study.
Acquaintance with the working notebook.
.
Teacher, Comrade, Houses, Mom.
This is the textbook!
The world.
Children take her in hand, consider the cover.
3. Meeting and motivation.
Regulatory Wood
"Let's say we will talk about what the surrounding world will be spent on our first lesson.
-What is the world around?
-What is it suddenly necessary to study it?
4. Recreation of new knowledge of children
Cognitive Uud.
Personal Wood
TEACHER. And now, let's use our first assistant - open the tutorial on the page. Carefully consider an illustration.
The teacher reads the poem.
TEACHER.
Look around, friend!
See the river, forest, meadow,
Bird flocks, plane,
What went to the flight.
Sky, wind, clouds,
Again the river, meadow river!
TEACHER. We are starting to learn the new academic subject - the "surrounding world". Consider a picture again, look out the window, on the sides, think and tell me what the world around? What and who is part of the world around?
Students. The world around us is what surrounds us around us. These are different creatures and objects, animals, sky, clouds, trees, houses, people.
TEACHER. Good, guys! Well done! And I want you to learn to watch the world around the world, study and explore it.
In the lesson of the surrounding world, we will find out why the day replaces the night? How many days a year? Why is the change of seasons? How diverse vegetable and animal world Earth? Why is it very important for a person to live in a family? What miracles can human hands create?
Game - Travel.
1 minute goes into the forest.
2 minutes goes to the underwater world.
3 row for a walk through our city.
- Transfer the objects of nature, which they saw there?
-As, two, three - returned from the journey. You guys turned out to be very observant, so many objects of the surrounding world called.
We sum up the first result.
-What examines the subject "Enough Peace"?
Pupils open textbooks and consider pictures.
The world around us is what surrounds us around us. These are different creatures and objects, animals, sky, clouds, trees, houses, people
Pupils can list several items around themselves.
1 row: girl, pond, duck with ducklings, trees, grass.
2 Right: starfish, vegetation, corals, bottom, water.
3rd: building, square, flowers, trees.
The world around the world studies the world of nature, the world of things, the world of people.
5. Former fix.
Regulatory Wood
Communicative Woods
Work on the textbook on with. 5z
Task: Divide the drawings into two groups. Explain your decision. You can use the hint.
- Transfer objects in the picture.
- What are the two groups divide them? Why?
- We try to speak a complete answer to the question: What is the world around?
1 Replies option: Live and non-fat nature.
2Variant: the world of nature, the world of people, the world of things.
According to the textbook: the world around us is what is around us: nature, people and everything that is created by a person.
The answers of children who can more accurately reproduce this definition.
6.Mostual work.
Communicative Woods
Cognitive Uud.
Personal Wood
Work in working notebooks on C.4-5
Task 1 on p.4.
- Occuping what belongs to wildlife.
Fizkultminthork for eyes and for hands.
TEACHER. We have worked well and your eyes and hands have deserved a small rest. They got up from their jobs, came out because of the desk, raise the handles up, omit. We repeat three times. Now let's try to rotate with your hands: Forward, back. They pulled hands to the side, bent in the elbows and rotate: Forward-back, now there were hands on the sides and rotate hands with hands: Forward-back. Now the hands lowered the hands down and take a little bit of hands. Close the eyes, imagine that you are on the shore of a gentle warm sea, lowered your hands in warm water, took out the brushes out of the water and try to shook the drops. Well done! Now let's look at the window on a big tree in the school yard, stop the view on the tree, we consider to 10 out loud. Okay! Now close your eyes and count to 10 again.
Children perform teacher instructions: rotate their hands, rotate their hands, bent in the elbows, rotate and shook with tassels, close their eyes.
Work on C.5. notebook.
- Avoid drawings in two groups. Explain your choice.
 The game "Pricycles to the train cars".
The game "Pricycles to the train cars".
Live and non-fat nature.
Calling to the board of two stupids-locominors. Children from the spot show their picture, the locomotives collect trailers.
TEACHER. Well done boys! True, all items found in nature, we can divide into two large groups - the objects of wildlife and objects of inanimate nature.
Flowers, butterfly, spruce, mushrooms.
Work in pairs: "Posted with a neighbor."
The dishes are non-fat nature, the rest of the objects of wildlife.
Lead active independent activities.
Control yourself and comrades during the game.
Control by pattern on the board.
Communicative Woods did not know new on the lesson?
–Who was hard? Interesting? Evaluation of your work.
In my opinion, the concept of "surrounding world" is quite multifacetedAnd everyone represents it in different ways. As for me, the world that surrounds us, I consider interesting and amazing, and happy that I live.
The world that surrounds us
What is the world around? For one person it will be spacethat directly surrounds it, but for another - Universe. Be agreed simple language, that's all that is around us:
- everything that is created by mankind;
- nature;
- inanimate nature.
However, the world is not just amazing, he more amazing than we can imagine. There is a huge number of animals, phenomena and plants, the existence of which most people do not even suspect.
Amazing in the world
Madagascar lives at all amazing Primates - Row Button. Because of her a little strange species, the locals relate to it very wary. Their beliefs bind this animal with evil spirits and evil spirits. There is a sign that if you meet this animal, then death will inevitably overtake during the year.

One of the most mysterious phenomena - cutting stonesfound at the bottom of the dry lake in the USA. Moving stones without assistance is not doubtful, however, no one happens - they move once a few years. Scientists suggest that this is possible due to changes in the temperature regime.

Coconut crab The right is considered the largest representative of crustaceans - its length often reaches 35 centimeters. It lives on land in Norahwhere it suits a soft "period" from the leaves of coconut palm trees.

The most amazing tree on the planet - baobab. The unique ability of this tree is to vitality: if you remove the bore, then in the shortest possible time you will grow a new one. The thickness of the barrel often reaches 10 meters, and wood like a sponge absorbs moisture. It is believed that the tree is capable of living thousands of years, but actually confirms it is impossible - there are no annual rings.

Ant-Panda Absolutely has nothing to do with a spotted bear, except for the appearance. Actually, it's not even ant, and OSA-German, sometimes called "velvet ant" due to a variety of hair that cover her body. Like any other wasp this "ant" may well be worryAnd the unpleasant sensations will be saved for several hours.
What is the world around? It would seem, a simple question, to answer who can even a child, a student in the first grade. However, it is worth digging a little deeper - and it turns out that in reality everything is much more difficult. And the older and the person formed, the more difficult and its answer version.
The reason for this is a large intellectual leap, which made humanity on the path of its evolution. A lot of religious flows, philosophical schools and scientific theories presented us with the opportunity to change the interpretation of an answer to this question at their own discretion. Therefore, let's try to find out what the world around is in reality.
Truth in simplicity
To begin with, consider this issue, based on the logic of a simple person, without deepening in the subtle matters of the universe. So surrounding the world is a space that surrounds us. And right at this moment the first controversial statements appear.
If you figure out, it is quite difficult to turn the boundaries separating one space from the other. After all, there are no specific standards capable of streamlining all of these knowledge in the head of billions of people. In this regard, if you ask the usual question about what around the world, we will get different answers.
For example, for some it may be that space that surrounds directly themselves. For others, everything is much more complicated, and under this concept they imply the entire planet or even the universe.
Surrounding World: Wildlife
However, despite all the diversity of answers, there are those that can be allocated in a separate group. This is due to the fact that, despite the minor differences, they still possess some similarities leading to the general idea.

In particular, many believe that the world around us is all living around us. The same forests, fields, rivers and deserts. Animals and plants also come here, as they are an integral part of this world.
What is the world around the eyes of philosophers?
The philosophers and theologians and theologians are more deeply considered. After all, for them our world is part of a more complex reality. For clarity, consider the main features of their views on the current order of things.
According to religion, our reality is a place where people live only part of the path prepared by him. That is, the world around the world is only shirma, closing the eye more beautiful place - paradise.
As for philosophers, they are more vaguely formulate the answer to this question. Depending on the school, the thinker can identify the concept of the surrounding world differently. For one, this is a material place, for the second - spiritual, and for third and at all is a combination of two previous ones.